Difference between revisions of "Aletris obovata"
(→Photo Gallery) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (109 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| binomial_authority = Nash | | binomial_authority = Nash | ||
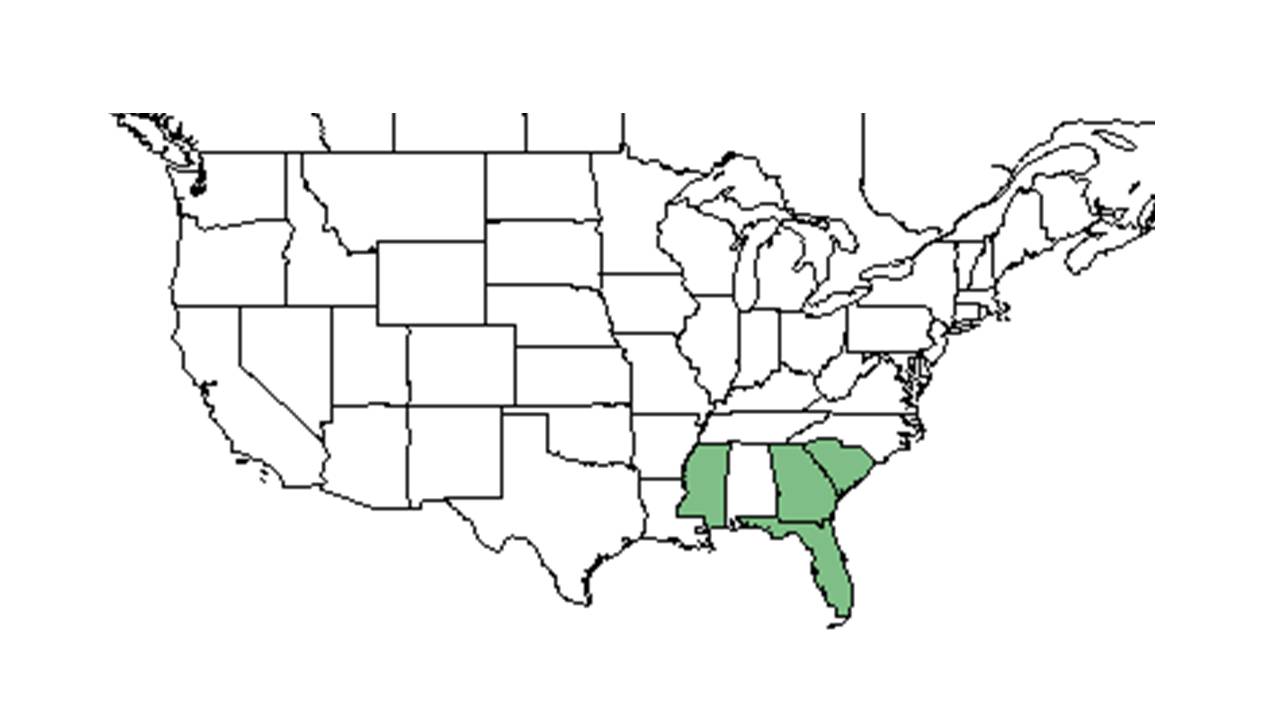
| range_map = ALET_OBOV_dist.jpg | | range_map = ALET_OBOV_dist.jpg | ||
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Aletris obovata'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov Plants Database]. | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Aletris obovata'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ALOB3 Plants Database]. |
}} | }} | ||
| + | Common names: White colicroot; Southern colicroot | ||
| + | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: none<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | A description of ''Aletris obovata'' is provided in [http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=242101326 The Flora of North America]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is similar to ''A. lutea'', however can be differentiated by having rounded flowers instead of tubular flowers and blooming later, between April and June.<ref name="hawthorn">[[http://hawthornhillwildflowers.blogspot.com/2010/09/white-colic-root-aletris-obovata.html]]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | Orignally native to Europe, ''Aletris obovata'' escaped from cultivation<ref name="hall">Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 242. Print.</ref> and is endemic to an area from southern South Carolina to peninsular Florida, but is primarily present in Florida.<ref>Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting | + | Habitats are moist areas and include longleaf pine/wiregrass flatwoods, moist slash pine/palmetto scrubs, sandy peat of grass-sedge bogs, open seepage slopes, and wet flats. Additionally, it can be found in disturbed areas such as along roadsides, ditches, and longleaf pine clearings. It usually grows in dry loamy or moist sands in high light.<ref name="fsu"/> |
| − | ===Seed dispersal=== | + | |
| − | ===Seed bank and germination=== | + | Associated species include ''[[Aletris lutea]]'' and hybrids; ''Lobelia, Andropogon'', longleaf pine, slash pine, saw palmetto, ''[[Lachnocaulon anceps]], Helianthus heterophylla, [[Polygala nana]], Lobelia paludosa, [[Centella asiatica]], Hypericum'', and others.<ref name="fsu">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, Loran C. Anderson, J. B. Nelson, R. L. Scott, William Lindsey, R. Kral, H. Larry Stripling, George R. Cooley, Carroll E. Wood, Jr., Kenneth A. Wilson, M. Kral, Sidney McDaniel, Gwynn W. Ramsey, Richard Mitchell, P. L. Redfearn, Steve L. Orzell, Edwin L. Bridges, R. Komarek, and R. A. Norris. States and Counties: Florida: Union, Liberty, Wakulla, Hamilton, Citrus, Levy, Nassau, Franklin, Leon, Alachua, Taylor, and Madison. Georgia: Thomas.</ref> |
| − | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | + | |
| − | ===Pollination=== | + | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> |
| − | === | + | ''Aletris obovata'' has been observed to flower from spring to fall reaching peak inflorescence in April and May.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016</ref><ref name="hall"/> It has been observed fruiting from April through July.<ref name="fsu"/> |
| − | ===Diseases and parasites=== | + | |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | In areas of overlapping distribution, ''A. obovata'' will hybridize with ''A. lutea''. Hybridization occurs in disturbed habitats where colonization and dispersal of hybrids was probably implemented by roadside maintenance.<ref name="sullivan">Sullivan, V. I. (1973). "Biosystematics of Aletris Lutea Small, Aletris obovata Nash, and Natural Hybrids (Liliaceae)." Brittonia 25(3): 294-303.</ref> |
| − | == | + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> |
| + | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Fire ecology===<!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | It grows well in recently burned areas.<ref name="fsu"/> | ||
| + | ===Pollination and Insect Hosting=== | ||
| + | ''Aletris obovata'' has been observed to host bees such as ''Bombus pensylvanicus'' (family Apidae), skippers from the family Hesperiidae such as ''Wollengrenia otho'', ''Nastra lherminier'' and ''Erynnis juvenalis'', swallowtail butterflies such as ''Papilio marcellus'' (family Papilionidae), and bee-flies such as ''Bombylius mexicanus'' (family Bombyliidae).<ref name="sullivan"/> | ||
| + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> | ||
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
| + | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:Aletris obovata_Gil.jpg| <center> ''Aletris obovata'' <p> Photo by Gil Nelson </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </nowiki></gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 12:06, 28 September 2023
| Aletris obovata | |
|---|---|
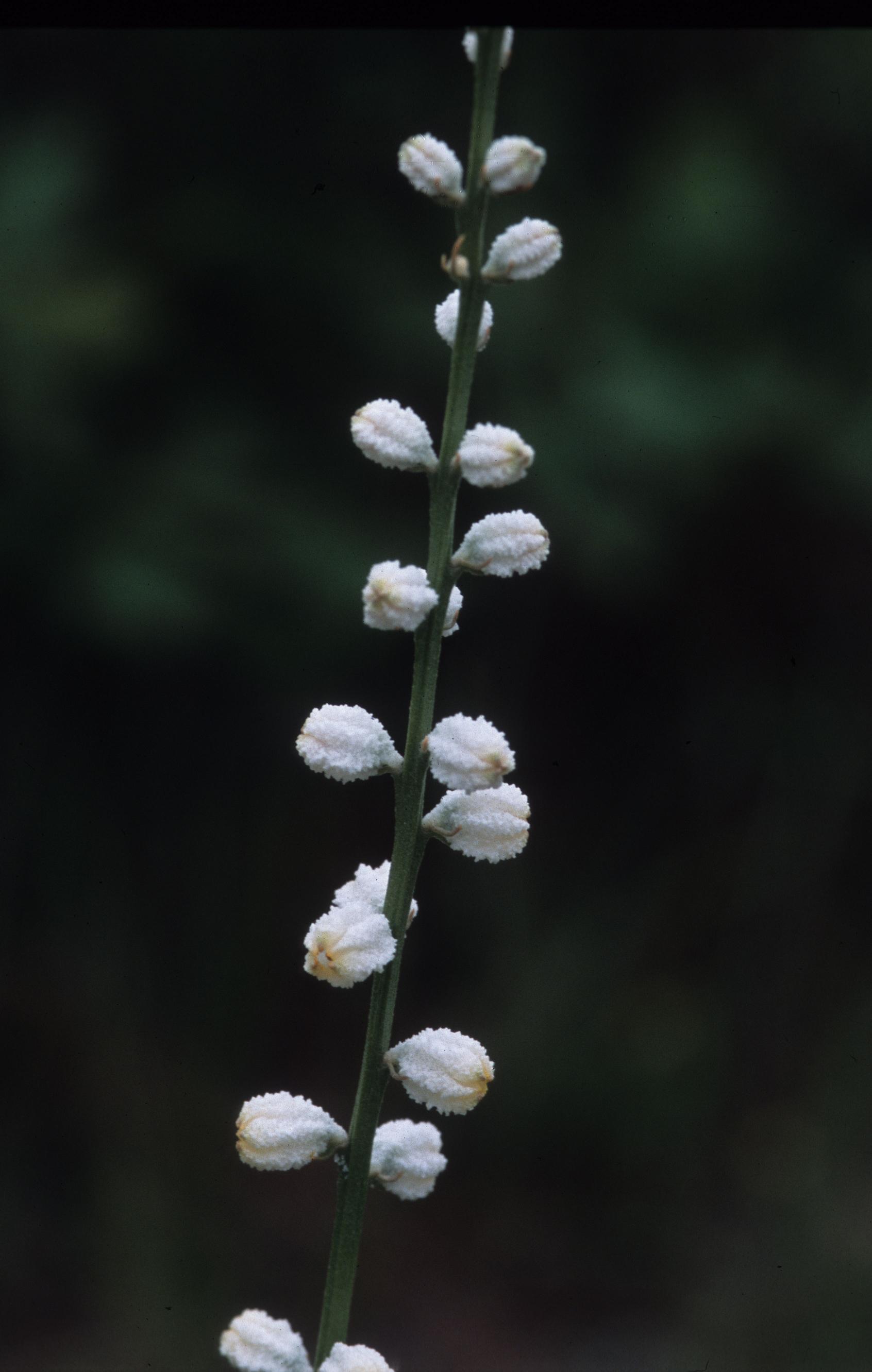

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Liliaceae |
| Genus: | Aletris |
| Species: | A. obovata |
| Binomial name | |
| Aletris obovata Nash | |
| |
| Natural range of Aletris obovata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: White colicroot; Southern colicroot
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
