Difference between revisions of "Bidens bipinnata"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→Seed dispersal) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | The barbed awns of the seeds allow for the seed to attach to animals and humans and be dispersed far distances<ref name="illinois"/> | + | The barbed awns of the seeds allow for the seed to attach to animals and humans and be dispersed far distances.<ref name="illinois"/> |
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
Revision as of 19:49, 10 August 2016
| Bidens bipinnata | |
|---|---|

| |
| photo by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Bidens |
| Species: | B. bipinnata |
| Binomial name | |
| Bidens bipinnata L. | |
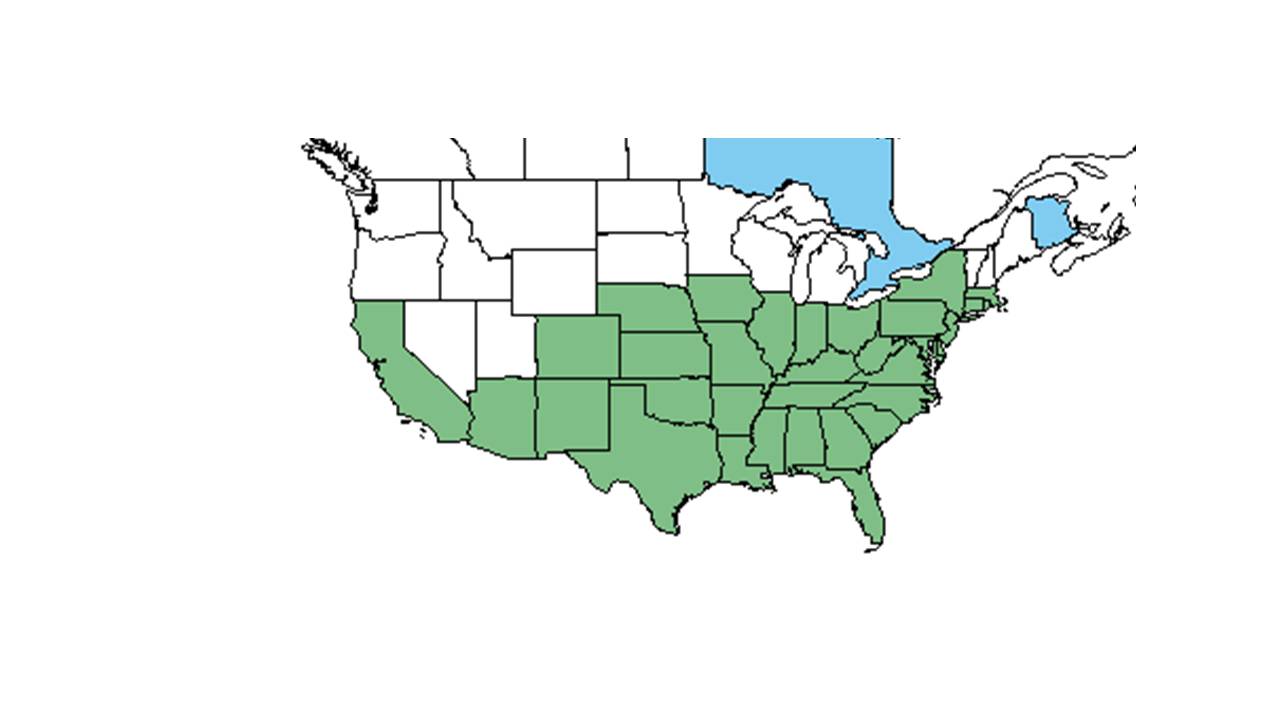
| |
| Natural range of Bidens bipinnata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Spanish needles
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Bidens bipinnata var. bipinnata
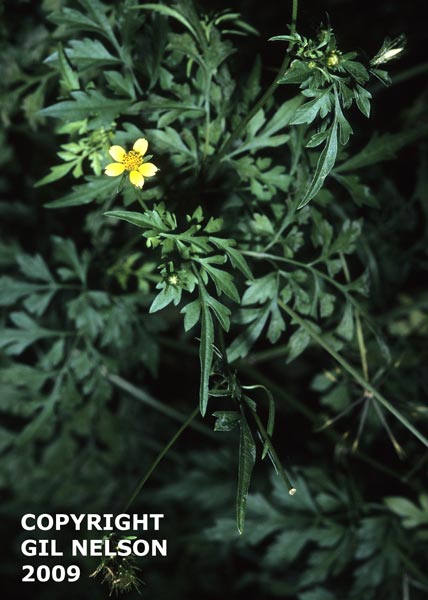
Description
A description of Bidens bipinnata is provided in The Flora of North America.
B. bipinnata is an annual herb. It tends to be a ruderal, weedy species.[1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
B. bipinnata is found in marsh and island communities, river bluffs, and pine-oak woodlands. It has also been found in disturbed areas including campgrounds, roadsides, ditches, disturbed coastal hammocks, old fields, and fire line. This species prefers shaded environments and moist sandy soil types like sandy loam, red sandy clay, and loamy sand.[1]
Associated species includes Quercus geminata, Desmodium ochroleucum, D. rotundifolium, Pinus, other Quercus's, Cornus florida, Liquidambar styraciflua, and others.[1]
Phenology
This species has been observed flowering and fruiting from July to October.[1]
Seed dispersal
The barbed awns of the seeds allow for the seed to attach to animals and humans and be dispersed far distances.[2]
Fire ecology
B. bipinnata is a seeder; 70% mortality when subjected to 100% leaf scorch[3]. It is fire tolerant and frequent in firebreaks[1].
Pollination
Pollinated by Honeybees, leaf-cutting bees (Megachile spp., Coelioxys sayi, Heriades leavitti), and the butterfly Pieris rapae[2].
Use by animals
Caterpillars of moths Cirrhophanus triangulifer, Condica confederata, Epiblema otiosana, Palthis asopialis, Platysenta mobilis, and Synchlora aerata feed on the foliage. Leaf beetles Calligrapha bidenticola and Calligrapha californica feed on the leaves. The aphid Aphis coreopsidis sucks juices from the flowering stalks. Seeds are eaten by birds such as the Ring-Necked Pheasant, Bobwhite, Wood Duck, Purple Finch, and Common Redpoll. The foliage is eaten by the cottontail rabbit[2].
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Cultivate in partial sunlight, moist to mesic conditions with fertile loamy soil[2].
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Bian Tan, Loran C. Anderson, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Richard S. Mitchell, R.K. Godfrey, R. Kral, Wilson Baker, R. Komarek, Andre F. Clewell, R.A. Norris, and Andre F. Clewell. States and Counties: Florida: Columbia, Wakulla, Bay, Calhoun, Leon, Franklin, Jackson, Jefferson, and Liberty. Georgia: Grady.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 (http://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/weeds/plants/spanish_needles.htmIllinois Wildflowers. Accessed: April 4, 2016
- ↑ []Fire Manager. Accessed: April 4, 2016