Difference between revisions of "Symphyotrichum patens"
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | Common name: late purple aster | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 14:50, 6 July 2015
| Symphyotrichum patens | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. patens |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum patens (Aiton) G.L. Nesom | |
| |
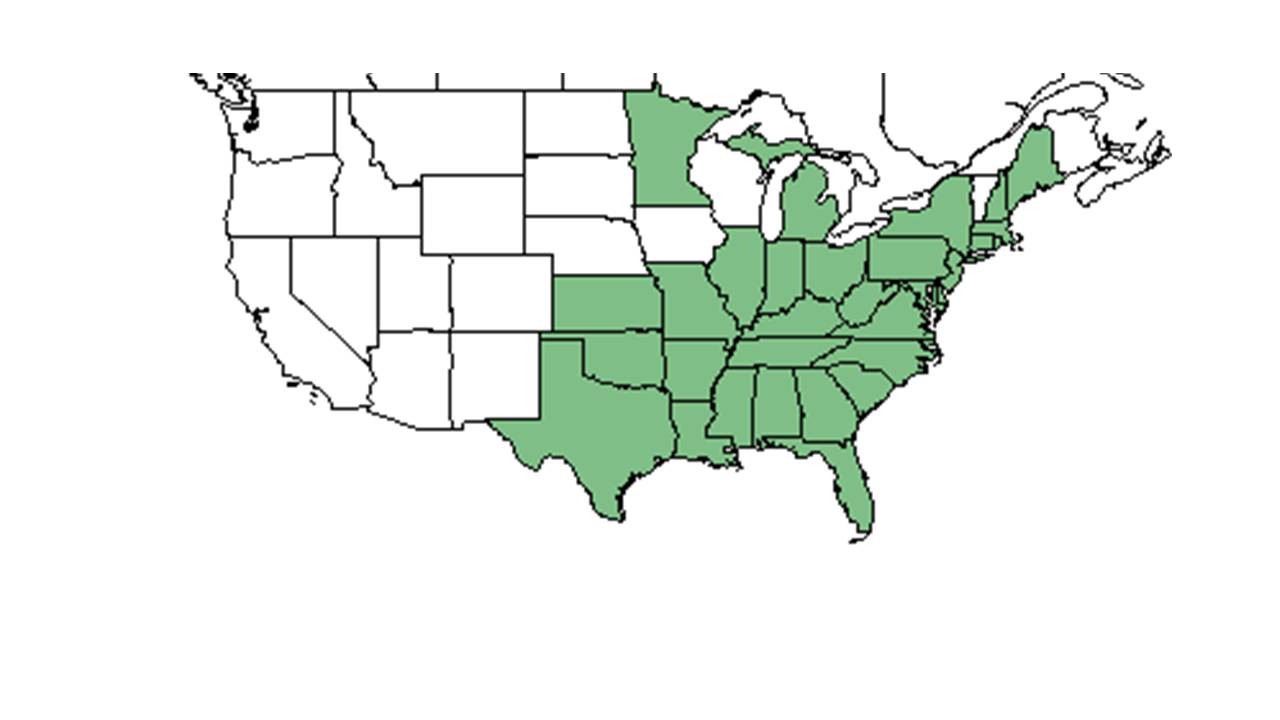
| Natural range of Symphyotrichum patens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
[hide]Description
Common name: late purple aster
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It can live in humid, subtropical climates (Burton 2009). Located in xeric limestone prairies of Illinois (McCain and Ebinger 2014). It can live in communities dominated by post oak (Burton 2009).
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Burton found that the percent cover of S. patens showed a positive linear response to increased fire frequency (Burton 2009).
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Burton, J. A. (2009). Fire frequency effects on vegetation of an upland old growth forest in eastern Oklahoma. Environmental Science. Stillwater, Oklahoma, Oklahoma State University. Bachelor: 78.
McClain, W. E. and J. E. Ebinger (2014). "Vascular Flora of Buettner Xeric Limestone Prairies, Monroe County, Illinois." Southern Appalachian Botanical Society.