Difference between revisions of "Chrysopsis mariana"
(→References and notes) |
(→Description) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | Common Name: Maryland goldenaster | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 2 July 2015
| Chrysopsis mariana | |
|---|---|
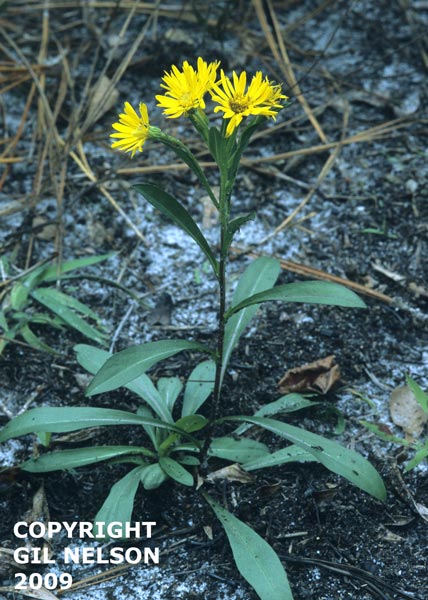

| |
| photo by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Chrysopsis |
| Species: | C. mariana |
| Binomial name | |
| Chrysopsis mariana (L.) Elliott | |
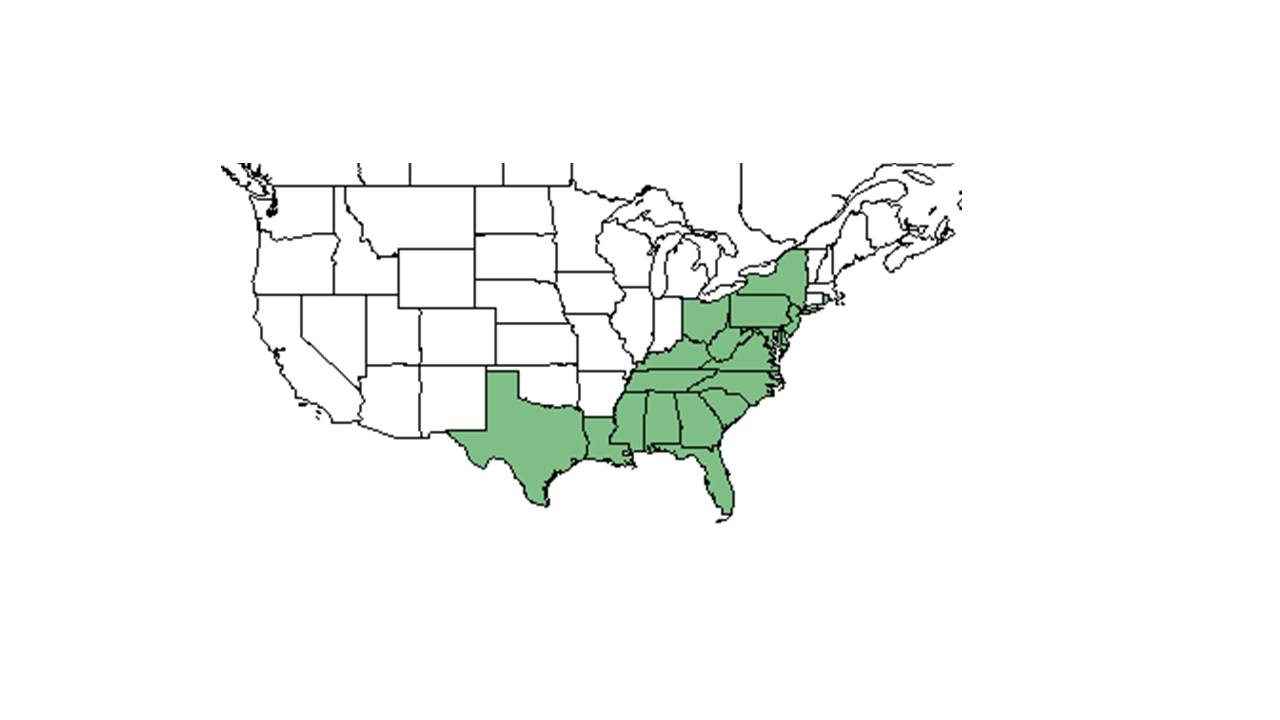
| |
| Natural range of Chrysopsis mariana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common Name: Maryland goldenaster
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It can live in humid and mild climates with plenty of rainfall throughout the year. It can tolerate temperatures ranging from 3 to 33 degrees Celsius. It is found in abundance in longleaf pine communities.[1]. Chrysopsis mariana is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia (Ostertag and Robertson 2007).
Phenology
It flowers in the fall.[2]
Seed dispersal
It is dispersed by the wind.[2]
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It is tolerant of fire.[1]
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kush, J. S., R. S. Meldahl, et al. (1999). "Understory plant community response after 23 years of hardwood control treatments in natural longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) forests." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1047-1054.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92(3): 409-421.