Difference between revisions of "Rivina humilis"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common names: | + | Common names: Bloodberry rougeplant, Rougeplant, Pigeonberry, Baby-pepper |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: none | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 29: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
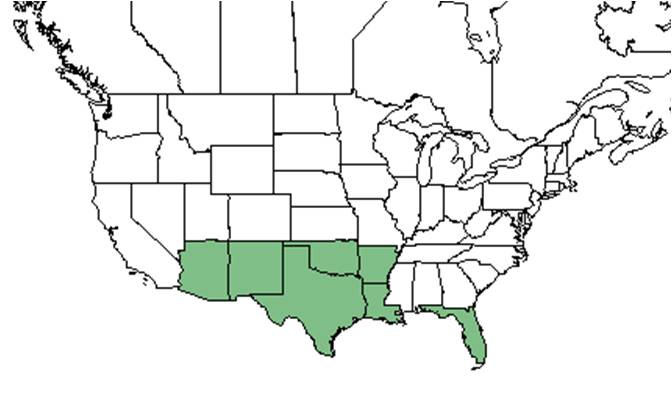
| − | It is found in southern North America from Florida to Arizona, north to Oklahoma and Arkansas, south through central America and the Caribbean to tropical South America<ref name="wildflower">[[http://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=RIHU2]]Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: March 10, 2016</ref> | + | It is found in southern North America from Florida to Arizona, north to Oklahoma and Arkansas, south through central America and the Caribbean to tropical South America.<ref name="wildflower">[[http://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=RIHU2]]Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: March 10, 2016</ref> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ''R. humilis'' has been found in sandy coastal hammocks, cabbage palm-mixed hardwoods, semi-deciduous forests, lake shores, mesic hammocks with limestone outcrops, shaded dunes, oak hammocks, and wetland shores.<ref name="FSU">Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2021. Collectors: R. Kral and Cecil Slaughter. States and counties: Florida: Orange and St. Lucie.</ref><ref name="UF"/> It has also been found in disturbed areas including along open roadsides, between soybean fields, cleared tropical evergreen forests, and burned restoration areas.<ref name="UF">University of Florida Herbarium Database. URL: https://www.floridamuseum.ufl.edu/herbarium. Last accessed: May 2021. Collectors: J. Richard Abbott, H. Adams, Paul Corogin, Caroline Easley, Jean Farabee, Doug Goldman, D. Grover, Jeffery Hubbard, Lucas C. Majure, Jill M. Scanlon, and M. Wingate. Countries and provinces: Bolivia: Chiquitos and Ñuflo de Chavez. Dominican Republic: La Altagracia. States and counties: Florida: Alachua, Brevard, Duval, Hernando, Marion.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species: ''Bursera simarouba, Pithecellobium unguis-cati, Trichostigma octandrum, Atriplex pentandra, Achyranthes aspera, Morinda royoc, M. citrifolia, Colubrina arborescens, Cenchrus sp., Oplonia microphyllus, Cassytha filiformis, Commicarpus sulcatus, Lantana involucrata, Juniperus virginiana, Sabal palmetto, Acer negundo, Fraxinus spp'', and ''Cassytha filiformis''.<ref name="UF"/> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | ===Seed dispersal=== | + | Blooms March through October.<ref name="wildflower"/> |
| − | ===Seed bank and germination=== | + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> |
| − | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | + | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> |
| − | ===Pollination=== | + | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> |
| − | + | <!--===Pollination===--> | |
| + | ''Rivina humilis'' was observed at the Archbold Biological Station with sweat bees from the Halictidae family such as ''Lasioglossum pectoralis''.<ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | ||
| + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> | ||
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| − | + | ==Cultural use== | |
| + | Used in the southwest as red dye.<ref name="plantdelight"/> This species is poisonous.<ref name="firefly">[[http://www.fireflyforest.com/flowers/2262/rivina-humilis-rougeplant/]] Accessed: March 10, 2016</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 58: | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 15:23, 15 July 2022
| Rivina humilis | |
|---|---|
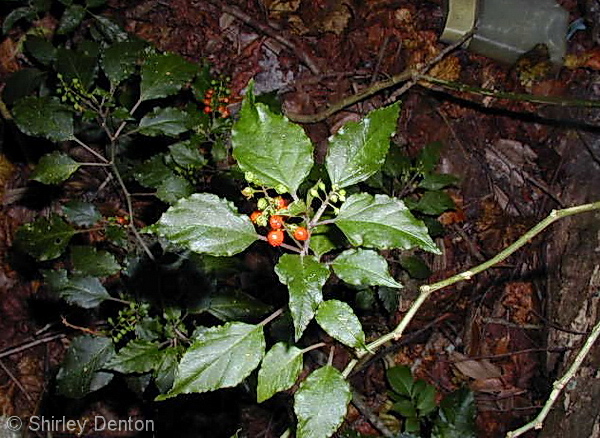

| |
| Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), Nature Photography by Shirley Denton | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Phytolaccaceae |
| Genus: | Rivina |
| Species: | R. humilis |
| Binomial name | |
| Rivina humilis L. | |
| |
| Natural range of Rivina humilis from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Bloodberry rougeplant, Rougeplant, Pigeonberry, Baby-pepper
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none
Varieties: none
Description
A description of Rivina humilis is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
It is found in southern North America from Florida to Arizona, north to Oklahoma and Arkansas, south through central America and the Caribbean to tropical South America.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
R. humilis has been found in sandy coastal hammocks, cabbage palm-mixed hardwoods, semi-deciduous forests, lake shores, mesic hammocks with limestone outcrops, shaded dunes, oak hammocks, and wetland shores.[2][3] It has also been found in disturbed areas including along open roadsides, between soybean fields, cleared tropical evergreen forests, and burned restoration areas.[3]
Associated species: Bursera simarouba, Pithecellobium unguis-cati, Trichostigma octandrum, Atriplex pentandra, Achyranthes aspera, Morinda royoc, M. citrifolia, Colubrina arborescens, Cenchrus sp., Oplonia microphyllus, Cassytha filiformis, Commicarpus sulcatus, Lantana involucrata, Juniperus virginiana, Sabal palmetto, Acer negundo, Fraxinus spp, and Cassytha filiformis.[3]
Phenology
Blooms March through October.[1] Rivina humilis was observed at the Archbold Biological Station with sweat bees from the Halictidae family such as Lasioglossum pectoralis.[4]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Used in the southwest as red dye.[5] This species is poisonous.[6]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 [[1]]Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: March 10, 2016
- ↑ Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2021. Collectors: R. Kral and Cecil Slaughter. States and counties: Florida: Orange and St. Lucie.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 University of Florida Herbarium Database. URL: https://www.floridamuseum.ufl.edu/herbarium. Last accessed: May 2021. Collectors: J. Richard Abbott, H. Adams, Paul Corogin, Caroline Easley, Jean Farabee, Doug Goldman, D. Grover, Jeffery Hubbard, Lucas C. Majure, Jill M. Scanlon, and M. Wingate. Countries and provinces: Bolivia: Chiquitos and Ñuflo de Chavez. Dominican Republic: La Altagracia. States and counties: Florida: Alachua, Brevard, Duval, Hernando, Marion.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedplantdelight - ↑ [[2]] Accessed: March 10, 2016