Difference between revisions of "Symphyotrichum patens"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
Common names: Late purple aster, Spreading aster | Common names: Late purple aster, Spreading aster | ||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''Aster patens'' Aiton var. ''patens''; ''Virgulus patens'' (Aiton) Reveal & Keener var. ''patens''; ''A. patens'' var. ''gracilis'' Hooker | + | Synonyms: ''Aster patens'' Aiton var. ''patens''; ''Virgulus patens'' (Aiton) Reveal & Keener var. ''patens''; ''A. patens'' var. ''gracilis'' Hooker.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| Line 32: | Line 29: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | This species can live in humid, subtropical climates in drying sandy loam on the edges of woodland remnants, shade of mesic woodlands, xeric limestone prairies, open old-field pine woods, and sandy clay of the Red Hills.<ref name="Burton 2009">Burton, J. A. (2009). Fire frequency effects on vegetation of an upland old growth forest in eastern Oklahoma. Environmental Science. Stillwater, Oklahoma, Oklahoma State University. Bachelor: 78.</ref><ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL:[http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Angus Gholson Jr., R. Kral, Robert K. Godfrey, Angela M. Reid, K. M. Robertson, Ann F. Johnson, and Wilson Baker. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden and Leon.</ref><ref name="McCain and Ebinger 2014">McClain, W. E. and J. E. Ebinger (2014). "Vascular Flora of Buettner Xeric Limestone Prairies, Monroe County, Illinois." Southern Appalachian Botanical Society | + | This species can live in humid, subtropical climates in drying sandy loam on the edges of woodland remnants, shade of mesic woodlands, xeric limestone prairies, open old-field pine woods, and sandy clay of the Red Hills.<ref name="Burton 2009">Burton, J. A. (2009). Fire frequency effects on vegetation of an upland old growth forest in eastern Oklahoma. Environmental Science. Stillwater, Oklahoma, Oklahoma State University. Bachelor: 78.</ref><ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL:[http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Angus Gholson Jr., R. Kral, Robert K. Godfrey, Angela M. Reid, K. M. Robertson, Ann F. Johnson, and Wilson Baker. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden and Leon.</ref><ref name="McCain and Ebinger 2014">McClain, W. E. and J. E. Ebinger (2014). "Vascular Flora of Buettner Xeric Limestone Prairies, Monroe County, Illinois." Southern Appalachian Botanical Society </ref> It can live in communities dominated by post oak as well.<ref name="Burton 2009"/> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | |||
