Difference between revisions of "Stylosanthes biflora"
Juliec4335 (talk | contribs) |
Juliec4335 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
When exposed to soil disturbance by military training in West Georgia, ''S. biflora'' responds negatively by way of absence.<ref>Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.</ref> It also responds negatively to soil disturbance by agriculture in Southwest Georgia.<ref>Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.</ref> ''S. biflora'' does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.<ref>Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.</ref> | When exposed to soil disturbance by military training in West Georgia, ''S. biflora'' responds negatively by way of absence.<ref>Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.</ref> It also responds negatively to soil disturbance by agriculture in Southwest Georgia.<ref>Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.</ref> ''S. biflora'' does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.<ref>Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.</ref> | ||
| − | ''Stylosanthes biflora'' is frequent and abundant in the Panhandle Xeric Sandhills community | + | ''Stylosanthes biflora'' is frequent and abundant in the Panhandle Xeric Sandhills and North Florida Subxeric Sandhills community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 16:25, 20 July 2020
| Stylosanthes biflora | |
|---|---|
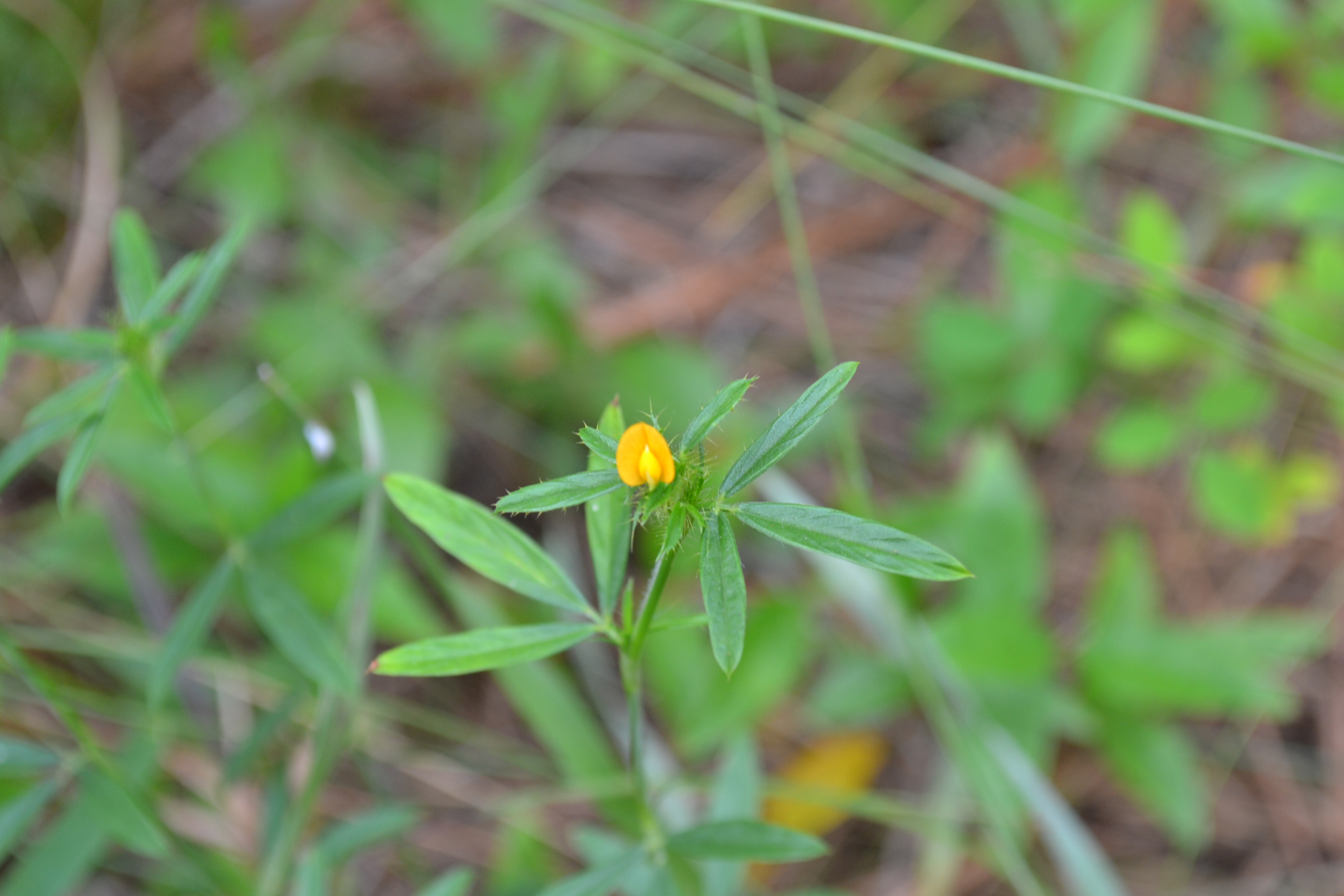

| |
| Photo taken by Michelle M. Smith | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Stylosanthes |
| Species: | S. biflora |
| Binomial name | |
| Stylosanthes biflora (L.) Britton, Sterns & Poggenb. | |
| |
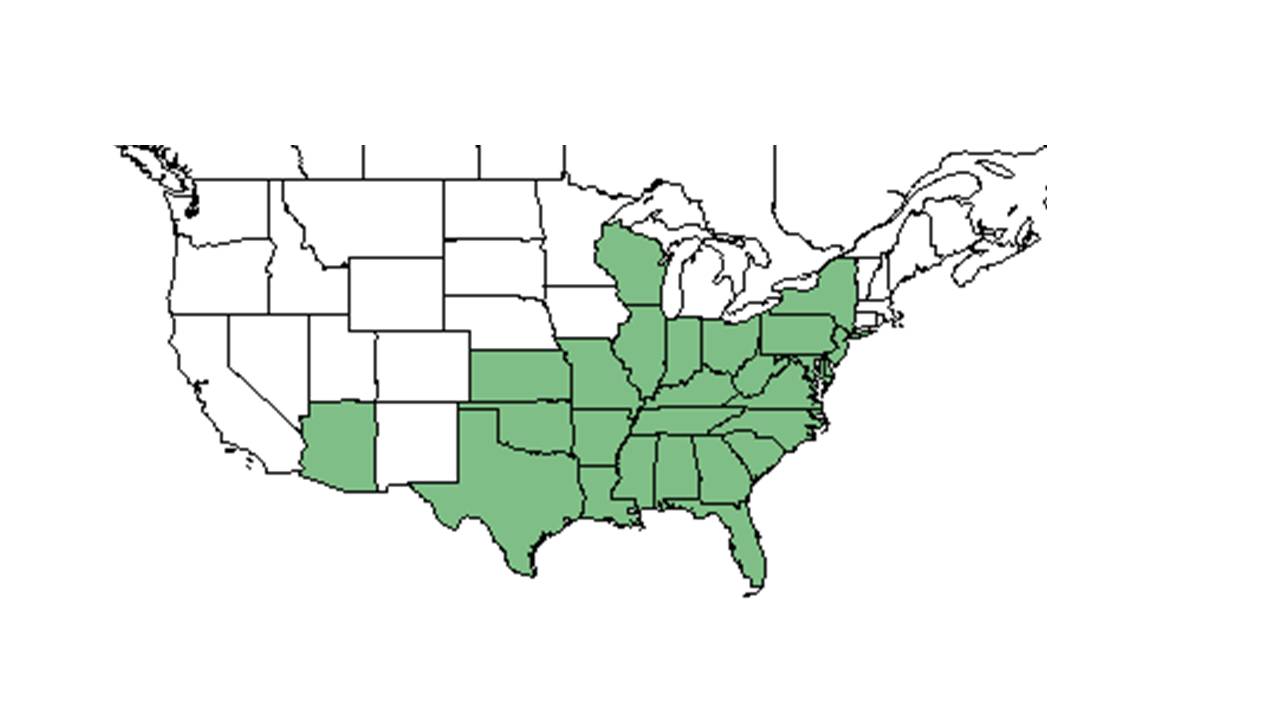
| Natural range of Stylosanthes biflora from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Sidebeak pencilflower
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Stylosanthes biflora var. biflora; S. biflora var. hispidissima (Michaux) Pollard & Ball; S. riparia Kearney; S. riparia var. riparia; S. riparia var. setifera Fernald
Description
"Prostrate to erect, perennial herb, stems few to many, 1-5 dm long, glabrate to bristly-hirsute. Leaves pinnately 3-foliolate; leaflets elliptic to oblanceolate, 1.5-4 cm long, entire, estipellate; stipules striate, finely pubescent to bristly hirsute, subulate, (0.4) 1-1.5 cm long, aristately tipped. Hypanthium pedicel-like, glabrous, 3-4 mm long. Calyx glabrous, tube short, campanulate above the filiform hypanthium, upper 2 lobes