Difference between revisions of "Croton glandulosus"
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | It is seasonal; it is mainly found from May to December, peaking in September in a study at Padre Island.<ref name="Lonard et al 2004"/> | + | It is seasonal; it is mainly found from May to December, peaking in September in a study at Padre Island.<ref name="Lonard et al 2004"/> It has been observed flowering and fruiting June through October and fruiting in December (FSU Herbarium). |
| + | |||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
Revision as of 20:01, 9 July 2015
| Croton glandulosus | |
|---|---|
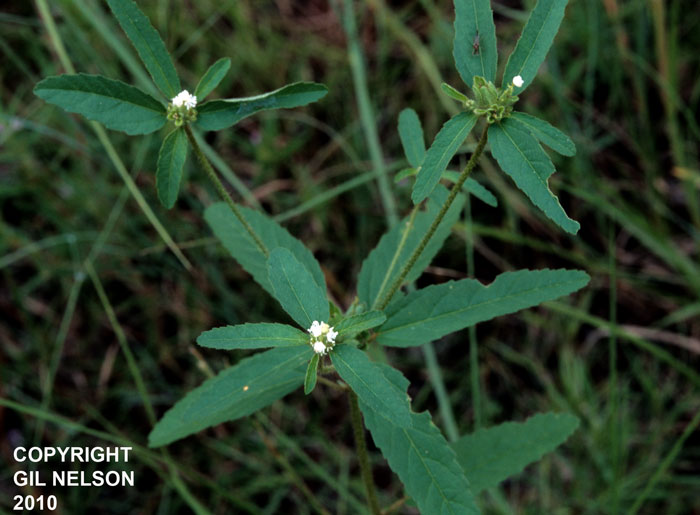

| |
| photo by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Croton |
| Species: | C. glandulosus |
| Binomial name | |
| Croton glandulosus L. | |
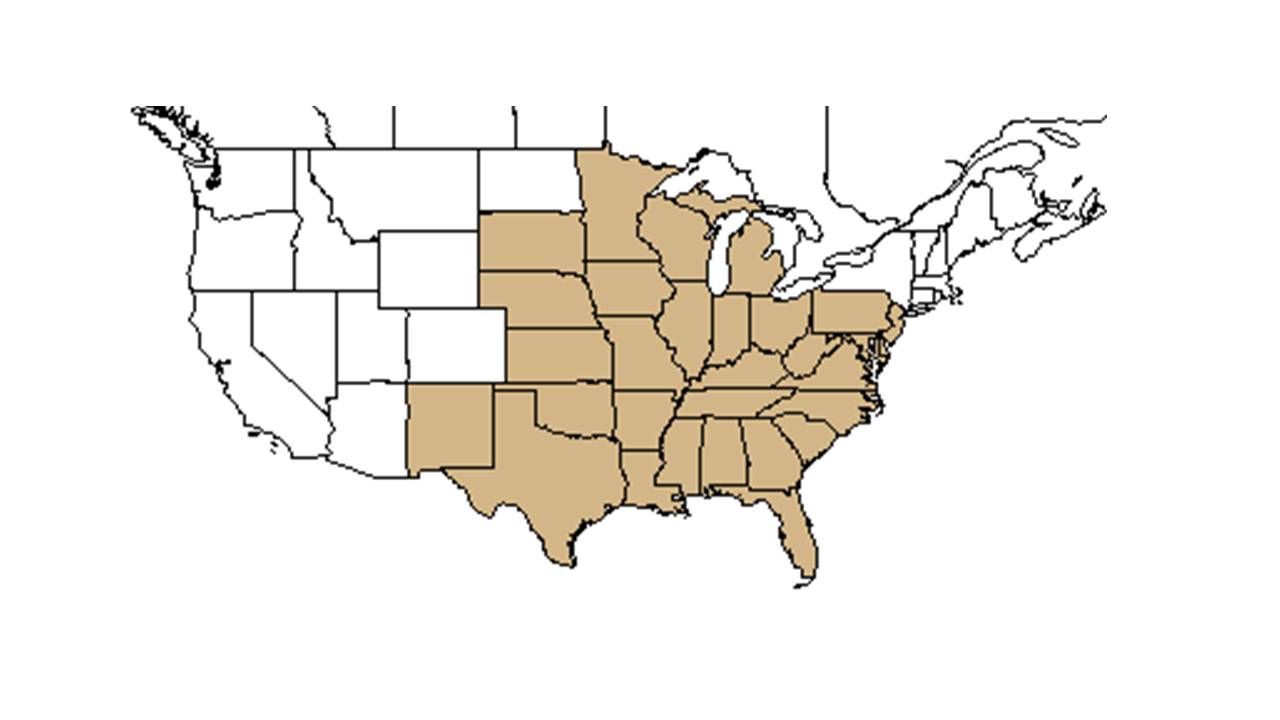
| |
| Natural range of Croton glandulosus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common Name: vente conmigo
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It can be found in mid-grass prairie communities.[1] It can also be found in longleaf pine communities, though it is not as common since they're dominated by perennial species.[2] This species has been observed in sandy and sandy loam soils of turkey oak ridges, open fields and clearings, wet borders of swamps, cabbage palm hammocks, dunes, and the ecotone between trees and shoreline of beaches (FSU Herbarium). This species also occurs in human disturbed areas such as grassy highway medians, grassy edges of parking lots, along railroad tracks, waste areas, sandy roadsides, corn fields, and citrus groves (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It is seasonal; it is mainly found from May to December, peaking in September in a study at Padre Island.[1] It has been observed flowering and fruiting June through October and fruiting in December (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
It germinates after fire.[1]
Fire ecology
Are included in the flowering plant survery – post burn – in Heuberger’s study[3]
Pollination
Mark Deyrup at Archbold Biological Station observed these Hymenoptera species on Croton glandulosus
Sphecidae: Cerceris blakei
Sphecidae: Philanthus ventilabris
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Lonard, R. I., F. W. Judd, et al. (2004). "Recovery of vegetation following a wildfire in a barrier island grassland, Padre Island National Seashore, Texas." Southwestern Naturalist 49: 173-188.
- ↑ Simkin, S. M., W. K. Michener, et al. (2001). "Plant response following soil disturbance in a longleaf pine ecosystem." Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 128: 208-218.
- ↑ Heuberger, K. A. and F. E. Putz (2003). "Fire in the suburbs: ecological impacts of prescribed fire in small remnants of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) sandhill." Restoration Ecology 11: 72-81.