Difference between revisions of "Lobelia amoena"
Lsandstrum (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | This species can be found in floodplain forests, semi-open wetlands, along river and stream banks, seepage bogs, and low depressions. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, W. W. Baker, A. Gholson Jr., James P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, D. Hall, R. Komarek, R. Kral, N. Lee, Sidney McDaniel, Richard S. Mitchell, Gil Nelson, R. A. Norris, Camm Swift, D. B. Ward, and Rodie White. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, Wakulla, Walton, Washington. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.</ref> It grows in shaded to deep shaded environments in wet or dry sands and loam of mesic wooded environments. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> ''L. amoena'' also grows in human disturbed areas such as roadside ditches and clear-cut woods. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> Associated species include ''Boltonia, Commelina, Coreopsis integrifolia, Physostegia virginiana, Woodwardia areolata, Quercus, Rhamnus, oakleaf hydrangea, Conoclinium, Pluchea, Leersia, Panicum, Schoenus, Juniperus, Solidago fistulosa,'' and ''Bidens alba''. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | This species can be found in floodplain forests, semi-open wetlands, along river and stream banks, seepage bogs, and low depressions. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, W. W. Baker, A. Gholson Jr., James P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, D. Hall, R. Komarek, R. Kral, N. Lee, Sidney McDaniel, Richard S. Mitchell, Gil Nelson, R. A. Norris, Camm Swift, D. B. Ward, and Rodie White. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, Wakulla, Walton, Washington. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.</ref> It grows in shaded to deep shaded environments in wet or dry sands and loam of mesic wooded environments. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> ''L. amoena'' also grows in human disturbed areas such as roadside ditches and clear-cut woods. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> ''L. amoena'' responds negatively to soil disturbance by heavy silvilculture in North Carolina.<ref>Cohen, S., R. Braham, and F. Sanchez. (2004). Seed Bank Viability in Disturbed Longleaf Pine Sites. Restoration Ecology 12(4):503-515.</ref> |
| + | Associated species include ''Boltonia, Commelina, Coreopsis integrifolia, Physostegia virginiana, Woodwardia areolata, Quercus, Rhamnus, oakleaf hydrangea, Conoclinium, Pluchea, Leersia, Panicum, Schoenus, Juniperus, Solidago fistulosa,'' and ''Bidens alba''. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 20:19, 9 July 2019
