Difference between revisions of "Trilisa paniculata"
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Revision as of 13:04, 8 June 2021
| Trilisa paniculata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Trilisa |
| Species: | T. paniculata |
| Binomial name | |
| Trilisa paniculata (J.F. Gmel.) Herb. | |
| |
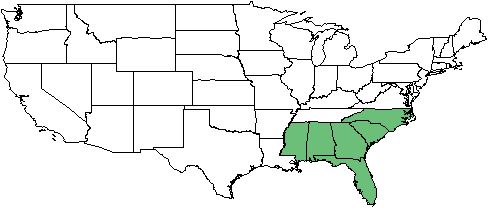
| Natural range of Trilisa paniculata from Weakley.[1] | |
Common Names: trilisa;[1] hairy chaffhead[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: Carphephorus paniculatus (J.F. Gmelin) Herbert.[3]
Description
T. paniculata is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.[2]
Distribution
This species occurs from southeastern North Carolina, south to southern Florida, and westward to the Florida panhandle and southern Alabama.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
T. paniculata occurs in savannas and flatwoods.[1]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, flowering occurs from August through October and fruiting from September through November.[1]
Fire ecology
In Georgia cut over pine forests, percent coverage of T. paniculata decreases with the number of growing seasons since fire, from 0.8 after one season, to 0.2 after two and three seasons, and 0.1 after eight.[4]
Use by animals
T. paniculata have been found in the stomachs of white-tailed deer in central peninsular Florida.[5]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 14 February 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Lemon PC (1949) Successional responses of herbs in the longleaf-slash pine forest after fire. Ecology 30(2):135-145.
- ↑ Harlow RF (1961) Fall and winter foods of Florida white-tailed deer. The Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Sciences 24(1):19-38.