Difference between revisions of "Viburnum nudum"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→Description) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
"Shrubs or less frequently small trees. Leaves simple, opposite, palmately lobed or toothed, rarely nearly entire; stipules absent, or present and adnate to the petioles. Cyme compound, flat-topped. Sepals 5, very small; corolla 5-lobed, rotate, white or pinkish, fertile flowers 5-8 mm broad; stamens 5. Sterile flowers, when present, usually zygomorphic, marginal and large. Drupe 1-seeded, usually laterally compressed." <ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 993. Print.</ref> | "Shrubs or less frequently small trees. Leaves simple, opposite, palmately lobed or toothed, rarely nearly entire; stipules absent, or present and adnate to the petioles. Cyme compound, flat-topped. Sepals 5, very small; corolla 5-lobed, rotate, white or pinkish, fertile flowers 5-8 mm broad; stamens 5. Sterile flowers, when present, usually zygomorphic, marginal and large. Drupe 1-seeded, usually laterally compressed." <ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 993. Print.</ref> | ||
| − | "Medium sized shrub. Similar to ''V. cassinoides.'' Leaves elliptic to elliptic-oblanceolate, 5-12 cm long, 2-6 cm wide, acute to acuminate, base cuneate to rarely rounded; petioles 0.5-2.5 cm long. Peduncles 1-4 cm long, rarely shorter, equaling or longer than the rays." <ref="Radford et al 1964"/> | + | "Medium sized shrub. Similar to ''V. cassinoides.'' Leaves elliptic to elliptic-oblanceolate, 5-12 cm long, 2-6 cm wide, acute to acuminate, base cuneate to rarely rounded; petioles 0.5-2.5 cm long. Peduncles 1-4 cm long, rarely shorter, equaling or longer than the rays." <ref name="Radford et al 1964"/> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 18:55, 18 August 2016
| Viburnum nudum | |
|---|---|

| |
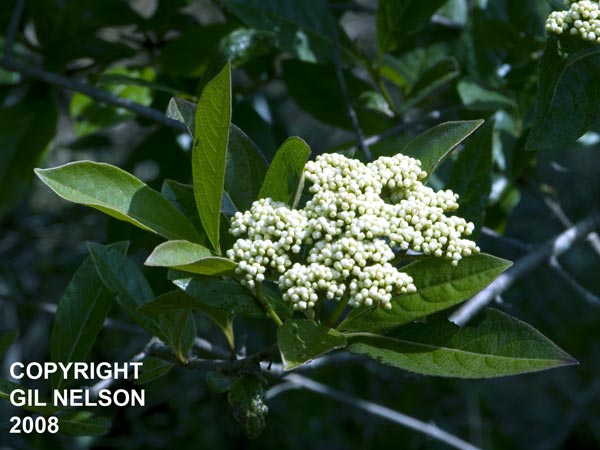
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Dipsacales |
| Family: | Caprifoliaceae |
| Genus: | Viburnum |
| Species: | V. nudum |
| Binomial name | |
| Viburnum nudum L. | |
| |
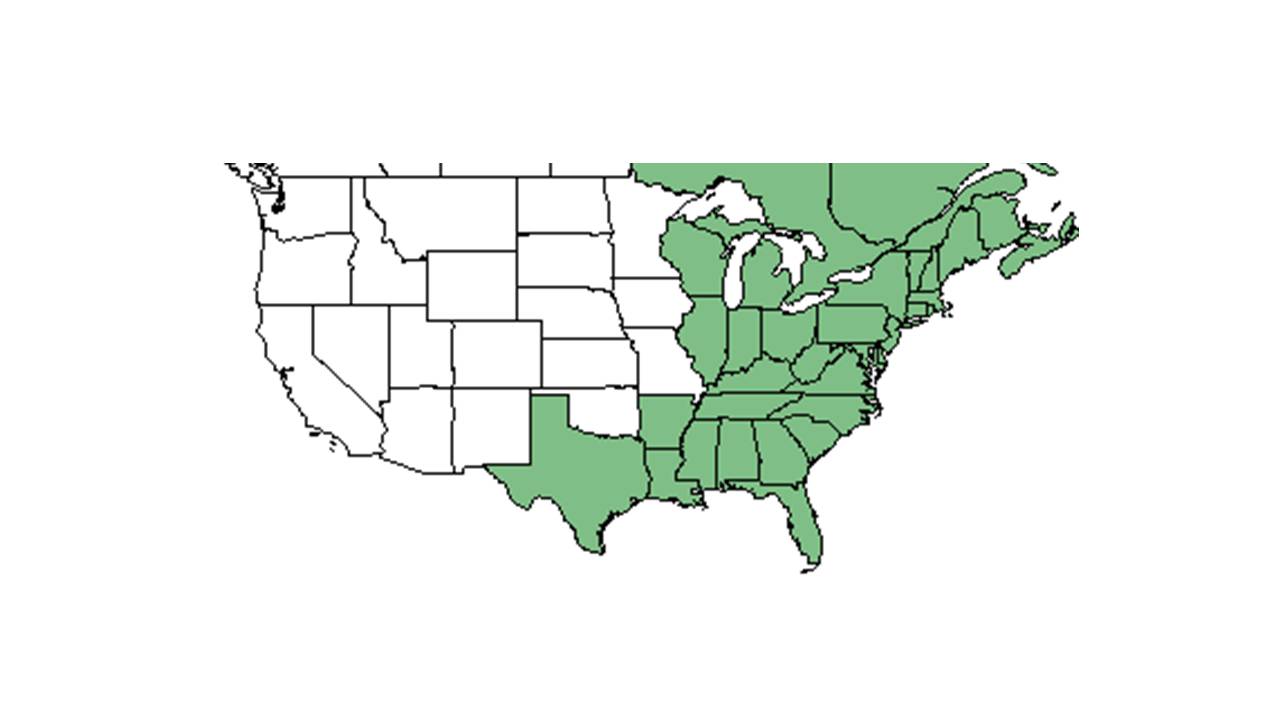
| Natural range of Viburnum nudum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: possumhaw
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Viburnum nudum var. nudum; Viburnum nudum var. angustifolium Torrey & A. Gray
Description
