Difference between revisions of "Solidago fistulosa"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | ''S. fistulosa'' has been observed growing in a recently burned pineland bay forest and an annually burned pine forest (FSU Herbarium). | ||
| + | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Solidago fistulosa'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Solidago fistulosa'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | ||
Revision as of 17:23, 19 November 2015
| Solidago fistulosa | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Solidago |
| Species: | S. fistulosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Solidago fistulosa Mill. | |
| |
| Natural range of Solidago fistulosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: pine barren goldenrod
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Solidago fistulosa is provided in The Flora of North America.
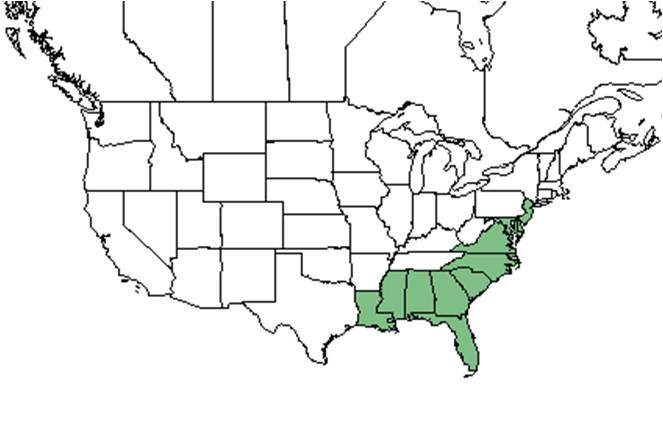
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, S. fistulosa has occurred in wet hammocks, cabbage palm-slash pine hammocks, slash pine woodlands, lake margins, open ditches bordering swamps, shores of cypress ponds, thickets bordering cypress-gum depressions, floodplain woodlands, a Cladium brackish marsh, dried out cypress depressions, and marshy areas. It also has been found in disturbed areas such as roadside depressions, black sandy peat of a logged over hillside bog, clear-cut sand pine scrub ridge, old pastures, and a drainage ditch bordering pine flatwoods (FSU Herbarium). Soils include loamy sand, sandy loam, sandy peat, and clay (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Euthamia minor, Eupatorium, Xyris, Rhynchospora fascicularis and Hypericum cistifolium (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowers in September through October and fruits in October (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
S. fistulosa has been observed growing in a recently burned pineland bay forest and an annually burned pine forest (FSU Herbarium).
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Solidago fistulosa at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera
Colletidae: Colletes mandibularis, C. thysanellae
Halictidae: Augochlorella gratiosa, Halictus poeyi, Sphecodes heraclei
Megachilidae: Coelioxys sayi
Sphecidae: Anacrabro ocellatus, Tachytes validus
Vespidae: Eumenes smithii, Parancistrocerus salcularis rufulus, Polistes dorsalis hunteri, Zethus spinipes
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.