united, obtuse, 1.2-1.8 mm long, the 2 lateral lobes oblong, obtuse, ca. 1 mm long, the lowermost lobe acute, ca. 2 mm long; petals orange-yellow to whitish, standard 5-9 mm long; stamens 10, monadelphous, anthers alternating between oblong and subglobose. Legume short-pubescent, obliquely ovate, 3-5 mm long, sessile, reticulate, usually only the upper segment maturing, the lower pedicel-like." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
It is a legume. [2]
Habitat
Occurs in frequently burned pinelands such as longleaf pine and scrub oak ridges. [3] Also occurs in pine, oak, hickory woods. [3] Also occurs in human disturbed areas such as roadsides and right-of-ways, in clearings, fallow fields, and in pastures. [3] Associated species include Phlox floridana, Stillingia sylvatica, Asimina longiflolia var. spathulata, Lactuca graminifolia, Stylosanthes biflora, Erigeron strigosa, Baptisia lanceloata, Hedyotis crassifolia, Tercauloon undulatum, Asclepias humistrata, Quercus hemisphaerica, Pinus palustris, Panicum, Andropogon. [3]
It can live in xeric areas.[4] It can survive in disturbed areas.[5] In Baker County, Georgia at Jones Ecological Research Center with native groundcover managed with frequent fire.[6] [7] It is common in longleaf pine communities.[4] Hainds and his team found that S. biflora occurred in 92.3% of the plots.[8] Longleaf pine flatwoods that are mesic, fire-maintained savannas or sparse woodlands with nutrient-poor soils. [9] Longleaf pine stands that originated from seed in Rapides Parish, Louisiana that have fine sandy loam soils.[10] In Buettner Xeric Limestone Prairies in Monroe County, Illinois they have outcrops along streams and river where a prescribed burn was conducted in the nearby woody area in 2010.[11]
When exposed to soil disturbance by military training in West Georgia, S. biflora responds negatively by way of absence.[12] It also responds negatively to soil disturbance by agriculture in Southwest Georgia.[13] S. biflora does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[14]
Stylosanthes biflora is frequent and abundant in the Panhandle Xeric Sandhills and North Florida Subxeric Sandhills community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).[15]
Phenology
S. biflora has observed flowering and fruiting from April to December with peak inflorescence in May.[3][16] It has a mid-summer flowering peak.[2] Following a lightning-season burn, it continues to reproduce through late summer and fall.[2]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [17]
