Difference between revisions of "Eupatorium rotundifolium"
Laurenloria (talk | contribs) |
Laurenloria (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | It has been observed flowering and fruiting from | + | It has been observed flowering and fruiting from May to November with peak inflorescence in July.<ref name=fsu/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 9 DEC 2016</ref> |
| + | |||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
This species disperses by wind. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | This species disperses by wind. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 20:33, 9 December 2016
| Eupatorium rotundifolium | |
|---|---|
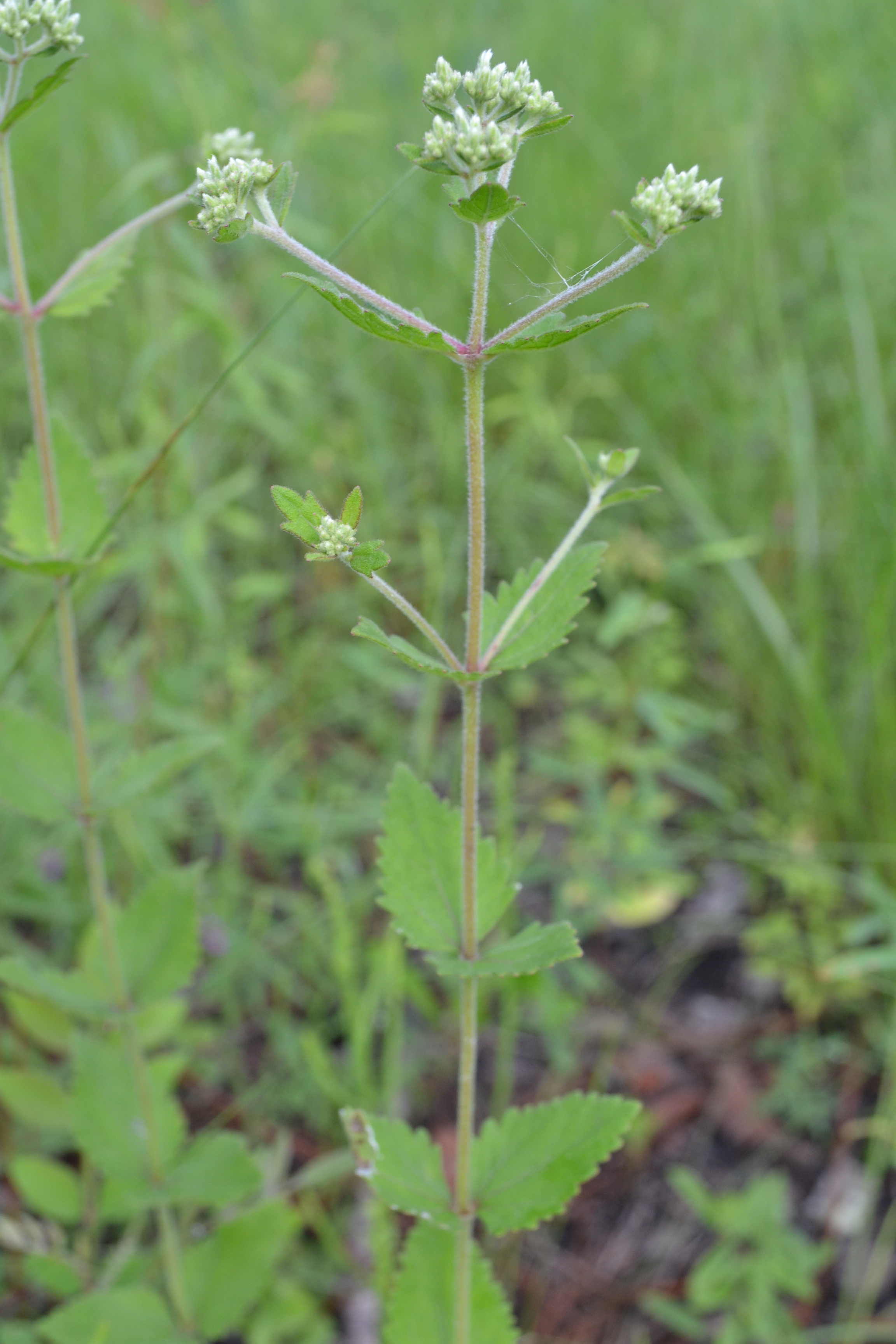

| |
| Photo was taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Eupatorium |
| Species: | E. rotundifolium |
| Binomial name | |
| Eupatorium rotundifolium L. | |
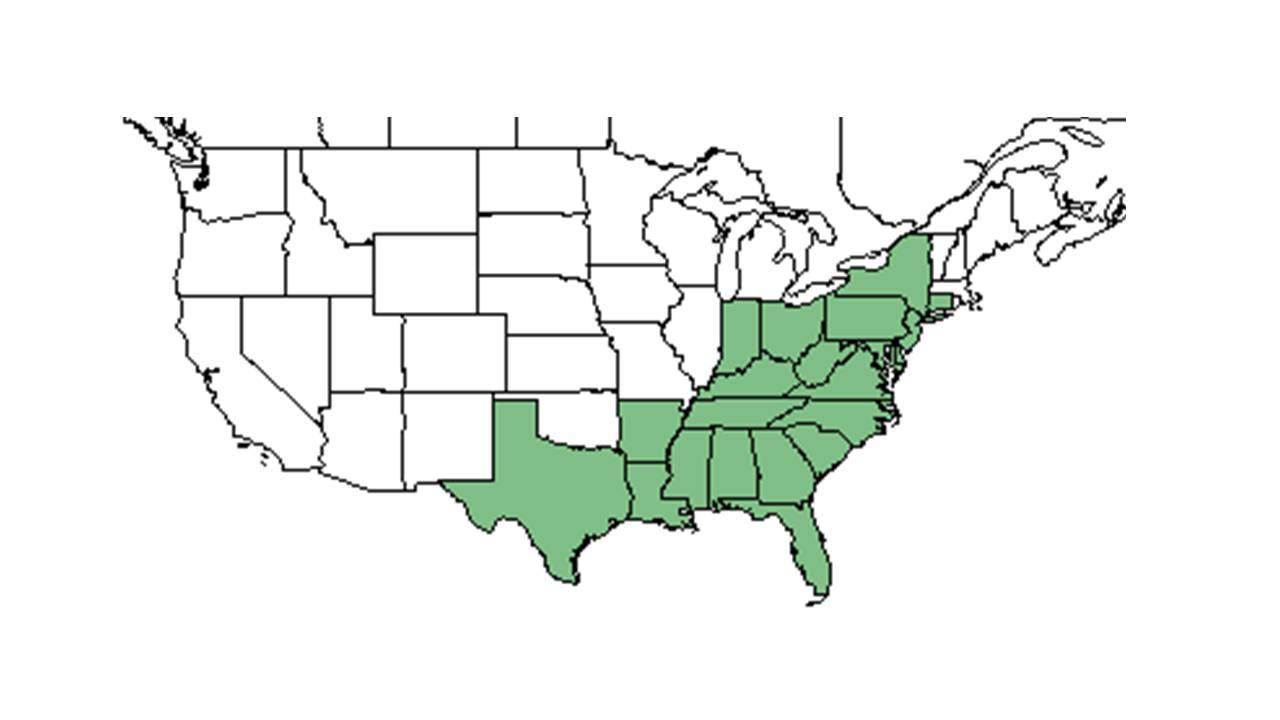
| |
| Natural range of Eupatorium rotundifolium from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Roundleaf thoroughwort
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Eupatorium rotundifolium var. rotundifolium; E. rotundifolium Linnaeus ssp. rotundifolium
Description
A description of Eupatorium rotundifolium is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
It has well-documented anticancer activities against various human cancer cell lines.[1]
Habitat
It is found i river bottoms, creek bluffs, slash pine-palmetto flatwoods, near streams, in open-dry habitats, mixed woodlands, savannas, marshy areas, bottomland woodlands, edges of thickets, edges of titi swamps, open boggy areas, Longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, and well-drained uplands.[2] It is also found in human disturbed areas such as pinelands that have been clear cut and plowed, roadside edges and ditches, in a drainage ditch, in roadside thickets, powerline corridors, in plowed pastures, and in fire breaks bordering pine flatwoods. [2] It can be found in areas regularly burned every 1 to 2 years in the winter. It can be found in longleaf pine savanna communities.