Difference between revisions of "Lespedeza repens"
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''Lespedeza repens'' is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.<ref name="USDA"/> | + | ''Lespedeza repens'' is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.<ref name="USDA"/> Its stems and peduncles are sparsely short-appressed-pubescent. Stems can grow to 1 m in length. Racemes typically contain 4-8 flowers that are 5-7 mm long.<ref name="Clewell 1966">Clewell AF (1966) Native North American species of ''Lespedeza'' (Leguminosae). Rhodora 68(775):359-405.</ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 16:45, 12 February 2018
| Lespedeza repens | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Southeastern Flora Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Lespedeza |
| Species: | L. repens |
| Binomial name | |
| Lespedeza repens L | |
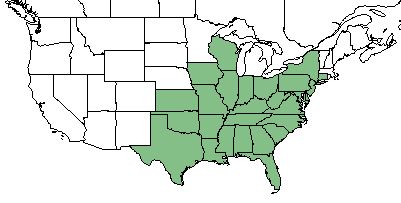
| |
| Natural range of Lespedeza repens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: smooth trailing lespedeza;[1] creeping lespedeza[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: Hedysarum repens[2]
Description
Lespedeza repens is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.[2] Its stems and peduncles are sparsely short-appressed-pubescent. Stems can grow to 1 m in length. Racemes typically contain 4-8 flowers that are 5-7 mm long.[3]
Distribution
This species occurs from Connecticut and New York, westward to northern Ohio, southern Wisconsin, Missouri, and Kansas, and southward to northern peninsular Florida, panhandle Florida, and central Texas.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
L. repens is occurs in woodlands and woodland borders.[1]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States flowering occurs from July through September and fruiting occurs from August through November.[1]
Use by animals
L. repens composes 2-5% of the diet of some large mammals and 10-25% of some terrestrial birds.[4]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 12 February 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Clewell AF (1966) Native North American species of Lespedeza (Leguminosae). Rhodora 68(775):359-405.
- ↑ Miller JH, Miller KV (1999) Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.