Difference between revisions of "Xyris curtissii"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''X. difformis'' var. ''curtissii''; ''X. bayardii''; ''X. neglecta''<ref | + | Synonyms: ''X. difformis'' Chapman var. ''curtissii''; ''X. bayardii'' Fernald; ''X. neglecta''.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''Xyris curtissii'' is a monoecious perennial forb/herb.<ref name="USDA"/> | + | ''Xyris curtissii'' is a monoecious perennial forb/herb.<ref name="USDA"/> However there are some suggestions that ''X. curtissii'' may be annual in northern portions of its range while individuals in the southern parts are biennial or perennial.<ref name="Kral 1960"/> It has linear leaves 5-10 cm long and 2-4 mm wide and its sheath occupies <sup>1</sup>/<sub>3</sub> to <sup>1</sup>/<sub>2</sub> the length of the straw-colored tawny leaves. Seeds are ellipsoid and around 0.4 mm long.<ref name="Malme 1937">Malme GOK (1937) Xyridacea. North American Flora 19(1):3-15.</ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | This species occurs from southeastern Virginia, south to northeastern Florida and | + | This species occurs from southeastern Virginia, south to northeastern Florida, western and southern Arkansas, and east-central Texas. Disjunct populations are found in southern New Jersey and Central America.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | '' | + | |
| + | ''X. curtissii'' occurs on moist savannas, pine woodlands, pine flatwoods, boggy seepage slopes, river banks, and wet depression prairies.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/><ref name="Kral 1960">Kral R (1960) The genus ''Xyris'' in Florida. Rhodora 62(743):295-319.</ref><ref name="Carr et al 2010">Carr SC, Robertson KM, Peet RK (2010) A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75(2):153-189.</ref><ref name="FSU"> Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R. A. Davidson, R.K. Godfrey, and R. F. Thorne. States and counties: Florida: Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Liberty, Nassau, and Santa Rosa.</ref> It is also found in disturbed areas including wet open ditches, powerline corridors, and dam margins.<ref name="FSU"/> Associated species: ''Rhynchospora spp., Juncus spp., Drosera spp.'', and ''Hypericum''.<ref name="FSU"/> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | Populations of ''Xyris curtissii'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burning. | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology=== <!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc.--> |
| − | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:33, 18 July 2022
| Xyris difformis | |
|---|---|
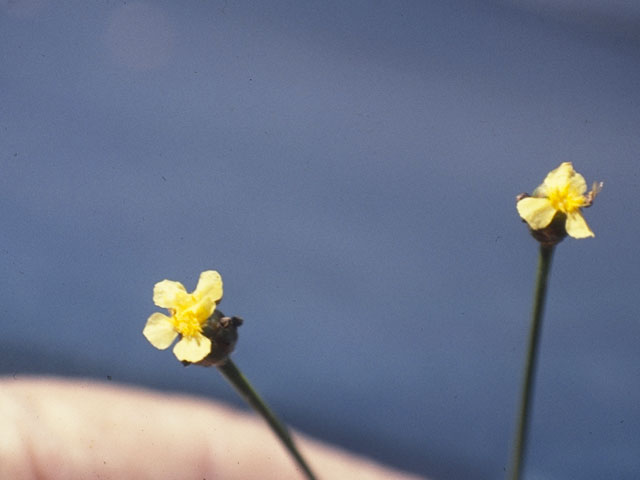

| |
| Photo by Robert L. Stone hosted at Wildflowers.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Commelinales |
| Family: | Xyridaceae |
| Genus: | Xyris |
| Species: | X. curtissii |
| Binomial name | |
| Xyris curtissii Kunth | |
| |
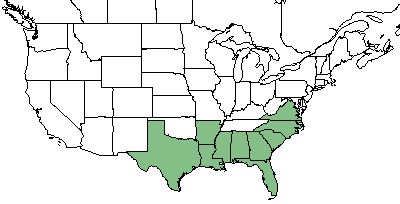
| Natural range of Xyris curtissii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name: Curtiss's yellow-eyed grass[1][2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: X. difformis Chapman var. curtissii; X. bayardii Fernald; X. neglecta.[3]
Description
Xyris curtissii is a monoecious perennial forb/herb.[2] However there are some suggestions that X. curtissii may be annual in northern portions of its range while individuals in the southern parts are biennial or perennial.[4] It has linear leaves 5-10 cm long and 2-4 mm wide and its sheath occupies 1/3 to 1/2 the length of the straw-colored tawny leaves. Seeds are ellipsoid and around 0.4 mm long.[5]
Distribution
This species occurs from southeastern Virginia, south to northeastern Florida, western and southern Arkansas, and east-central Texas. Disjunct populations are found in southern New Jersey and Central America.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
X. curtissii occurs on moist savannas, pine woodlands, pine flatwoods, boggy seepage slopes, river banks, and wet depression prairies.[1][4][6][7] It is also found in disturbed areas including wet open ditches, powerline corridors, and dam margins.[7] Associated species: Rhynchospora spp., Juncus spp., Drosera spp., and Hypericum.[7]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, flowering occurs from July through August.[1]
Fire ecology
Populations of Xyris curtissii have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 07 February 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kral R (1960) The genus Xyris in Florida. Rhodora 62(743):295-319.
- ↑ Malme GOK (1937) Xyridacea. North American Flora 19(1):3-15.
- ↑ Carr SC, Robertson KM, Peet RK (2010) A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75(2):153-189.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R. A. Davidson, R.K. Godfrey, and R. F. Thorne. States and counties: Florida: Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Liberty, Nassau, and Santa Rosa.