Difference between revisions of "Solidago stricta"
(→Seed dispersal) |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | + | This species is thought to be dispersed by wind.<ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> |
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Revision as of 18:26, 13 May 2021
| Solidago stricta | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Solidago |
| Species: | S. stricta |
| Binomial name | |
| Solidago stricta Aiton | |
| |
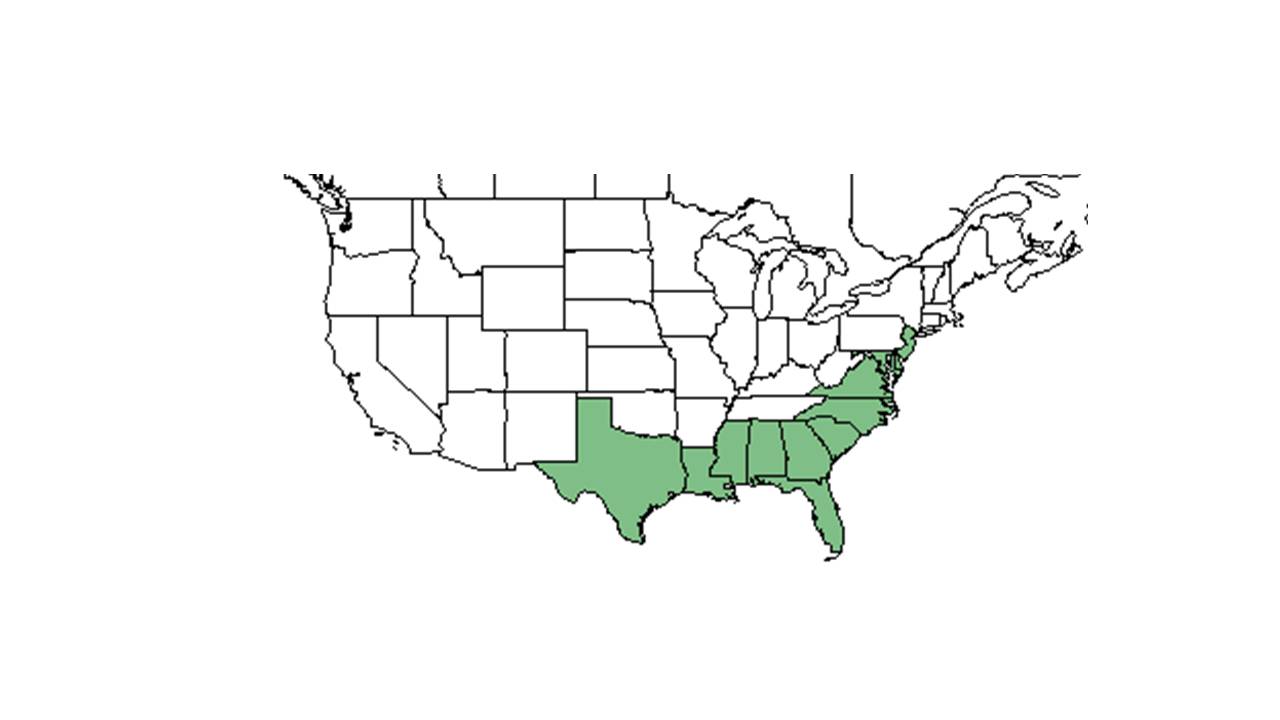
| Natural range of Solidago stricta from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Wand goldenrod, Pine barren bog goldenrod, Willow-leaf goldenrod
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Solidago perlonga Fernald; S. gracillima
Subspecies: S. stricta Aiton ssp. gracillima (Torrey & A. Gray) Semple
Description
A description of Solidago stricta is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, S. stricta can be found in open woodlands, pine flatwoods, pine-palmetto flatwoods, ditches, lagoon edges, banks of brackish marshes, high pinelands, longleaf pine-turkey oak ridges, salt flats bordering mangrove swamps, recently burned longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, seepage bogs, banks of ephemeral ponds, tidal marshes, sandhills, and coastal dunes.[1] It can also be found in lawns, clobbered slash pines, recently planted slash pine plantations, roadsides, vacant lots, powerline corridors, and logged over hillside bogs. It tends to be more common in mesic and wet areas than dry areas.[2] Substrates include loamy sand, peaty sand, alluvial sands, limerock, sand, and sandy peat.[1] When exposed to soil disturbance by military training in West Georgia, S. stricta responds negatively by way of absence.[3] Associated species include Vigna luteola, Liatris, Pityopsis, Aristida stricta, Pinus palustris, Andropogon, Solidago sempervirens, Senecio and Euthamia.[1]
Solidago stricta is an indicator species for the Upper Panhandle Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[4]
Phenology
S. stricta has been observed flowering year round and fruiting February through December.[1][5]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind.[6]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Cecil R Slaughter, Ann F. Johnson, Roomie Wilson, Robert L. Lazor, William P. Adams, R.K. Godfrey, William Reese, Paul Redfearn, John Morrill, R. Kral, M. Darst, Angus Gholson, F. C. Creager, D. B. Creager, Delzie Demaree, C. T. Reed, O. Lakela, J. B. Nelson, Sidney McDaniel, John Morrill, J. D. Lazor, V. I. Sullivan, A. H. Curtiss, A. F. Clewell, George R. Cooley, H. E. Grelen, Richard Carter, K. Craddock Burks, K. Studenroth, C. Florko, J. D. Lazor, Mark A Garland, Gary Knight, H. S. Conard, Rodie White, R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, Thomas E. Miller. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Bay, Broward, Calhoun, Charlotte, Dade, Dixie, Duval, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hillsborough, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, Monroe, Nassau, Okaloosa, Pinellas, Polk, Putnam, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Walker, J. and R. K. Peet. 1983. Composition and species diversity of pine-wiregrass savannas of the Green Swamp, North Carolina. Vegetatio 55:163-179.
- ↑ Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.