Difference between revisions of "Diospyros virginiana"
(→Distribution) |
(→Phenology) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
===Phenology=== | ===Phenology=== | ||
| − | General flowering time of ''D. virginiana'' is from May to June with fruiting occurring between September and December and persisting.<ref name= "Weakley"/> It has been observed flowering in April and May as well.<ref name= "Pan Flora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 21 MAY 2018</ref> | + | General flowering time of ''D. virginiana'' is from May to June with fruiting occurring between September and December and persisting.<ref name= "Weakley"/> It has been observed flowering in April and May as well.<ref name= "Pan Flora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 21 MAY 2018</ref> Preferred fruit-bearing age is between 25 to 50 years, even though fruit can start producing on 10 year old years.<ref name= "guide"/> |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
Revision as of 13:30, 3 May 2019
Common Names: common persimmon[1]; American persimmon; possumwood
| Diospyros virginiana | |
|---|---|

| |
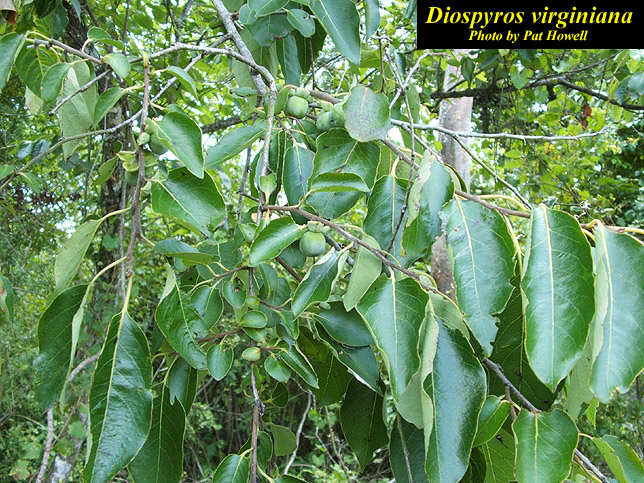
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Ebenales |
| Family: | Ebenaceae |
| Genus: | Diospyros |
| Species: | D. virginiana |
| Binomial name | |
| Diospyros virginiana L. | |
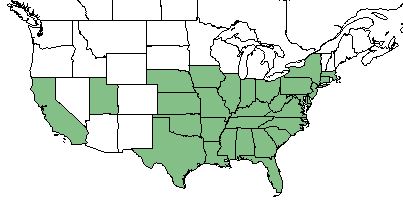
| |
| Natural range of Diospyros virginiana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: D. virginiana L. var. pubescens (Pursh), D. virginiana L. var. platycarpa (Sargent), D. mosieri (Small)
Description
D. virginiana is a perennial tree of the Ebenaceae family native to North America. [1] The tree can reach heights of 5 to 21 meters tall, with mature bark that is thick, blocky, and dark grey in color. Leaves simple, deciduous, alternately arranged, ovate to elliptic or oblong in shape, and entire with an acuminate apex as well as a rounded base. The underside of the leaves are usually lighter-colored, more often on younger leaves. Flowers staminate or pistillate borne on separate trees located on the shoots of the current year's growth. Pistillate flowers are short-stalked or sessile, bell-shaped, fragrant, corolla greenish-yellow to creamy, and 4 lobes. Staminate flowers are borne in clusters of 2 to 3 flowers, tubularly shaped, and greenish-yellow in color. Fruit is a greenish-yellow berry that contains a highly astringent pulp before ripe, and turns a yellow-orange color when ripe with 1 to 8 flat seeds inside.[2] East from the Mississippi River, D. virginiana has cuneate to rounded leaves at the base that are glabrous or glabrescent, while D. virginiana west of the Mississippi River have subcordate leaves that are persistently pubescent. These differences could be worthy of varietal recognition.[3]
Distribution
D. virginiana is found throughout the east coast and southeastern United States as well as California and Nevada. [1] While it is sparingly in other areas, its dominant distribution is in the east-central and southeastern United States.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
D. virginiana is easily adaptable to a wide range of soils and climates; it prefers moist and well-drained soils, but can also tolerate dry, hot, and poor soils. Habitats include from dry, sterile, and sandy woodlands to rocky hillsides and river bottoms. However, best growth is usually on clay and heavy loam soil on terraces of large streams and river bottoms. In the Mississippi Delta, it grows on shallow sloughs, wet flats, and swamp margins. It is shade tolerant, but grows best in full sun. In disturbed sites, it is usually an early pioneer species, and can commonly be found along fencerows and roadsides. It can also be found to grow in thickets in pastures and open fields.[2] D. virginiana is considered one of the most common mid-story vegetation in the Upper Panhandle Savanna. [4] As well, a variety of habitats have been visited for samples of D. virginiana including mixed woodlands, pine wiregrass community, lowland woodlands, old field, dry sandy soils, edge of branch swamp, and sandy ridge near swamp. [5]
Phenology
General flowering time of D. virginiana is from May to June with fruiting occurring between September and December and persisting.[3] It has been observed flowering in April and May as well.[6] Preferred fruit-bearing age is between 25 to 50 years, even though fruit can start producing on 10 year old years.[2]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by consumption by vertebrates. [7]
Fire ecology
Prescribed burns can be used to control the species, but fire exclusion can decrease its likelihood of surviving. [1]
Pollination
This plant is dioecious, meaning that male and female plants are separate individuals.[3]
Use by animals
This species consists of approximately 50-10% of the diet for large mammals, small mammals, and various terrestrial birds.[8] Bees use the nectar from the flowers for honey. White-tailed deer eat the twigs and leaves. The fruit of the tree is eaten by squirrel, fox, skunk, deer, bear, coyote, racoon, opossum, quail, wild turkey, catbird, cedar waxwing and other various birds.[2] It is an edible fruit for humans as well, known for being sweet yet can be bitter if the fruit is not fully ripe.[3] The fruit can be used to make cookies, puddings, custard, cakes, and sherbet, and the seeds can be dried, roasted, and ground to make a substitute for coffee. The wood can be used for textile shuttles and heads for driver golf clubs due to it being smooth, hard, and even textured. The inner bark and unripe fruit can be used medicinally to treat fevers, diarrhea, and hemorrhage.[2]
Conservation and Management
D. virginiana is listed as a species for special concern by the Connecticut Department of Environmental Protection, and it is listed as endangered by the New York Department of Environmental Conservation, Division of Land and Forests.[1]
Cultivation and restoration
D. virginiana is a good species to utilize for erosion control due to its deep taproot.[2]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Nesom, G. and L. Moore (2006). Plant Guide: Common Persimmon Diospyros virginiana. N.R.C.S. United States Department of Agriculture. Baton Rouge, LA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, Cecil Slaughter, Loran Anderson, T.Lott, B. Lund, Tom Barnes, Richard Mitchel, Gary Knight, Patricia Elliot, Bruce Hansen, Anne Perkins, Gwynn Ramsey, Karen MacClendon, M. Boothe, Leon Neel, Richard Gaskalla, R. Komarek, A. Johnson, M, Jenkins, Richard Carter. States and counties: Florida (Marion, Massau, Liberty, Franklin, Leon, Alachua, Wakulla, Highlands, Hernando, Jackson, Taylor, Collier, Lee, Sarasota, Gadsden, Suwannee, Calhoun, Washington, Holmes, Gulf) Georgia (Thomas, Grady, Lee)
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 21 MAY 2018
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Yarrow, G.K., and D.T. Yarrow. 1999. Managing wildlife. Sweet Water Press. Birmingham.