Difference between revisions of "Dichanthelium strigosum"
Ruthstetler (talk | contribs) |
Ruthstetler (talk | contribs) (→Seed dispersal) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | + | Seed dispersed by gravity.<ref name="Kirkman et al 2004">Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92(3): 409-421.</ref> | |
| + | |||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Revision as of 19:24, 13 July 2015
| Dichanthelium strigosum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Dichanthelium |
| Species: | D. strigosum |
| Binomial name | |
| Dichanthelium strigosum (Muhl. ex Elliott) Freckmann | |
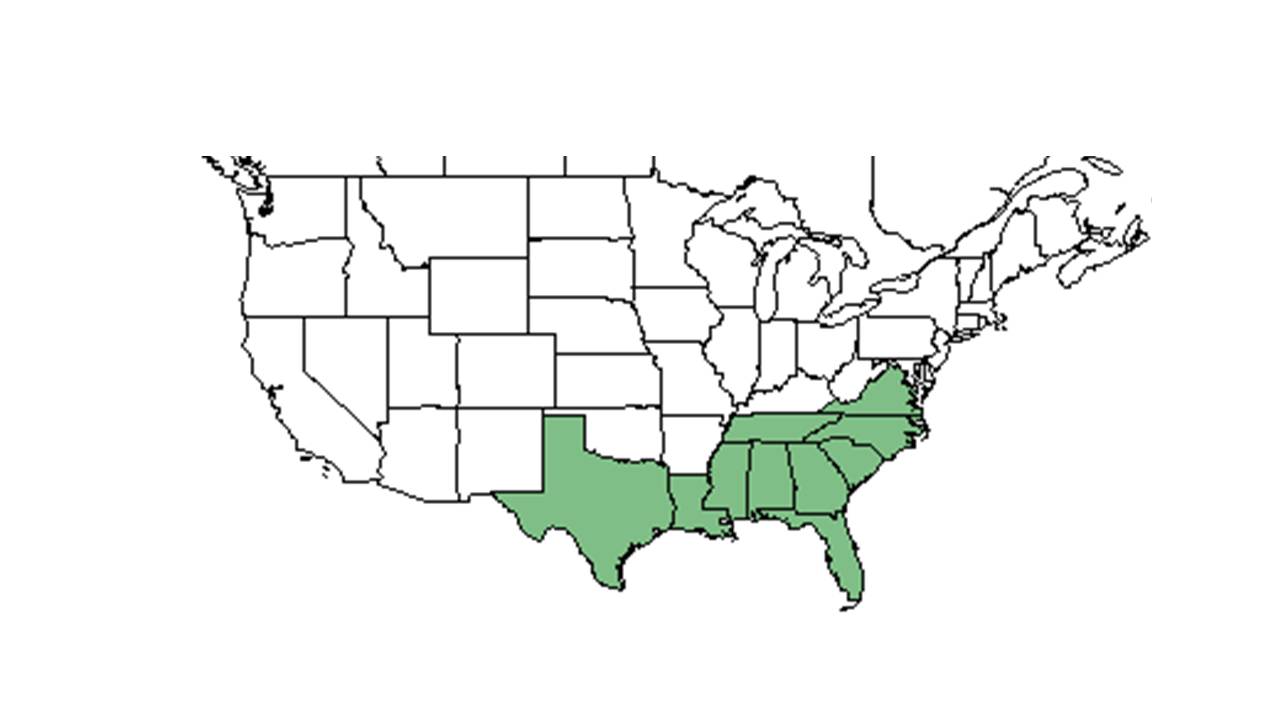
| |
| Natural range of Dichanthelium strigosum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common Name: roughhair rosette grass
Synonym Name: Panicum strigosum Muhl. ex Elliott
Dichanthelium strigosum is a perennial graminoid theat tends to grow in thick mats (FSU Herbarium).
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It can be found in relatively undisturbed areas,[1] including longleaf pine savannas,[2] saw palmetto-wax myrtle thickets, sandhill ridges, and bogs (FSU Herbarium). However, D. strigosum also occurs in disturbed areas like power line corridors, roadsides, fields, and clear-cuts (FSU Herbarium). This species seems to prefer moist sandy soils (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowering and fruiting has been observed in February, as well as April through August (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed dispersed by gravity.[3]
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It can tolerate biennial, early growing season prescribed fires.[2]
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014.
Collectors: Cecil R. Slaughter, Loran C. Anderson, S. W. Leonard, A. E. Radford, H. L. Blomquist, D. S. Correll, Wm. G. Atwater, Robert Kral, O. Lakela, R. Komarek, K. E. Blum, R.K. Godfrey, Ed Tyson, A. F. Clewell, Annie Schmidt, Wilson Baker, Richard W. Pohl, Frank W. Gould, and H. Kurz.
States and Counties: Alabama: Convington. Florida: Bay, Brevard, Dade, Escambia, Franklin, Hillsborough, Indian River, Jefferson, Lafayette, Lee, Leon, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Polk, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia : Baker and Thomas. North Carolina: Brunswick. South Carolina: Greenwood and Jasper.
Other Countries: Panama (United States of America).
- ↑ Thaxton, J. M. (2003). Effects of fire intensity on groundcover shrubs in a frequently burned longleaf pine savanna. Ann Arbor, MI, Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College. Ph.D.: 146. Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92(3): 409-421.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Thaxton, J. M. (2003). Effects of fire intensity on groundcover shrubs in a frequently burned longleaf pine savanna. Ann Arbor, MI, Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College. Ph.D.: 146.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92(3): 409-421.