Difference between revisions of "Callicarpa americana"
(→Conservation and management) |
(→Ecology) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Callicarpa americana'' at Archbold Biological Station: <ref name=dey> Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Callicarpa americana'' at Archbold Biological Station: <ref name=dey> Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | ||
| Line 48: | Line 47: | ||
Megachilidae: ''Megachile brevis pseudobrevis'' | Megachilidae: ''Megachile brevis pseudobrevis'' | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| + | It is a moderate portion of large mammal diets, ranging from 10-25% of their average diet, and a low portion of small mammal and terrestrial bird diets, from 5-10% of their diet.<ref name= "Miller">Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.</ref><ref name= "Yarrow">Yarrow, G.K., and D.T. Yarrow. 1999. Managing wildlife. Sweet Water Press. Birmingham.</ref> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
Revision as of 13:39, 29 March 2019
| Callicarpa americana | |
|---|---|
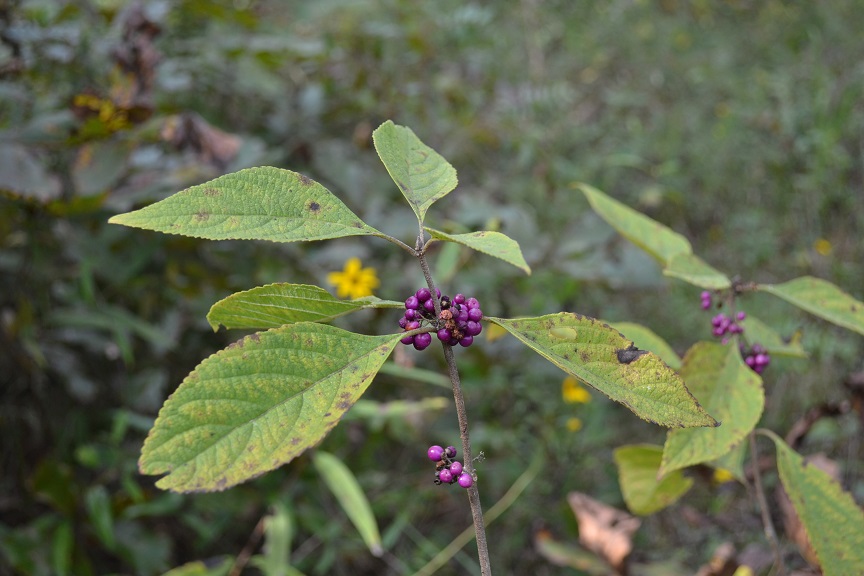

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson (2015) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Verbenaceae |
| Genus: | Callicarpa |
| Species: | C. americana |
| Binomial name | |
| Callicarpa americana L. | |
| |
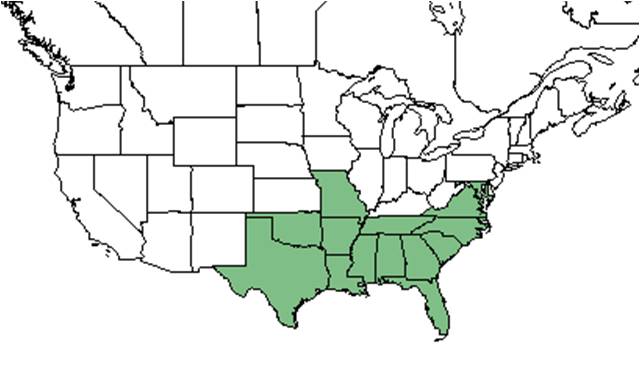
| Natural range of Callicarpa americana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: American beautyberry; French-mulberry
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none
Varieties: none
Description
Generally for the Callicarpa genus, they grow up to 1-2.5 m tall with twigs having stellate pubescence while being scrurfy when touched. The leaves are simple, opposite or subopposite, have short pubescent above, and ovate, ovate-lanceolate, or elliptic, acute to acuminate, petiolate in shape. The flowers are in axillary cymes. The calyx is shallowly 5-toothed, grows 0.5-2 mm long. The petals are united ca. 1/2-2/3 their length. The lobes 5, are spreading, are lavender to pinkish in color, grow 3-5 mm long. The stamens are exserted. The stigma is slightly 2-lobed. The drupe is 4-seeded, are lavendar to purple in color, are rarely white in color, and are globose. The seeds are light yellow to brown in color, are ellipsoid to orbicular rounded on the back, and are flattened on the inner surface. [1]
Specifically, for Callicarpa americana, the leaves are ovate to ovate-lanceolate in shape, there are stellate pubescence beneath the leaves, and grow 7-15 cm wide, are crenate to serrate, and at the base are widely cuneate or rounded. The petioles grow 1.5-3.5 cm long, and are scurfy stellate like the twigs. The cymes are shorter than the subtending petioles. The peduncles grow 1-5 mm long. The drupe grows 3-5 mm long. The pyrenes grow 2.3 mm long. [1]
Distribution
C. ameriana is native to the southeastern United States, ranging from Maryland to south Florida and Texas. It can also be found in Mexico and the West Indies.[2]
Ecology
Phenology
C. americana has been observed flowering from May to August with peak inflorescence in June.[3]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Callicarpa americana at Archbold Biological Station: [4]
Apidae: Apis mellifera
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlora pura, Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum placidensis
Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis
Use by animals
It is a moderate portion of large mammal diets, ranging from 10-25% of their average diet, and a low portion of small mammal and terrestrial bird diets, from 5-10% of their diet.[5][6]
Conservation and management
It is listed as endangered and extirpated by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources.[7]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 894. Print.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.
- ↑ Yarrow, G.K., and D.T. Yarrow. 1999. Managing wildlife. Sweet Water Press. Birmingham.
- ↑ USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 29 March 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.