Difference between revisions of "Carya tomentosa"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | ===Seed dispersal=== | |
| + | ''C. tomentosa'' is dispersed through various mammals found in the pine sandhills community <ref name= "Myster"> Myster, R. W. and S. T. A. Pickett (1993). "Effects of litter, distance, density and vegetation patch type on post dispersal tree seed predation in old fields." Oikos 66: 381-388. </ref>. | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Revision as of 13:35, 21 May 2018
| Carya tomentosa | |
|---|---|
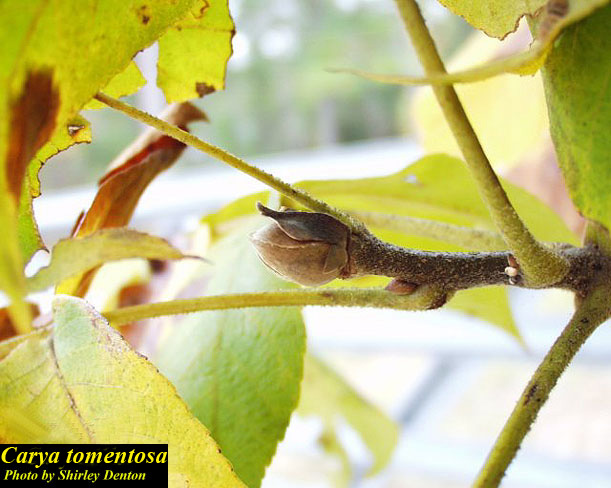

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Juglandales |
| Family: | Juglandaceae |
| Genus: | Carya |
| Species: | C. tomentosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Carya tomentosa Lam. | |
| |
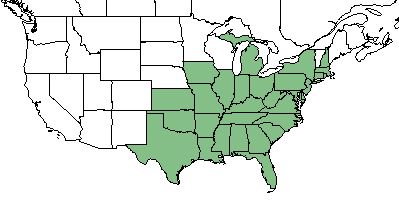
| Natural range of Carya tomentosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Carya alba (L.) Nuttall ex Elliott, Hicoria alba (L.) Britton
Varieties: none
Description
C. tomentosa, also known as mockernut hickory, is a native perennial in the Juglandaceae family with a tree growth habit [1].
Distribution
The species can be found throughout most of Eastern United States, ranging from Texas and Kansas to New Hampshire and Michigan [1].
Ecology
Habitat
C. tomentosa can be found in communities ranging from mesic hammocks to pine sandhills [2].
Associated species: Pinus palustris, Quercus hemisphaerica, Quercus incana, Quercus falcata, Quercus virginiana, and Quercus laevis [2].
Seed dispersal
C. tomentosa is dispersed through various mammals found in the pine sandhills community [3].
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CATO6
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Heuberger, K. A. and F. E. Putz (2003). "Fire in the suburbs: ecological impacts of prescribed fire in small remnants of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) sandhill." Restoration Ecology 11: 72-81.
- ↑ Myster, R. W. and S. T. A. Pickett (1993). "Effects of litter, distance, density and vegetation patch type on post dispersal tree seed predation in old fields." Oikos 66: 381-388.