Difference between revisions of "Asimina triloba"
| (49 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| name = Asimina triloba | | name = Asimina triloba | ||
| − | | image = Asimina_triloba_Gil. | + | | image = Asimina_triloba_Gil.jpg |
| − | | image_caption = | + | | image_caption = Photo taken by Gil Nelson |
| regnum = Plantae | | regnum = Plantae | ||
| divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | | divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
| ordo = Magnoliales | | ordo = Magnoliales | ||
| familia = Annonaceae | | familia = Annonaceae | ||
| − | | genus = ''Asimina | + | | genus = ''Asimina'' |
| − | | species = ''''' | + | | species = '''''A. triloba ''' |
| binomial = ''Asimina triloba'' | | binomial = ''Asimina triloba'' | ||
| binomial_authority = (L.) Dunal | | binomial_authority = (L.) Dunal | ||
| range_map = ASIM_TRIL_dist.jpg | | range_map = ASIM_TRIL_dist.jpg | ||
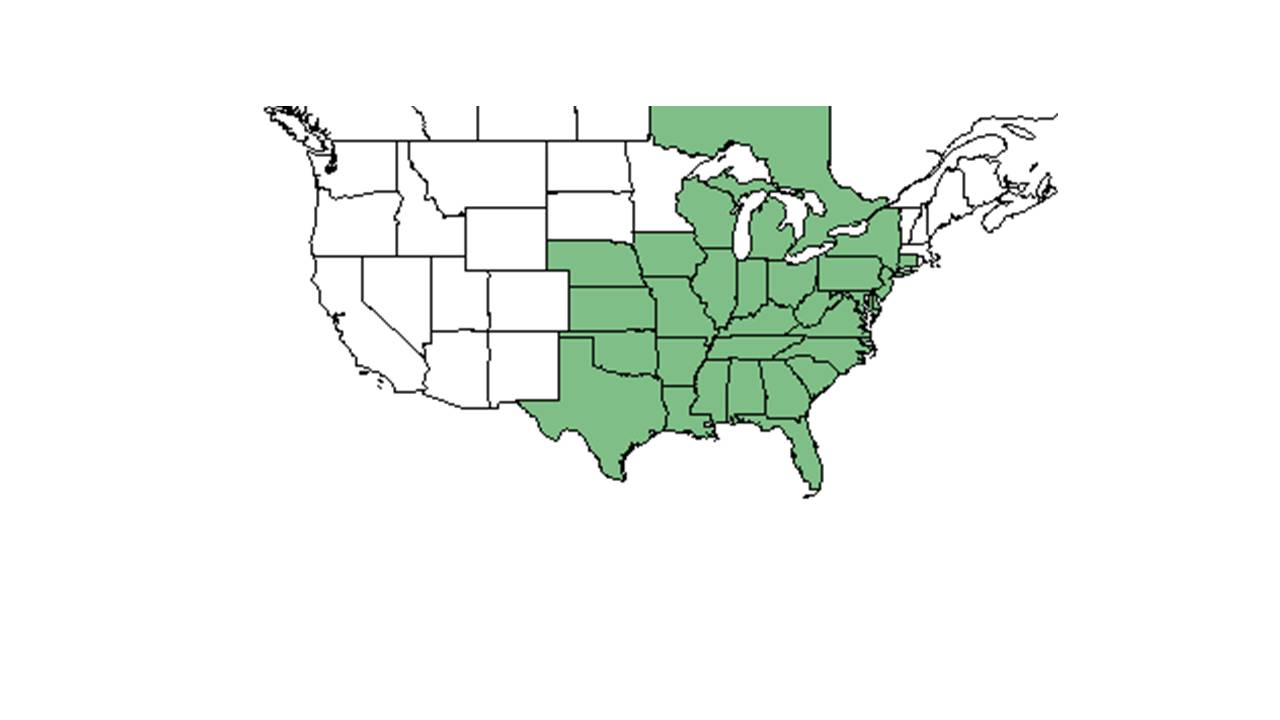
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Asimina triloba'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov Plants Database]. | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Asimina triloba'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ASTR Plants Database]. |
}} | }} | ||
| + | Common name: Pawpaw, common pawpaw, Indian-banana | ||
| + | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: none<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | A description of ''Asimina triloba'' is provided in [http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=220001231 The Flora of North America]. | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| − | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | + | ===Habitat===<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> |
| − | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting | + | This species is found in calcareous woodlands on bluffs, middle and lower slopes of mesic wooded bluffs, rich ravines with limestone outcrops, and mesic magnolia-oak-pine woods.<ref name="fsu">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey, A. Gholson Jr., Travis MacClendon, and Karen MacClendon. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Gadsden, and Jackson.</ref> It is frost tolerant and adapted to humid climates.<ref name="eol">[[http://eol.org/pages/1054816/details]]Encyclopedia of Life. Accessed: March 31, 2016</ref> |
| − | ===Seed dispersal=== | + | |
| − | ===Seed bank and germination=== | + | Associated species includes ''Fagus grandifolia, Hydrongea quercifolia, Dirca palustris, Liriodendron tulipifera, [[Magnolia grandiflora]]'' and others.<ref name="fsu"/> |
| − | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | + | |
| − | ===Pollination=== | + | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> |
| − | === | + | Flowers of ''A. triloba'' are monoecious, purple, bell-shaped and flower April to May. In north Florida, they have been observed flowering in February and March.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016</ref> The fruits are edible and are similar to a small banana or papaya.<ref name="wildflower">[[http://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=ASTR]]Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: March 31, 2016</ref> This species is also about to reproduce vegetatively by root suckering.<ref name="fs"/> |
| − | ===Diseases and parasites=== | + | |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> |
| − | == | + | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> |
| + | <!--===Fire ecology===--><!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Herbivory and toxicology=== | ||
| + | The smell of the flowers resembles rotting carrion and therefore attracts flesh flies (''Sarcophagidae sp.''), and blowflies (''Calliphoridae sp.'').<ref name="illinois">[[http://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/trees/plants/pawpaw.htm]]Illinois Wildflowers. Accessed: March 31, 2016</ref> The fruit is consumed by raccoons, gray foxes, opossums, squirrels, and black bears.<ref name="fs">[[http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/plants/tree/asitri/all.html]]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
