Difference between revisions of "Helianthus radula"
Ruthstetler (talk | contribs) (→Description) |
Ruthstetler (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | Wade Tract has been burned biennially.<ref name="Gilliam et al 2006">Gilliam, F. S., W. J. Platt, et al. (2006). "Natural disturbances and the physiognomy of pine savannas: A phenomenological model." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 83-96.</ref> | + | This species has been found in habitat that is burned frequently (FSU Herbarium). For example, the Wade Tract has been burned biennially.<ref name="Gilliam et al 2006">Gilliam, F. S., W. J. Platt, et al. (2006). "Natural disturbances and the physiognomy of pine savannas: A phenomenological model." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 83-96.</ref> |
| + | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 15:59, 14 July 2015
| Helianthus radula | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Helianthus |
| Species: | H. radula |
| Binomial name | |
| Helianthus radula (Pursh) Torr. & A. Gray | |
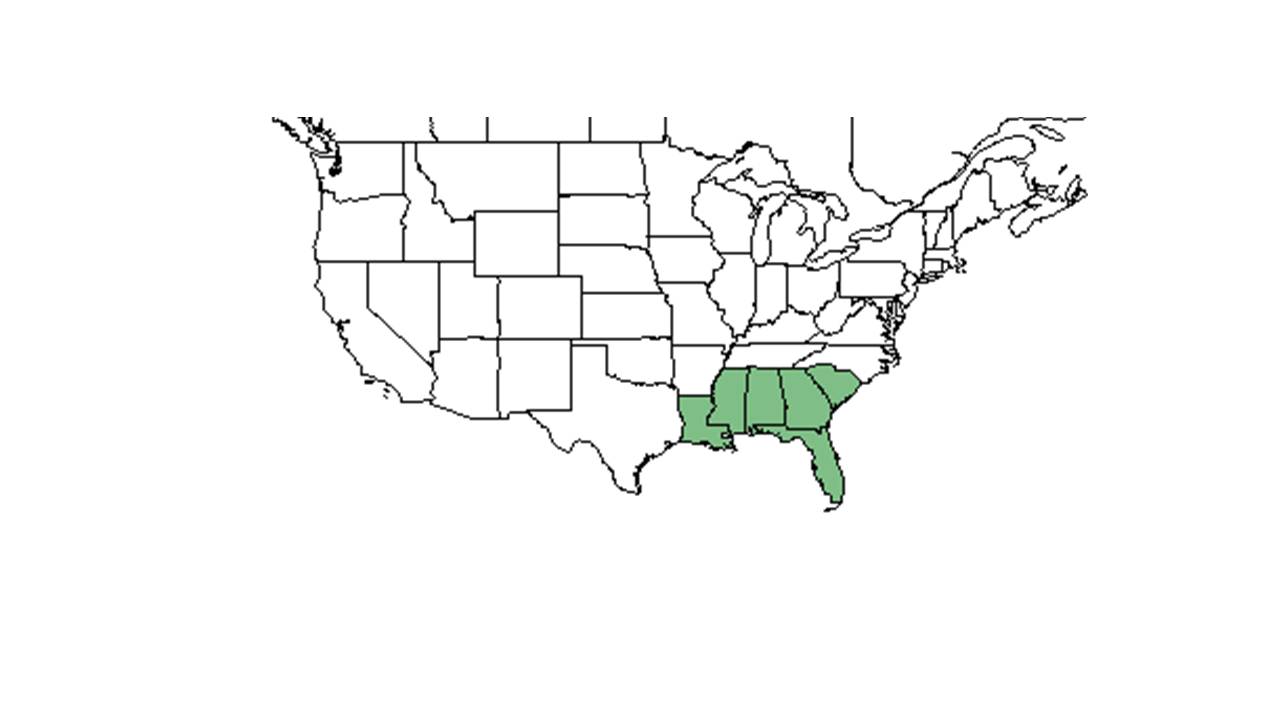
| |
| Natural range of Helianthus radula from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common Name: rayless sunflower
Helianthus radula is a perennial herbaceous species.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It can live in loblolly or slash pine communities.[1] Censused on mid-slope at the Wade Tract, GA.[2] “The fire-maintained forest structure is savanna-like with an open canopy of P. palustris and P. elliotii Engelm. (slash pine), little to no subcanopy, and diverse ground cover dominated by grasses…and forbs…”[3] Commonly found species in the forests of camp Shelby Training Site within Pine Woods subprovince of the Gulf Coastal Plain physiographic region of Mississippi.[1]
Phenology
Flowering and fruiting has been observed in August through November (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
This species has been found in habitat that is burned frequently (FSU Herbarium). For example, the Wade Tract has been burned biennially.[2]
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014.
Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Roomie Wilson, Delzie Demaree, C. Ritchie Bell, F. H. Sargent, Samuel B. Jones, John W. Thieret, Almut G. Jones, A. F. Clewell, R. K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, JoAnn Hansen, Robert L. Lazor, R. Kral, J. P. Gillespie, R. E. Perdue, Jr., Paul L. Redfearn, Jr., Kurt E. Blum, D. B. Ward, S. S. Ward, John B. Nelson, G. R. Knight, Cecil R Slaughter, Nancy E. Jordan, R. A. Norris, and R. Komarek.
States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Citrus, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Holmes, Jefferson, Lake, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Orange, Osceola, Putnam, St Johns, Taylor, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Thomas. Louisiana: Tangipahoa and Washington. Mississippi: Jackson, Lamar, and Pearl River. South Carolina: Colleton.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Yager, L. Y., M. G. Hinderliter, et al. (2007). "Gopher tortoise response to habitat management by prescribed burning." The Journal of Wildlife Management 71: 428-434.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Gilliam, F. S., W. J. Platt, et al. (2006). "Natural disturbances and the physiognomy of pine savannas: A phenomenological model." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 83-96.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. K., M. B. Drew, et al. (1998). "Effects of experimental fire regimes on the population dynamics of Schwalbea americana L." Plant Ecology 137: 115-137.