Difference between revisions of "Smilax auriculata"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain, specifically in Florida and Georgia, ''S. auriculata'' can be found bordering mesic woodlands, longleaf pine turkey oak sand ridges, <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert A. Norris, R. Komarek, Cindi Stewart, Cecil R Slaughter, Marc Minno, Bob Fewster, Lisa Keppner. States and Counties: Florida: Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Camden. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> palmetto flatwoods | + | In the Coastal Plain, specifically in Florida and Georgia, ''S. auriculata'' can be found bordering mesic woodlands, longleaf pine turkey oak sand ridges, <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert A. Norris, R. Komarek, Cindi Stewart, Cecil R Slaughter, Marc Minno, Bob Fewster, Lisa Keppner. States and Counties: Florida: Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Camden. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> palmetto flatwoods,<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> <ref name=olano> Olano, J. M., E. S. Menges, et al. (2006). "Carbohydrate storage in five resprouting Florida scrub plants across a fire chronosequence." New Phytologist 170: 99-105.</ref> oak-saw palmetto scrubs,<ref name=foster> Foster, Tammy E., Paul A. Schmalzer. (2003). "The effect of season of fire on the recovery of Florida scrub". Dynamac Corporation, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. 2B.7. </ref> sandhill communities,<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> <ref name=rein> Reinhart, K. O. and E. S. Menges (2004). "Effects of re-introducing fire to a central Florida sandhill community." Applied Vegetation Science 7: 141-150.</ref> xeric longleaf pine woodlands (Peet and Allard 1993), and unburned scrubby flatwoods.<ref name=menges1995> Menges, E. and N. Kohfeldt (1995). "Life History Strategies of Florida Scrub Plants in Relation to Fire." Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 122(4): 282-297</ref> It can also be found along railroads, powerline corridors, and disturbed longleaf pine restoration sites. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> Soil types include loamy sand <ref name="FSU herbarium"/> <ref name=foster/> and sandy, siliceous, hyperthermic Ultic haplaquod of the Pomona series. <ref name=moore> Moore, W. H., B. F. Swindel, et al. (1982). "Vegetative response to prescribed fire in a north Florida flatwoods forest." Journal of Range Management 35: 386-389.</ref> In habitats that include ''Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Q. incana, Sporobolus junceus'' and ''Licania michauxii'', ''S. auriculata'' accounts for most of the groundcover density.<ref name=prov> Provencher, L. M., B. J. Herring, et al. (2001). "Effects of hardwood reduction techniques on longleaf pine sandhill vegetation in northwest Florida." Restoration Ecology 9: 13-27.</ref> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | Flowering has been observed in May and fruiting June through July. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | Flowering has been observed in May and fruiting June through July.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by being consumed by vertebrates (being assumed). <ref name="KK"> Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015. </ref> | + | According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by being consumed by vertebrates (being assumed).<ref name="KK"> Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015. </ref> |