"Shrubs or less frequently small trees. Leaves simple, opposite, palmately lobed or toothed, rarely nearly entire; stipules absent, or present and adnate to the petioles. Cyme compound, flat-topped. Sepals 5, very small; corolla 5-lobed, rotate, white or pinkish, fertile flowers 5-8 mm broad; stamens 5. Sterile flowers, when present, usually zygomorphic, marginal and large. Drupe 1-seeded, usually laterally compressed." [1]
"Medium sized shrub. Similar to V. cassinoides. Leaves elliptic to elliptic-oblanceolate, 5-12 cm long, 2-6 cm wide, acute to acuminate, base cuneate to rarely rounded; petioles 0.5-2.5 cm long. Peduncles 1-4 cm long, rarely shorter, equaling or longer than the rays." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, V. nudum can be found in mesic thickets, mesic woodlands, along spring-fed lakes, swampy woodlands, creek heads, ravine seepage areas, stagnant branch swamps, bottomland hardwood stands, pine-titi flats, floodplains, acid flatwoods in sweet bay swamps, pine flatwoods, pine-saw palmetto flatwoods, annually burned pinelands, coastal hammocks, and hickory-oak-magnolia forests. [2] It has also been found along gas pipeline corridors, nature trails, powerline cooridors, and logged pine flatwoods. It has been found to grow in sandy peat soils and loamy sand. [2]
Associated species include Gordonia, Illicium, Magnolia, Stewartia, Myrica cerifera, Vitis rotundifolia, Lyonia lucida, Thelypteris palustris, Itea virginica, Clethra alnifolia, Leucothoe racemosa, Solidago, Nyssa biflora, Taxodium ascendens, Smilax laurifolia, Acer rubrum, and Magnolia virginiana. [2]
Phenology
Flowers and fruits March through November. [2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 993. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, H. Kurz, Ann F. Johnson, Angus Gholson, Wilson Baker, R. R. Smith, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert Kral, P. L. Redfearn, K. Craddock Burks, Bruce Hansen, G. Robinson, Andre F. Clewell, J. P. Gillespie, E. S. Ford, P. White, Bruce Nelson, L. B. Trott, Lloyd H. Shinners, Robert J Lemaire, A. G. Shuey, R.A. Norris, R. Komarek, Cecil R Slaughter, Michael Keys, Annie Schmidt. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Clay, Columbia, DeSoto, Duval, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Okaloosa, Osceola, Polk, Santa Rosa, St. Johns, Union, Wakulla, Walton. Georgia: Clinch, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.