Difference between revisions of "Solidago petiolaris"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''S. petiolaris'' has been found in open mixed hardwood remnant; mixed second growth hardwood woodland on slopes of sand ridge; moist sandy loam of oak-pine woods; longleaf pine-turkey oak sand ridge; open, upland, oak-hickory woodland; wooded upper rim of steephead; borders of mixed forests; pine-oak-hickory woods; scrub course; and in shaded pine-oak woods.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Richard S. Mitchell, Robert K. Godfrey, Angus Gholson, R. Kral, Andre F. Clewell, Angela M. Reid, K. M. Robertson, Billie Bailey, Cindi Stewart, MacClendons. States and Counties: Florida: Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Okaloosa, Walton. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> In disturbed habitats, it has been found in campgrounds, picnic areas, and roadsides. Soil types include sandy loam, loamy sand and loamy soil.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''S. petiolaris'' has been found in open mixed hardwood remnant; mixed second growth hardwood woodland on slopes of sand ridge; moist sandy loam of oak-pine woods; longleaf pine-turkey oak sand ridge; open, upland, oak-hickory woodland; wooded upper rim of steephead; borders of mixed forests; pine-oak-hickory woods; scrub course; and in shaded pine-oak woods.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Richard S. Mitchell, Robert K. Godfrey, Angus Gholson, R. Kral, Andre F. Clewell, Angela M. Reid, K. M. Robertson, Billie Bailey, Cindi Stewart, MacClendons. States and Counties: Florida: Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Okaloosa, Walton. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> In disturbed habitats, it has been found in campgrounds, picnic areas, and roadsides. Soil types include sandy loam, loamy sand and loamy soil.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
