Difference between revisions of "Toxicodendron radicans"
Juliec4335 (talk | contribs) |
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | Varieties: ''T. radicans'' var. ''vulgaris'' (Michaux) A.P. de Candolle forma ''negundo'' (Greene) Fernald; ''T. radicans'' var. ''pubens''; '' | + | Varieties: ''T. radicans'' var. ''vulgaris'' (Michaux) A.P. de Candolle forma ''negundo'' (Greene) Fernald; ''T. radicans'' var. ''pubens''; ''Toxicodendron radicans'' (Linnaeus) Kuntze var. ''negundo'' (Greene) Reveal.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
Revision as of 14:59, 25 May 2021
| Toxicodendron radicans | |
|---|---|

| |
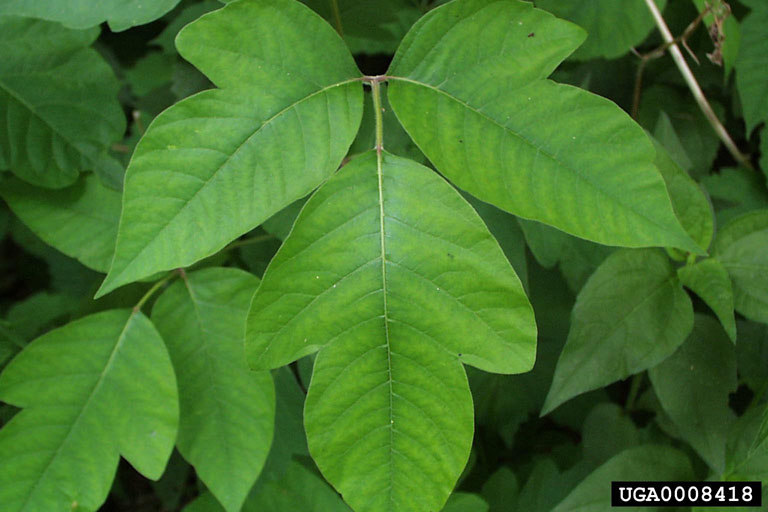
| Photo by Paul Wray, Iowa State University, Bugwood.org hosted at Forestryimages.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Anacardiaceae |
| Genus: | Toxicodendron |
| Species: | T. radicans |
| Binomial name | |
| Toxicodendron radicans (L.) Kuntze | |
| |
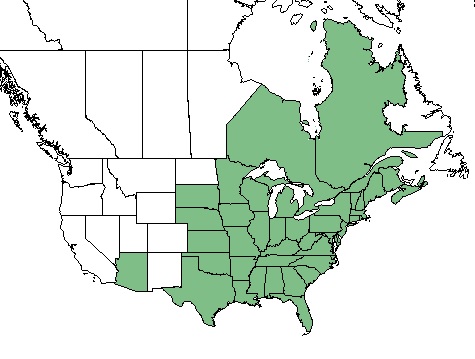
| Natural range of Toxicodendron radicans from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): Midwestern poison ivy[1], eastern poison ivy[1][2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Varieties: T. radicans var. vulgaris (Michaux) A.P. de Candolle forma negundo (Greene) Fernald; T. radicans var. pubens; Toxicodendron radicans (Linnaeus) Kuntze var. negundo (Greene) Reveal.[3]
Description
Toxicodendron radicans is a dioecious perennial that grows in the form of a forb/herb, shrub, subshrub, or vine.[2] Leaves are deciduous, alternate, trifoliate, ovate with dentate margins and can change to a deep orange or red color in the fall. It requires partial to full shade. All parts of this plant are considered poisonous. Oils on the plant contain urushiol, a severe skin irritant, which can cause severe skin redness, itching, swelling and blistering following direct or indirect contact.[4] This toxicity is expected to increase as atmospheric CO2 levels increase.[5]
Distribution
It can be found from Texas north to South Dakota and Minnesota and in all of the states eastward. It has also been reported in southern Arizona and the Ontario and Quebec provinces of Canada.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
T. radicans is found throughout a wide range of habitats including mesic forests, rock outcrops, open areas, disturbed areas, xeric limestone sites, swamp forests, brackish marshes, bottomlands, maritime forests.[1] In a Mississippi study, T. radicans composed 7% of the understory biomass in a pine/hardwood habitat.[6] In New Jersey old field successional habitat, T. radicans's relative abundance was one of two dominant species after 14 years of succession.[7] It responds positively to soil disturbance by heavy silvilculture in North Carolina.[8] However, T. radicans responds negatively or not at all to soil disturbance by improvement logging in Mississippi.[9] It does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[10]
Tocicodendron radicans is frequent and abundant in the Calcareous Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[11]
Phenology
T. radicans has been observed flowering March to May with fruits appearing in August through October.[1][12] Flowers can contain colors of white, green and/or brown. Fruits are amber in color and 0.25 in (6.4 mm) in diameter.[4]
Fire ecology
Selective herbicides and a three year fire frequency over a period of 10 years did not significantly impact the biomass of T. radicans.[6]
Pollination
In Iowa, T. radicans was observed being pollenated by 37 different floral associates consisting of coleopterans (beetles), dipterans (flies), hemipterans (true bugs), hymenopterans (ants, bees, wasps), and lepidopterans (butterflies). This diverse assemblage may partially explain its success across varied habitats.[13]
Use by animals
T. radicans attracts butterflies and is highly resistant to deer herbivory.[4] It comprises 10-25% of the diet of large mammals and 5-10% for small mammals and terrestrial birds.[2] Humans use the urushiol compounds of T. radicans to test the efficacy of skin protectant against chemical warfare agents.[14]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 20 December 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Plant database: Toxicodendron radicans. (20 December 2017).Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=TORA2
- ↑ Mohan J.E., Ziska L. H., Schlesinger W. H., Thomas R. B., Sicher R. C., George K., and Clark J. S. (2006). Biomass and toxicity responses of poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans) to elevated atmospheric CO2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 103(24):9086-9089.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Iglay R. B., Leopold B. D., Miller D. A., and Burger, Jr. L. W. (2010). Effect of plant community composition on plant response to fire and herbicide treatments. Forest Ecology and Management 260:543-548.
- ↑ Myster R. W. and Pickett S. T. A. (1990). Initial conditions, history and successional pathways in ten contrasting old fields. American Midland Naturalist 124(2):231-238.
- ↑ Cohen, S., R. Braham, and F. Sanchez. (2004). Seed Bank Viability in Disturbed Longleaf Pine Sites. Restoration Ecology 12(4):503-515.
- ↑ McComb, W.C. and R.E. Noble. (1982). Response of Understory Vegetation to Improvement Cutting and Physiographic Site in Two Mid-South Forest Stands. Southern Appalachian Botanical Society 47(1):60-77.
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 20 DEC 2017
- ↑ Senchina D. S. and Summerville K. S. (2007). Great diversity of insect floral associates may partially explain ecological success of poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans subsp. negundo [Greene] Gillis, Anacardiaceae). The Great Lakes Entomologist 40(3-4):120-128.
- ↑ Liu D. K., Wannemacher R. W., Snider T. H., and Hayes T. L. (1999). Efficacy of the topical skin protectant in advanced development. Journal of Applied Toxicology 19(supp 1):S41-S45.