Fire ecology
It seems to thrive under frequent burning around the summertime. Lightning-season burns seem to significantly increase flowering, but only after a dramatic delay.[2] Density of S. biflora was greater after frequent late dormant-season fires.[18] S. biflora was found only in annual winter and annual summer long-term (20 years) burned loblolly pine plots, and even then, only rarely. [19]
Use by animals
Gopher tortoises (Gopherus polyphemus) graze on Stlosanthes bioflora.[6]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 604. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Hiers, J. K., R. Wyatt, et al. (2000). "The effects of fire regime on legume reproduction in longleaf pine savannas: is a season selective?" Oecologia 125: 521-530.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: August 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Lisa Keppner, Ed Keppner, Nancy E. Jordan, Gary R. Knight, Robert K. Godfrey, F. S. Earle, C. F. Baker, S. W. Leonard, Gwen Roney, C. Jackson, Robert Kral, Mabel Kral, Gwynn W. Ramsey, Richard S. Mitchell, O. Lakela, D. B. Ward, L. J. Brass, Robert L. Lazor, Jean W. Wooten, S. C. Hood, R. C. Phillips, William Reese, Paul Redfearn, Leon Neel, R. Komarek, R. A. Norris, Andre F. Clewell, Chris Cooksey, M. Davis, Cecil R Slaughter, Peter H. Raven, Tamra Engelhorn Raven, C. L. Huff, C. Ritchie Bell, James W. Hardin, Wilbur H Duncan, Effie Boon, M. Morgan, R. L. Wilbur, H. K. Svenson, A. B. Seymour, D. S. Correll, H. B. Correll, H. R. Reed, Delzie Demaree, I. M. Johnston, G. Edwin, L. J. Uttal, Norlan C. Henderson, L. B. Smith, A. R. Hodgdon, M. A, Chrysler, S. J. Ewer, Roy Hood, R. D. Houk, Kurtz, Angus Gholson, Jr., David M. DuMond, Clarke Hudson, John W. Thieret, S. B. Jones, Bob Mills, Champ Clark, Sidney McDaniel, Samuel B. Jones, Jr., James G. Teer, Roomie Wilson, P. L. R., Elizabeth Ann Bartholomew, Edward S. Steele, Duane Isely, A. J. Sharp, S.M. Tracy, F. H. Sargent, W. W. Ashe, David Moreland, John R. Wood. States and Counties: Alabama: Clarke, Covington, Cullman, Escambia, Henry, Lee. Arkansas: Columbia, Hot Spring, Logan, Pulaski, Saline. Florida: Bay, Citrus, Duval, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hillsborough, Jackson, Jefferson, Lafayette, Leon, Liberty, Okaloosa, Putnam, Suwannee, Taylor, Wakulla, Walton, Washington. Georgia: Decatur, Grady, Johnson, Mitchell, Rabun, Seminole, Taylor, Thomas, Toombs. Illinois: Lawrence. Kansas: Montgomery. Louisiana: Bienville, Claiborne, Natchitoches, Tangipahoa. Mississippi: Amite, Covington, Harrison, Jackson, Jones, Lamar, Marion, Panola. Missouri: Benton, Carter, Dallas, Dent, Jefferson, McDonald, Ozark, Polk, St Clair. New Jersey: Atlantic. North Carolina: Burke, Catawba, Craven, Guilford, Iredell, Lee, Warren. South Carolina: Oconee, Union. Tennessee: Bledsoe, Coffee. Texas: Brazos, Harris, Morris, Shelby, Walker. Virginia: Dinwiddie, Greensville, Henry, Montgomery, Prince William, Roanoke, Rockingham. West Virginia: Wirt.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Carter, R. E., M. D. MacKenzie, et al. (2004). "Species composition of fire disturbed ecological land units in the Southern Loam Hills of south Alabama." Southeastern Naturalist 3: 297-308.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92: 409-421.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Birkhead, R. D., C. Guyer, et al. (2005). "Patterns of folivory and seed ingestion by gopher tortoises (Gopherus polyphemus) in a southeastern pine savanna." American Midland Naturalist 154: 143-151.
- ↑ Simkin, S., W. Michener, et al. (2001). "Plant Response Following Soil Disturbance in a Longleaf Pine Ecosystem." Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 128(3): 208-218.
- ↑ Hainds, M. J., R. J. Mitchell, et al. (1999). "Distribution of native legumes (Leguminoseae) in frequently burned longleaf pine (Pinaceae)-wiregrass (Poaceae) ecosystems." American Journal of Botany 86: 1606-1614.
- ↑ Brewer, J. S. and S. P. Cralle (2003). "Phosphorus addition reduces invasion of a longleaf pine savanna (southeastern USA) by a non-indigenous grass (Imperata cylindrica)." Plant Ecology 167: 237-245.
- ↑ Haywood, J. D., A. Marti, et al. (1998). Seasonal biennial burning and woody plant control influence native vegetation in loblolly pine stands. Research Paper SRS-14. Asheville, NC, USDA Forest Service.
- ↑ McClain, W. E. and J. E. Ebinger (2014). "Vascular Flora of Buettner Xeric Limestone Prairies, Monroe County, Illinois." Southern Appalachian Botanical Society.
- ↑ Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.
- ↑ Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Sparks, J. C., R. E. Masters, et al. (1998). "Effects of late growing-season and late dormant-season prescribed fire on herbaceous vegetation in restored pine-grassland communities." Journal of Vegetation Science 9: 133-142.
- ↑ Lewis, C. E. and T. J. Harshbarger (1976). "Shrub and herbaceous vegetation after 20 years of prescribed burning in the South Carolina coastal plain." Journal of Range Management 29: 13-18.