| − | Associated species include ''Solidago auriculata, Verbesina virginica, Aster'' and ''Desmodium.''<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | Associated species include ''[[Solidago auriculata]], [[Verbesina virginica]], Aster'' and ''Desmodium.''<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 12:37, 30 July 2021
| Solidago petiolaris | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Solidago |
| Species: | S. petiolaris |
| Binomial name | |
| Solidago petiolaris Aiton | |
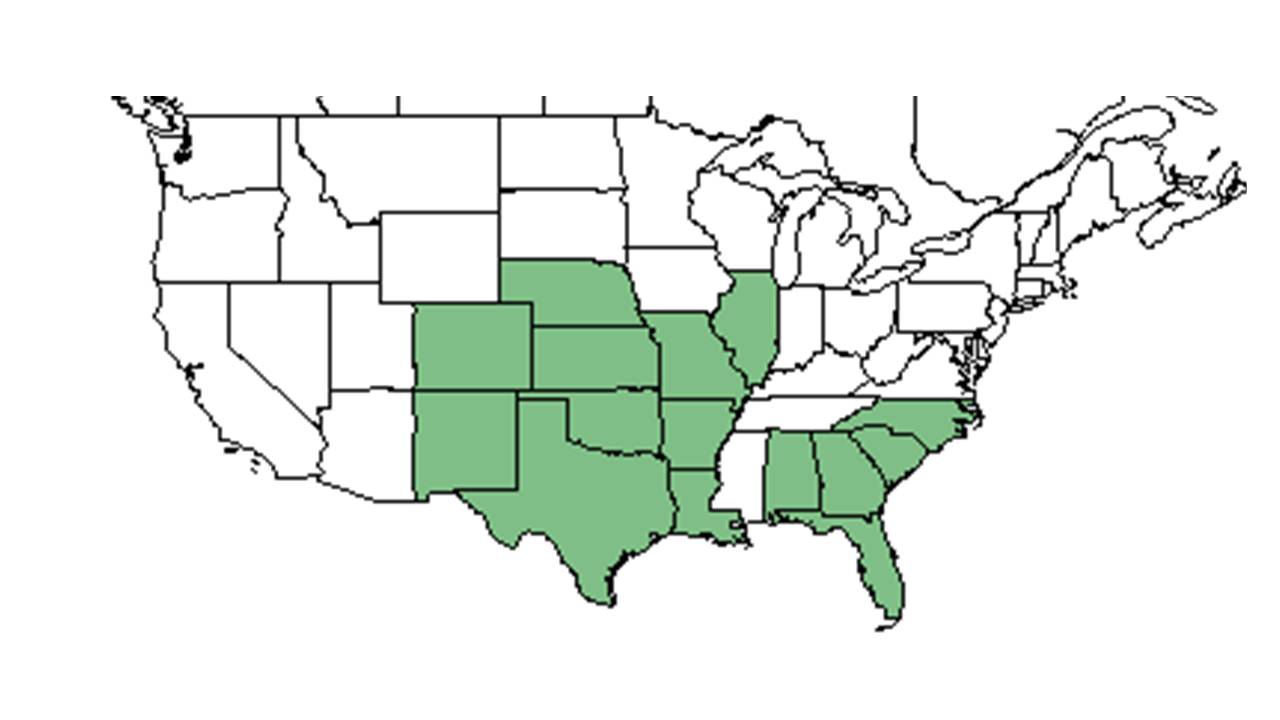
| |
| Natural range of Solidago petiolaris from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Downy ragged goldenrod
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic notes
Synonym: S. milleriana Mackenzie; S. harperi Mackenzie in Small
Varieties: Solidago petiolaris Aiton var. petiolaris
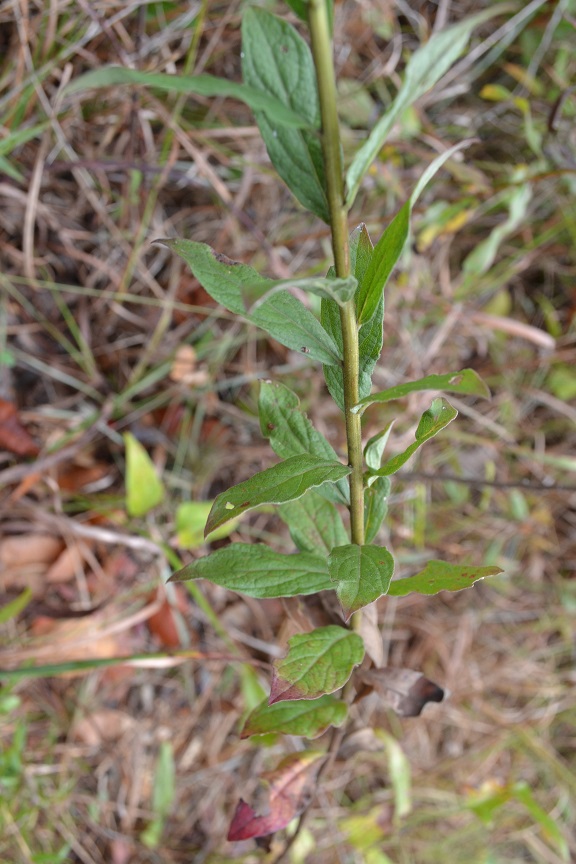
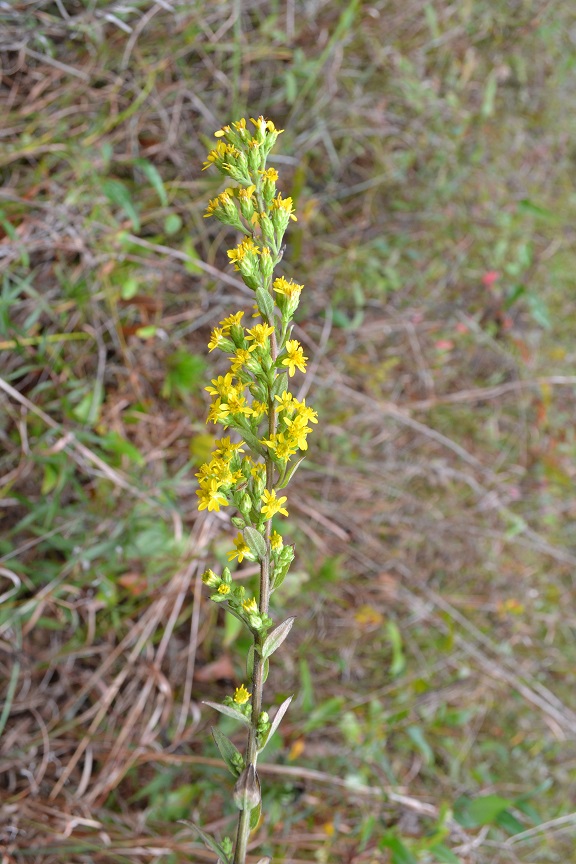
Description
A description of Solidago petiolaris is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, S. petiolaris has been found in open mixed hardwood remnant; mixed second growth hardwood woodland on slopes of sand ridge; moist sandy loam of oak-pine woods; longleaf pine-turkey oak sand ridge; open, upland, oak-hickory woodland; wooded upper rim of steephead; borders of mixed forests; pine-oak-hickory woods; scrub course; and in shaded pine-oak woods.[1] In disturbed habitats, it has been found in campgrounds, picnic areas, and roadsides. Soil types include sandy loam, loamy sand and loamy soil.[1]
Associated species include Solidago auriculata, Verbesina virginica, Aster and Desmodium.[1]
Phenology
It has been recorded flowering and fruiting May, September, October and November.[1]
Fire ecology
Populations of Solidago petiolaris have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[2]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Richard S. Mitchell, Robert K. Godfrey, Angus Gholson, R. Kral, Andre F. Clewell, Angela M. Reid, K. M. Robertson, Billie Bailey, Cindi Stewart, MacClendons. States and Counties: Florida: Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Okaloosa, Walton. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- Jump up ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.
