Difference between revisions of "Lilium catesbaei"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | ''L. catesbaei'' | + | ''L. catesbaei'' is endemic to the longleaf pine forest range<ref>Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.</ref> from southeastern North Carolina, south to Florida, and west to Louisiana.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''L. catesbaei'' proliferate in pine savannas and sandhill seeps.<ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> Specimens have been collected from moist sandy soil with wiregrass, sandy peat of savanna, pine flatwoods, cypress pond slash pine, open longleaf pine stand, pine savanna, and roadsides.<ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Daniel B. Ward, S.S. Ward, Lovette E. Williams, Robert Bral, Olga Lakeela, R.K. Godfrey, Robert Lazor, John Lazor, Bruce Hansen, S.W. Leonard, D.L. Fichtner, Paul Redfearn, D.S. Correll, Paul O. Schallert, Cecil Slaughter, Jennifer Hancock, Wilson Baker, Grady W. Reinert, R.A. Norris, R. Komarek, R.L. Wilbur, Rodie White, S.B. Jones, Carleen Jones, John W. Carter, S.L. Orzell, P. Sheridan. States and counties:Florida (Alachua, Bay, Charlotte, Citrus, Escambia, Gulf, Highlands, Hillsborough, Jackson, Liberty, Orange, Palm Beach, St. Johns, Union, Wakulla, Walton, Okaloosa, Nassau, Flagler, Osceola) Georgia (Coffee, Worth, Charlton, Grady, Thomas) North Carolina (Columbus, Pender, Bladen) Alabama (Mobile) Mississippi (Forrest) South Carolina (Corchester)</ref> ''L. catesbaei'' | + | ''L. catesbaei'' proliferate in pine savannas and sandhill seeps.<ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> Specimens have been collected from moist sandy soil with wiregrass, sandy peat of savanna, pine flatwoods, cypress pond slash pine, open longleaf pine stand, pine savanna, and roadsides.<ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Daniel B. Ward, S.S. Ward, Lovette E. Williams, Robert Bral, Olga Lakeela, R.K. Godfrey, Robert Lazor, John Lazor, Bruce Hansen, S.W. Leonard, D.L. Fichtner, Paul Redfearn, D.S. Correll, Paul O. Schallert, Cecil Slaughter, Jennifer Hancock, Wilson Baker, Grady W. Reinert, R.A. Norris, R. Komarek, R.L. Wilbur, Rodie White, S.B. Jones, Carleen Jones, John W. Carter, S.L. Orzell, P. Sheridan. States and counties:Florida (Alachua, Bay, Charlotte, Citrus, Escambia, Gulf, Highlands, Hillsborough, Jackson, Liberty, Orange, Palm Beach, St. Johns, Union, Wakulla, Walton, Okaloosa, Nassau, Flagler, Osceola) Georgia (Coffee, Worth, Charlton, Grady, Thomas) North Carolina (Columbus, Pender, Bladen) Alabama (Mobile) Mississippi (Forrest) South Carolina (Corchester)</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | ''L. catesbaei'' was found to increase its occurrence of flowering plants in response to soil disturbance by restoration roller chopping with and without fire in Southwest Florida. It has shown regrowth in reestablished native habitat that was disturbed by these practices.<ref>Huffman, J.M. and P.A. Werner. (2000). Restoration of Florida Pine Savanna: Flowering Response of ''Lilium catesbaei'' to Fire and Roller-Chopping. Natural Areas Journal 20(1):12-23.</ref> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 45: | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
Pollinators of this species include a variety of butterflies; the most effective being swallowtails. Observed possible pollinators include spicebush swallowtail, cloudless sulfur (Phoebis sennae), Palamedes, eastern black swallowtail, and green lynxes.<ref name ="FFE">Observation by Peter May, Edwin Bridges, Linda Cooper, John Hummer; On Peter May post in Heart Island Conservation area, Milton, ON, Canada, September 19, 2016, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group. </ref> The Florida Dust Skipper is an uncommon species that has been spotted on ''Lilium catesbaei'' as well.<ref name ="FFE-2">Observation by Steve Coleman post, comment by Linda Cooper; Liberty County, Fl, Jult 14, 2017, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group July 2017. </ref> | Pollinators of this species include a variety of butterflies; the most effective being swallowtails. Observed possible pollinators include spicebush swallowtail, cloudless sulfur (Phoebis sennae), Palamedes, eastern black swallowtail, and green lynxes.<ref name ="FFE">Observation by Peter May, Edwin Bridges, Linda Cooper, John Hummer; On Peter May post in Heart Island Conservation area, Milton, ON, Canada, September 19, 2016, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group. </ref> The Florida Dust Skipper is an uncommon species that has been spotted on ''Lilium catesbaei'' as well.<ref name ="FFE-2">Observation by Steve Coleman post, comment by Linda Cooper; Liberty County, Fl, Jult 14, 2017, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group July 2017. </ref> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> |
| − | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
Latest revision as of 18:33, 14 July 2022
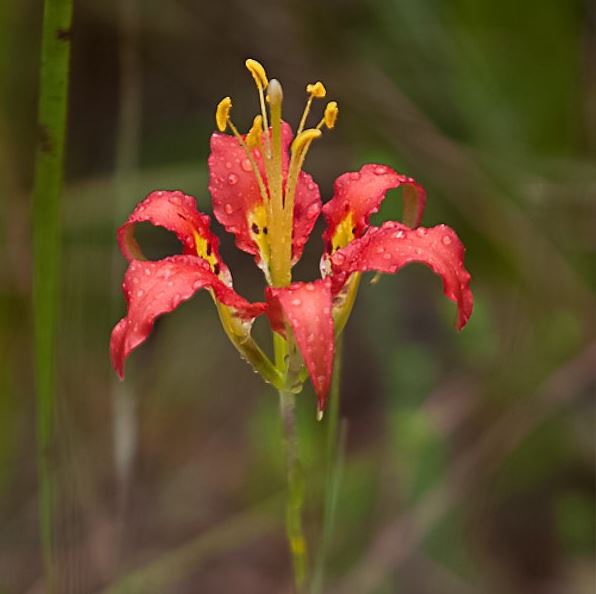
Common name: pine lily[1], Catesby's lily[2], leopard lily[2]
| Lilium catesbaei | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John B | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Liliaceae |
| Genus: | Lilium |
| Species: | L. catesbaei |
| Binomial name | |
| Lilium catesbaei Walter | |
| |
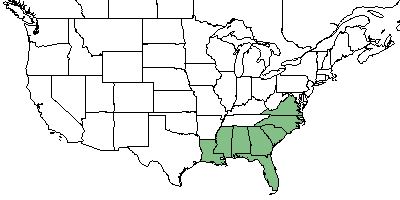
| Natural range of Lilium catesbaei from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: none.[3]
Varieties: none.[3]
Description
L. catesbaei is a perennial forb/herb of the Liliaceae family native to North America.[1]
Distribution
L. catesbaei is endemic to the longleaf pine forest range[4] from southeastern North Carolina, south to Florida, and west to Louisiana.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
L. catesbaei proliferate in pine savannas and sandhill seeps.[2] Specimens have been collected from moist sandy soil with wiregrass, sandy peat of savanna, pine flatwoods, cypress pond slash pine, open longleaf pine stand, pine savanna, and roadsides.[5]
L. catesbaei was found to increase its occurrence of flowering plants in response to soil disturbance by restoration roller chopping with and without fire in Southwest Florida. It has shown regrowth in reestablished native habitat that was disturbed by these practices.[6]
Phenology
L. catesbaei has been observed flowering June through October.[7]
Fire ecology
L. catesbaei flowers more conspicuously following a fire.[8]
Pollination
Pollinators of this species include a variety of butterflies; the most effective being swallowtails. Observed possible pollinators include spicebush swallowtail, cloudless sulfur (Phoebis sennae), Palamedes, eastern black swallowtail, and green lynxes.[9] The Florida Dust Skipper is an uncommon species that has been spotted on Lilium catesbaei as well.[10]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
L. catesbaei is listed as threatened by the Florida Department of Agriculture & Consumer Services Division of Plant Industry.[1]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=LICA4
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Daniel B. Ward, S.S. Ward, Lovette E. Williams, Robert Bral, Olga Lakeela, R.K. Godfrey, Robert Lazor, John Lazor, Bruce Hansen, S.W. Leonard, D.L. Fichtner, Paul Redfearn, D.S. Correll, Paul O. Schallert, Cecil Slaughter, Jennifer Hancock, Wilson Baker, Grady W. Reinert, R.A. Norris, R. Komarek, R.L. Wilbur, Rodie White, S.B. Jones, Carleen Jones, John W. Carter, S.L. Orzell, P. Sheridan. States and counties:Florida (Alachua, Bay, Charlotte, Citrus, Escambia, Gulf, Highlands, Hillsborough, Jackson, Liberty, Orange, Palm Beach, St. Johns, Union, Wakulla, Walton, Okaloosa, Nassau, Flagler, Osceola) Georgia (Coffee, Worth, Charlton, Grady, Thomas) North Carolina (Columbus, Pender, Bladen) Alabama (Mobile) Mississippi (Forrest) South Carolina (Corchester)
- ↑ Huffman, J.M. and P.A. Werner. (2000). Restoration of Florida Pine Savanna: Flowering Response of Lilium catesbaei to Fire and Roller-Chopping. Natural Areas Journal 20(1):12-23.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 24 MAY 2018
- ↑ Abrahamson, W. G. (1984). "Species Responses to Fire on the Florida Lake Wales Ridge." American Journal of Botany 71(1): 35-43.
- ↑ Observation by Peter May, Edwin Bridges, Linda Cooper, John Hummer; On Peter May post in Heart Island Conservation area, Milton, ON, Canada, September 19, 2016, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group.
- ↑ Observation by Steve Coleman post, comment by Linda Cooper; Liberty County, Fl, Jult 14, 2017, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group July 2017.