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | It increases in abundance after fire.<ref name=menges1995/> Its rapid recovery post-fire can be attributed to large specialized storage organs. <ref name=olano/> However, it was figured out that ''S. auriculata'' decreased to almost nonexistent following a May fire, suggesting that season of burning is important for this species. <ref name=green> Greenberg, C. H. (2003). "Vegetation recovery and stand structure following a prescribed stand-replacement burn in sand pine scrub." Natural Areas Journal 23: 141-151. </ref> | + | It increases in abundance after fire.<ref name=menges1995/> Its rapid recovery post-fire can be attributed to large specialized storage organs.<ref name=olano/> However, it was figured out that ''S. auriculata'' decreased to almost nonexistent following a May fire, suggesting that season of burning is important for this species.<ref name=green> Greenberg, C. H. (2003). "Vegetation recovery and stand structure following a prescribed stand-replacement burn in sand pine scrub." Natural Areas Journal 23: 141-151.</ref> |
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Smilax auriculata'' at Archbold Biological Station | + | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Smilax auriculata'' at Archbold Biological Station:<ref name="deyrup2015"> Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> |
Apidae: ''Apis mellifera'' | Apidae: ''Apis mellifera'' | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
Megachilidae: ''Coelioxys dolichos, Megachile mendica, M. xylocopoides'' | Megachilidae: ''Coelioxys dolichos, Megachile mendica, M. xylocopoides'' | ||
| − | Deyrup (2002)observed these bees, ''Augochlora pura, Coelioxys dolichos, Megachile mendica, M. xylocopoides, Apis mellifera, Xylocopa micans, X. virginica krombeini'', on ''S. auriculata''. <ref name=deyrup2002> Deyrup, Mark., Jayanthi Edirisinghe, Beth Norden. (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). Insecta Mundi. Vol. 16. No.1-3. Pages 87-102. </ref> | + | Deyrup (2002)observed these bees, ''Augochlora pura, Coelioxys dolichos, Megachile mendica, M. xylocopoides, Apis mellifera, Xylocopa micans, X. virginica krombeini'', on ''S. auriculata''. <ref name=deyrup2002> Deyrup, Mark., Jayanthi Edirisinghe, Beth Norden. (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). Insecta Mundi. Vol. 16. No.1-3. Pages 87-102.</ref> |
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''S. auriculata'' was found in 5.5% of the ''Gopherus polyphemus'' scat <ref name=carl> Carlson, J. E., E. S. Menges, et al. (2003). "Seed dispersal by Gopherus polyphemus at Archbold Biological Station, Florida." Florida Scientist 66: 147-154.</ref> therefore, the gopher tortoise serves as an agent of seed dispersal. | + | ''S. auriculata'' was found in 5.5% of the ''Gopherus polyphemus'' scat<ref name=carl> Carlson, J. E., E. S. Menges, et al. (2003). "Seed dispersal by Gopherus polyphemus at Archbold Biological Station, Florida." Florida Scientist 66: 147-154.</ref> therefore, the gopher tortoise serves as an agent of seed dispersal. |
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
Revision as of 17:58, 18 August 2016
| Smilax auriculata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Smilacaceae |
| Genus: | Smilax |
| Species: | S. auriculata |
| Binomial name | |
| Smilax auriculata Walter | |
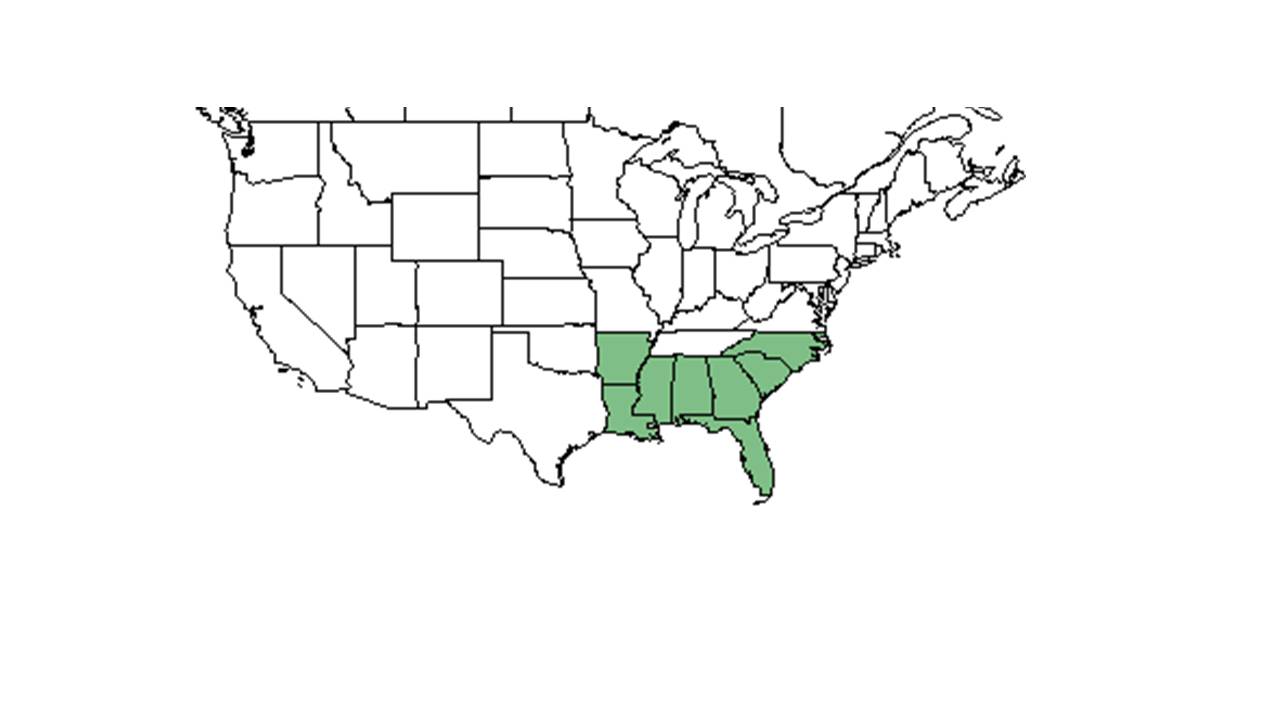
| |
| Natural range of Smilax auriculata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: earleaf greenbrier