| + | The fruit of ''A. triloba'' is known to be sweet and custard-like. It was often used in baking, pie filling, or eaten raw. The fruits fall from the tree early and must be harvested from the ground to ripen later.<ref> Fernald, et al. 1958. Edible Plants of Eastern North America. Harper and Row Publishers, New York.</ref> For medicinal purposes, the seeds can be used to induce vomiting or to treat head lice when powdered, and the fruit juice can be a treatment for intestinal worms.<ref> Korchmal, Arnold & Connie. 1973. A Guide to the Medicinal Plants of the United States. The New York Times Book Company, New York.</ref> Caution should be exercised though, as some people exhibit an allergic reaction of dermatitis to the fruit.<ref> Burrows, G.E., Tyrl, R.J. 2001. Toxic Plants of North America. Iowa State Press.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 14:31, 22 May 2023
| Asimina triloba | |
|---|---|
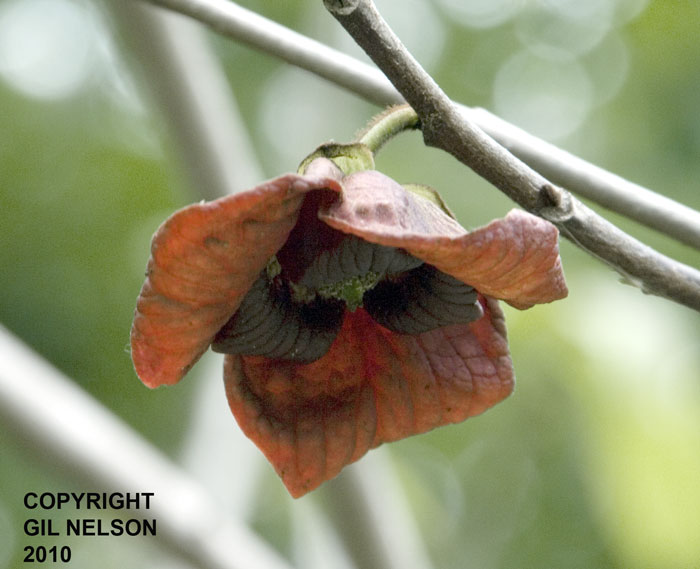

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Magnoliales |
| Family: | Annonaceae |
| Genus: | Asimina |
| Species: | A. triloba |
| Binomial name | |
| Asimina triloba (L.) Dunal | |
| |
| Natural range of Asimina triloba from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Pawpaw, common pawpaw, Indian-banana
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
A description of Asimina triloba is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found in calcareous woodlands on bluffs, middle and lower slopes of mesic wooded bluffs, rich ravines with limestone outcrops, and mesic magnolia-oak-pine woods.[2] It is frost tolerant and adapted to humid climates.[3]
Associated species includes Fagus grandifolia, Hydrongea quercifolia, Dirca palustris, Liriodendron tulipifera, Magnolia grandiflora and others.[2]
Phenology
Flowers of A. triloba are monoecious, purple, bell-shaped and flower April to May. In north Florida, they have been observed flowering in February and March.[4] The fruits are edible and are similar to a small banana or papaya.[5] This species is also about to reproduce vegetatively by root suckering.[6]
Herbivory and toxicology
The smell of the flowers resembles rotting carrion and therefore attracts flesh flies (Sarcophagidae sp.), and blowflies (Calliphoridae sp.).[7] The fruit is consumed by raccoons, gray foxes, opossums, squirrels, and black bears.[6]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
The fruit of A. triloba is known to be sweet and custard-like. It was often used in baking, pie filling, or eaten raw. The fruits fall from the tree early and must be harvested from the ground to ripen later.[8] For medicinal purposes, the seeds can be used to induce vomiting or to treat head lice when powdered, and the fruit juice can be a treatment for intestinal worms.[9] Caution should be exercised though, as some people exhibit an allergic reaction of dermatitis to the fruit.[10]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey, A. Gholson Jr., Travis MacClendon, and Karen MacClendon. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Gadsden, and Jackson.
- ↑ [[1]]Encyclopedia of Life. Accessed: March 31, 2016
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016
- ↑ [[2]]Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: March 31, 2016
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 [[3]]
- ↑ [[4]]Illinois Wildflowers. Accessed: March 31, 2016
- ↑ Fernald, et al. 1958. Edible Plants of Eastern North America. Harper and Row Publishers, New York.
- ↑ Korchmal, Arnold & Connie. 1973. A Guide to the Medicinal Plants of the United States. The New York Times Book Company, New York.
- ↑ Burrows, G.E., Tyrl, R.J. 2001. Toxic Plants of North America. Iowa State Press.