Difference between revisions of "Polypremum procumbens"
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
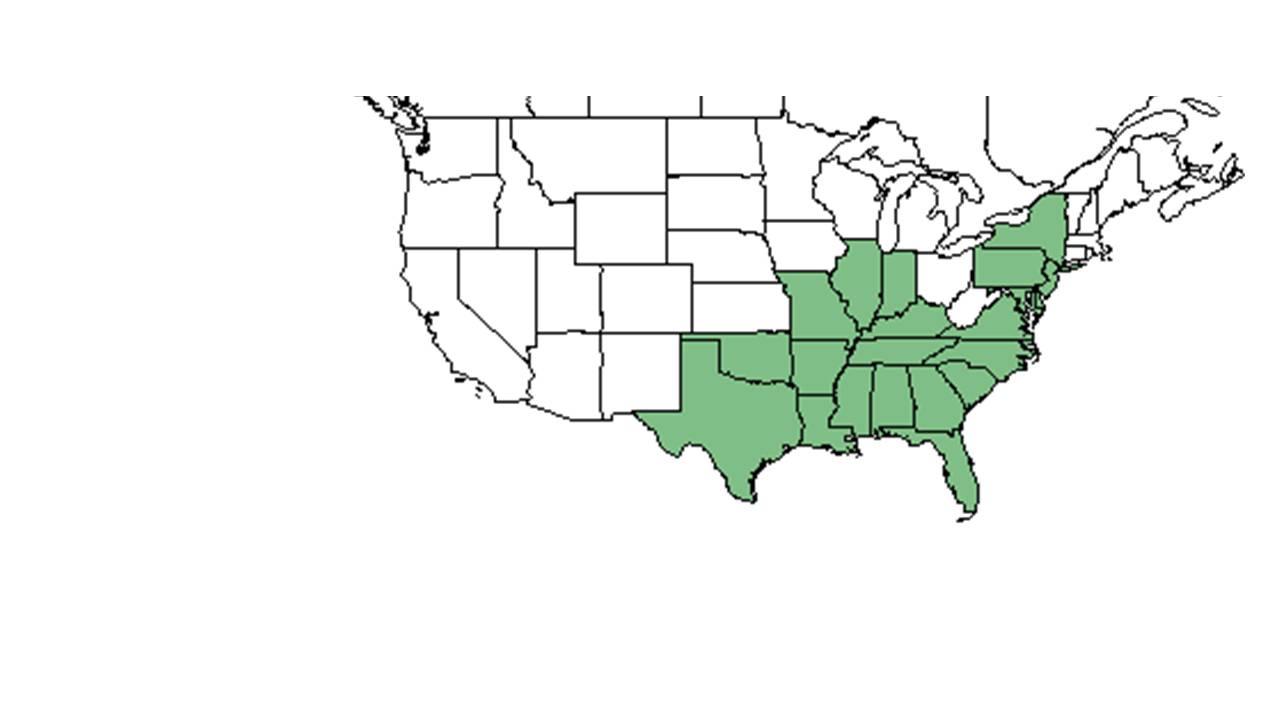
| range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Polypremum procumbens'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov Plants Database]. | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Polypremum procumbens'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov Plants Database]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Common name: juniper leaf | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | + | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Polypremum procumbens'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | |
| − | Halictidae: Lasioglossum nymphalis | + | Halictidae: ''Lasioglossum nymphalis'' |
| − | Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis | + | Megachilidae: ''Megachile brevis pseudobrevis'' |
| − | Sphecidae: Cerceris blakei | + | Sphecidae: ''Cerceris blakei, Microbembex monodonta'' |
| − | + | Vespidae: ''Stenodynerus fundatiformis'' | |
| − | |||
| − | Vespidae: Stenodynerus fundatiformis | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 48: | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (2003). "Influence of deer, cattle grazing and timber harvest on plant species diversity in a longleaf pine bluestem ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 175: 49-69. | Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (2003). "Influence of deer, cattle grazing and timber harvest on plant species diversity in a longleaf pine bluestem ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 175: 49-69. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA. | ||
Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3). | Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3). | ||
Revision as of 17:57, 11 August 2015
| Polypremum procumbens | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Buddlejaceae |
| Genus: | Polypremum |
| Species: | P. procumbens |
| Binomial name | |
| Polypremum procumbens L. | |
| |
| Natural range of Polypremum procumbens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: juniper leaf
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Polypremum procumbens at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Halictidae: Lasioglossum nymphalis
Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis
Sphecidae: Cerceris blakei, Microbembex monodonta
Vespidae: Stenodynerus fundatiformis
Use by animals
Deyrup observed this bee, Dialictus nymphalis, on P. procumbens (Deyrup et al 2002). Cover of P. procumbens decreased significantly through time after three grazing treatments (no grazing by deer or cattle, grazing by deer, or grazing by deer and cattle) in thinned and clearcut forested areas (Brockway and Lewis 2003).
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (2003). "Influence of deer, cattle grazing and timber harvest on plant species diversity in a longleaf pine bluestem ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 175: 49-69.
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).