A description of Aletris obovata is provided in The Flora of North America.
It is similar to A. lutea, however can be differentiated by having rounded flowers instead of tubular flowers and blooming later, between April and June.[2]
Distribution
Orignally native to Europe, Aletris obovata escaped from cultivation[3] and is endemic to an area from southern South Carolina to peninsular Florida, but is primarily present in Florida.[4]
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats are moist areas and include longleaf pine/wiregrass flatwoods, moist slash pine/palmetto scrubs, sandy peat of grass-sedge bogs, open seepage slopes, and wet flats. Additionally, it can be found in disturbed areas such as along roadsides, ditches, and longleaf pine clearings. It usually grows in dry loamy or moist sands in high light.[5]
Associated species include Aletris lutea and hybrids; Lobelia, Andropogon, longleaf pine, slash pine, saw palmetto, Lachnocaulon anceps, Helianthus heterophylla, Polygala nana, Lobelia paludosa, Centella asiatica, Hypericum, and others.[5]
Phenology
Aletris obovata has been observed to flower from spring to fall reaching peak inflorescence in April and May.[6][3] It has been observed fruiting from April through July.[5]
In areas of overlapping distribution, A. obovata will hybridize with A. lutea. Hybridization occurs in disturbed habitats where colonization and dispersal of hybrids was probably implemented by roadside maintenance.[7]
Fire ecology
It grows well in recently burned areas.[5]
Pollination and Insect Hosting
Aletris obovata has been observed to host bees such as Bombus pensylvanicus (family Apidae), skippers from the family Hesperiidae such as Wollengrenia otho, Nastra lherminier and Erynnis juvenalis, swallowtail butterflies such as Papilio marcellus (family Papilionidae), and bee-flies such as Bombylius mexicanus (family Bombyliidae).[7]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ [[1]]
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 242. Print.
- ↑ Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, Loran C. Anderson, J. B. Nelson, R. L. Scott, William Lindsey, R. Kral, H. Larry Stripling, George R. Cooley, Carroll E. Wood, Jr., Kenneth A. Wilson, M. Kral, Sidney McDaniel, Gwynn W. Ramsey, Richard Mitchell, P. L. Redfearn, Steve L. Orzell, Edwin L. Bridges, R. Komarek, and R. A. Norris. States and Counties: Florida: Union, Liberty, Wakulla, Hamilton, Citrus, Levy, Nassau, Franklin, Leon, Alachua, Taylor, and Madison. Georgia: Thomas.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Sullivan, V. I. (1973). "Biosystematics of Aletris Lutea Small, Aletris obovata Nash, and Natural Hybrids (Liliaceae)." Brittonia 25(3): 294-303.