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Smilax auriculata is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain, specifically in Florida and Georgia, S. auriculata can be found bordering mesic woodlands, longleaf pine turkey oak sand ridges, [1] palmetto flatwoods,[1] [2] oak-saw palmetto scrubs,[3] sandhill communities,[1] [4] xeric longleaf pine woodlands (Peet and Allard 1993), and unburned scrubby flatwoods.[5] It can also be found along railroads, powerline corridors, and disturbed longleaf pine restoration sites. [1] Soil types include loamy sand [6] [3] and sandy, siliceous, hyperthermic Ultic haplaquod of the Pomona series. [7] In habitats that include Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Q. incana, Sporobolus junceus and Licania michauxii, S. auriculata accounts for most of the groundcover density.[8]
Phenology
Flowering has been observed in May and fruiting June through July.[1]
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by being consumed by vertebrates (being assumed).[9]
Seed bank and germination
It can reproduce by resprouting, clonal spreading, and seeding.[5]
Fire ecology
It increases in abundance after fire.[5] Its rapid recovery post-fire can be attributed to large specialized storage organs.[2] However, it was figured out that S. auriculata decreased to almost nonexistent following a May fire, suggesting that season of burning is important for this species.[10]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Smilax auriculata at Archbold Biological Station:[11]
Apidae: Apis mellifera
Halictidae: Augochlora pura
Megachilidae: Coelioxys dolichos, Megachile mendica, M. xylocopoides
Deyrup (2002)observed these bees, Augochlora pura, Coelioxys dolichos, Megachile mendica, M. xylocopoides, Apis mellifera, Xylocopa micans, X. virginica krombeini, on S. auriculata. [12]
Use by animals
S. auriculata was found in 5.5% of the Gopherus polyphemus scat[13] therefore, the gopher tortoise serves as an agent of seed dispersal.
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert A. Norris, R. Komarek, Cindi Stewart, Cecil R Slaughter, Marc Minno, Bob Fewster, Lisa Keppner. States and Counties: Florida: Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Camden. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Olano, J. M., E. S. Menges, et al. (2006). "Carbohydrate storage in five resprouting Florida scrub plants across a fire chronosequence." New Phytologist 170: 99-105.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Foster, Tammy E., Paul A. Schmalzer. (2003). "The effect of season of fire on the recovery of Florida scrub". Dynamac Corporation, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. 2B.7.
- ↑ Reinhart, K. O. and E. S. Menges (2004). "Effects of re-introducing fire to a central Florida sandhill community." Applied Vegetation Science 7: 141-150.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Menges, E. and N. Kohfeldt (1995). "Life History Strategies of Florida Scrub Plants in Relation to Fire." Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 122(4): 282-297
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedFSU herbarium - ↑ Moore, W. H., B. F. Swindel, et al. (1982). "Vegetative response to prescribed fire in a north Florida flatwoods forest." Journal of Range Management 35: 386-389.
- ↑ Provencher, L. M., B. J. Herring, et al. (2001). "Effects of hardwood reduction techniques on longleaf pine sandhill vegetation in northwest Florida." Restoration Ecology 9: 13-27.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.
- ↑ Greenberg, C. H. (2003). "Vegetation recovery and stand structure following a prescribed stand-replacement burn in sand pine scrub." Natural Areas Journal 23: 141-151.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Deyrup, Mark., Jayanthi Edirisinghe, Beth Norden. (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). Insecta Mundi. Vol. 16. No.1-3. Pages 87-102.
- ↑ Carlson, J. E., E. S. Menges, et al. (2003). "Seed dispersal by Gopherus polyphemus at Archbold Biological Station, Florida." Florida Scientist 66: 147-154.