| Lobelia amoena | |
|---|---|
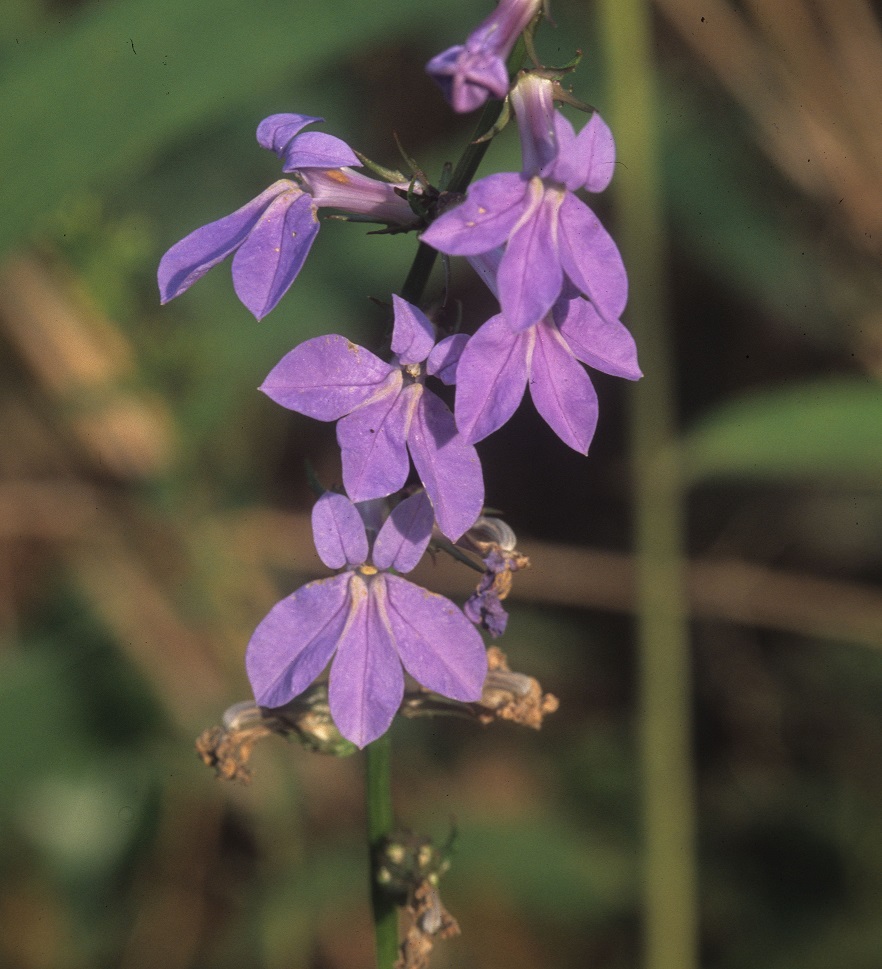

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Campanulales |
| Family: | Campanulaceae |
| Genus: | Lobelia |
| Species: | L. amoena |
| Binomial name | |
| Lobelia amoena Michx. | |
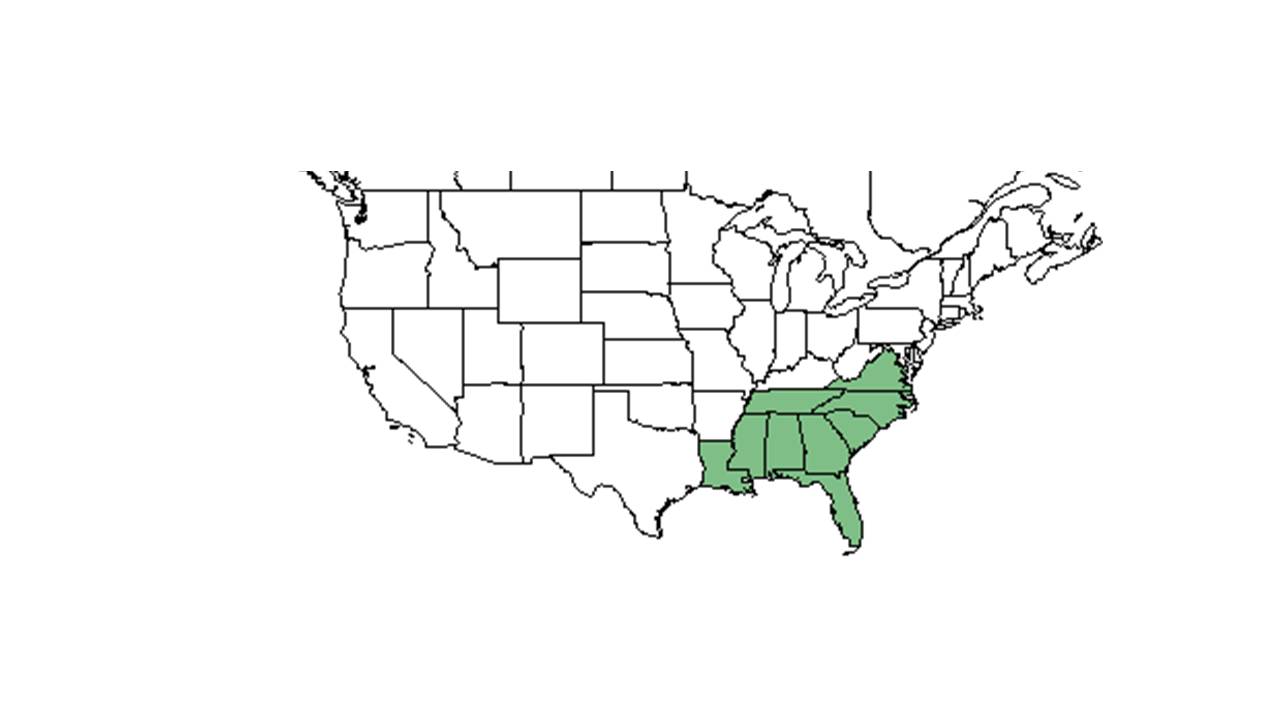
| |
| Natural range of Lobelia amoena from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Southern lobelia
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Lobelia amoena var. amoena
Description
"Perennial or annual herbs, stems erect, strict or freely branched. Leaves crenate, serrate or entire. Raceme terminal ,bracteate, often very leafy and the flowers appearing axillary. Calyx 5-lobed, more or less actinomorphic; corolla zygomorphic, fenestrate, 2-lipped, upper lip 2-lobbed, lower 3-lobbed. Stamens 5, completely united. Capsule dehiscent by apical pores. Seeds yellowish brown, tuberculate, oblong, 0.6-1 mm long." [1]
"Similar to L. elongata. Leaves elliptic to lanceolate, 4-15 cm long, 2-4 cm wide. Sepals entire or remotely glandular-serrate; corolla tube 7-9 mm long; filament tube 5-7 mm long. Capsule 6-8 mm broad." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
This species can be found in floodplain forests, semi-open wetlands, along river and stream banks, seepage bogs, and low depressions. [2] It grows in shaded to deep shaded environments in wet or dry sands and loam of mesic wooded environments. [2] L. amoena also grows in human disturbed areas such as roadside ditches and clear-cut woods. [2] L. amoena responds negatively to soil disturbance by heavy silvilculture in North Carolina.[3] Associated species include Boltonia, Commelina, Coreopsis integrifolia, Physostegia virginiana, Woodwardia areolata, Quercus, Rhamnus, oakleaf hydrangea, Conoclinium, Pluchea, Leersia, Panicum, Schoenus, Juniperus, Solidago fistulosa, and Bidens alba. [2]
Phenology
This species has been observed flowering from September to November. [2]
Fire ecology
This species has been found in annually burned areas. [2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 1005-7. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, W. W. Baker, A. Gholson Jr., James P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, D. Hall, R. Komarek, R. Kral, N. Lee, Sidney McDaniel, Richard S. Mitchell, Gil Nelson, R. A. Norris, Camm Swift, D. B. Ward, and Rodie White. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, Wakulla, Walton, Washington. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
- ↑ Cohen, S., R. Braham, and F. Sanchez. (2004). Seed Bank Viability in Disturbed Longleaf Pine Sites. Restoration Ecology 12(4):503-515.