''S. patens'' has been observed flowering in January, March through May, October, and November and fruiting between October and November.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016</ref> | ''S. patens'' has been observed flowering in January, March through May, October, and November and fruiting between October and November.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016</ref> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| − | |||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Burton (2009) found that the percent cover of S. patens showed a positive linear response to increased fire frequency.<ref name="Burton 2009"/> | Burton (2009) found that the percent cover of S. patens showed a positive linear response to increased fire frequency.<ref name="Burton 2009"/> | ||
| − | <!--===Pollination===--> | + | <!--===Pollination===--> |
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> |
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
| + | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 13:24, 15 July 2022
| Symphyotrichum patens | |
|---|---|
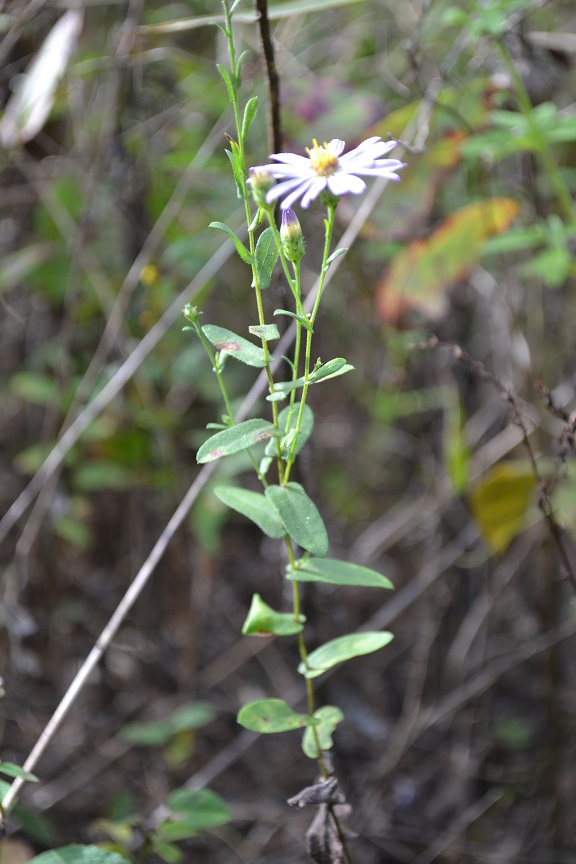

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. patens |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum patens (Aiton) G.L. Nesom | |
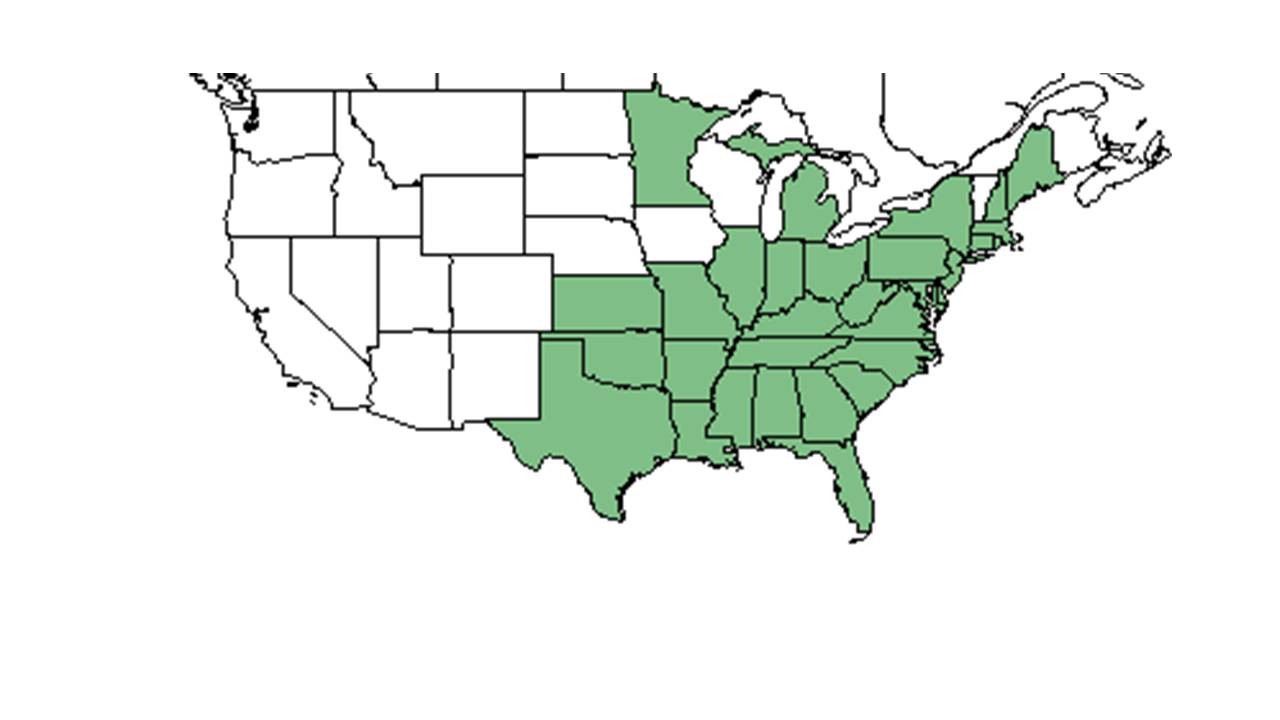
| |
| Natural range of Symphyotrichum patens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Late purple aster, Spreading aster
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Aster patens Aiton var. patens; Virgulus patens (Aiton) Reveal & Keener var. patens; A. patens var. gracilis Hooker.[1]
Description
A description of Symphyotrichum patens is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
This species can live in humid, subtropical climates in drying sandy loam on the edges of woodland remnants, shade of mesic woodlands, xeric limestone prairies, open old-field pine woods, and sandy clay of the Red Hills.[2][3][4] It can live in communities dominated by post oak as well.[2]
Phenology
S. patens has been observed flowering in January, March through May, October, and November and fruiting between October and November.[3][5]
Fire ecology
Burton (2009) found that the percent cover of S. patens showed a positive linear response to increased fire frequency.[2]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Burton, J. A. (2009). Fire frequency effects on vegetation of an upland old growth forest in eastern Oklahoma. Environmental Science. Stillwater, Oklahoma, Oklahoma State University. Bachelor: 78.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL:http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Angus Gholson Jr., R. Kral, Robert K. Godfrey, Angela M. Reid, K. M. Robertson, Ann F. Johnson, and Wilson Baker. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden and Leon.
- ↑ McClain, W. E. and J. E. Ebinger (2014). "Vascular Flora of Buettner Xeric Limestone Prairies, Monroe County, Illinois." Southern Appalachian Botanical Society
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016