[3] Associated species include Pinus taeda, P. palutris, P. elliottii, Serenoa repens, Taxodium distichum, Liquidambar styraciflua, Sabatia, Lilium, Eupatorium pilosum, E. semiserratum, E. recurvans, E. leucolepis, E. compositifolium, Ceanothus microphyllus, Ctenium, Rhus, Rubus, Aster spinulosus, Myrica cerifera, Magnolia virginiana, Aristida stricta, Cyrilla racemiflora.[2]
Phenology
It has been observed flowering and fruiting from May to November with peak inflorescence in July.[2][4]
Seed dispersal
This species disperses by wind. [5]
Fire ecology
It is fire-tolerant.[3]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Kintzios, S. E. (2007). "Terrestrial plant-derived anticancer agents and plant species used in anticancer research." Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 25: 79-113.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, Jean Wooten, Victoria Sullivan, Delzie Demaree, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Clarke Hudson, Carol Havlik, Loran C. Anderson, Nancy E. Jordan, J. P. Gillespie, J. Wooten, J. Lazor, R.L. Lazor, Gwynn W. Ramsey, Richard S. Mitchell, A. F. Clewell, K. Craddock Burks, R. Kral, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., Olga Lakela, Kurt Blum, Doug Gae, R. A. Norris, and Cecil R Slaughter. States and Counties: Arkansas: Lafayette and Sevier. Florida: Alachua, Bay, Calhoun, Citrus, Columbia, Duval, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Gulf, Hernando, Highlands, Hillsborough, Holmes, Jackson, Jefferson, Lake, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Okeechobee, Orange, Osceola, Pasco, Polk, Putnam, Santa Rosa, Sarasota, St. John’s, Suwannee, Taylor, Union, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Grady and Thomas. South Carolina: Jasper.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Brewer, J. S. and S. P. Cralle (2003). "Phosphorus addition reduces invasion of a longleaf pine savanna (southeastern USA) by a non-indigenous grass (Imperata cylindrica)." Plant Ecology 167: 237-245.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 9 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.