Difference between revisions of "Juncus biflorus"
(→Description) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
| + | Common names: Two-flowered rush, Bog rush, Large Grass-leaved Rush<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''Juncus marginatus'' Rostkovius, | + | Synonyms: ''Juncus marginatus'' Rostkovius, ''Juncus aristulatus'' Michaux var. ''biflorus'' (Elliott) Small.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| − | Varieties: none | + | Varieties: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | Also known as bog rush, ''J. biflorus'' is a native perennial graminoid that is a member of the Juncaceae family. It has a rapid rhizomatous growth form reaching a mature height of 3.5 feet. <ref name= "USDA"> USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=JUBI </ref> | + | Also known as bog rush, ''J. biflorus'' is a native perennial graminoid that is a member of the Juncaceae family. It has a rapid rhizomatous growth form reaching a mature height of 3.5 feet.<ref name= "USDA"> USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=JUBI </ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
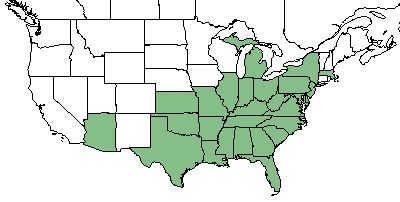
| + | ''J. biflorus'' can be found in the Southeastern United States from Mississippi and up to Michigan as well as along the Atlantic coast to New Jersey.<ref name= "USDA"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | < | + | The main communities ''J. biflorus'' can be found include pine savannahs, pine flatwoods, mesic portions of sandhill-pocosin ecotones, and even roadsides, wet meadows, interdune swales, tidal marshes, and ditches.<ref name= "Weakley"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> As well, ''J. biflorus'' has been observed on the margin of an old wet fireland, margin of wet woods, and in a flooded depression.<ref name= "Herbarium"> Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: John B. Nelson, Wade Biltoft, Keith Bradley, Daniel Castillo, and Richard D. Porcher. States and counties: South Carolina: Berkely and Orangeburg. </ref> |
| + | |||
| + | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | Blooming occurs June through October.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> |
| − | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| + | ''J. biflorus'' is listed as endangered in the state of New York, and is listed as threatened in the state of Pennsylvania.<ref name= "USDA"/> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:08, 14 July 2022
Common names: Two-flowered rush, Bog rush, Large Grass-leaved Rush[1]
| Juncus biflorus | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Photo by Gary Fleming at the Digital Atlas of the Virginia Flora | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Juncales |
| Family: | Juncaceae |
| Genus: | Juncus |
| Species: | J. biflorus |
| Binomial name | |
| Juncus biflorus Ell. | |
| |
| Natural range of Juncus biflorus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Juncus marginatus Rostkovius, Juncus aristulatus Michaux var. biflorus (Elliott) Small.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
Also known as bog rush, J. biflorus is a native perennial graminoid that is a member of the Juncaceae family. It has a rapid rhizomatous growth form reaching a mature height of 3.5 feet.[2]
Distribution
J. biflorus can be found in the Southeastern United States from Mississippi and up to Michigan as well as along the Atlantic coast to New Jersey.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
The main communities J. biflorus can be found include pine savannahs, pine flatwoods, mesic portions of sandhill-pocosin ecotones, and even roadsides, wet meadows, interdune swales, tidal marshes, and ditches.[3] As well, J. biflorus has been observed on the margin of an old wet fireland, margin of wet woods, and in a flooded depression.[4]
Phenology
Blooming occurs June through October.[1]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
J. biflorus is listed as endangered in the state of New York, and is listed as threatened in the state of Pennsylvania.[2]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=JUBI
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: John B. Nelson, Wade Biltoft, Keith Bradley, Daniel Castillo, and Richard D. Porcher. States and counties: South Carolina: Berkely and Orangeburg.