Difference between revisions of "Andropogon gerardii"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | Big bluestem can be found in prairies, open woods, along riverbanks, meadows, and even roadsides. It is particularly abundant in lowland prairies and sandy areas <ref name= "USDA"/>. It develops best in mesic communities. <ref name= "Copeland"/> | + | Big bluestem can be found in prairies, open woods, along riverbanks, meadows, and even roadsides. It is particularly abundant in lowland prairies and sandy areas <ref name= "USDA"/>. It develops best in mesic communities. <ref name= "Copeland"/> It is usually the dominant species within the ground community. <ref name= "Howe"> Howe, H. F. (1995). "Succession and Fire Season In Experimental Prairie Plantings." Ecology 76(6): 1917-1925. </ref> |
Associated species - ''Panicum virgatum'', ''Schizachyrium scoparium'', and ''Sorghastrum nutans'' <ref name= "Abrams"> Abrams, M. (1988). "Effects of Burning Regime on Buried Seed Banks and Canopy Coverage in a Kansas Tallgrass Prairie." The Southwestern Naturalists 33(1): 65-70. </ref> | Associated species - ''Panicum virgatum'', ''Schizachyrium scoparium'', and ''Sorghastrum nutans'' <ref name= "Abrams"> Abrams, M. (1988). "Effects of Burning Regime on Buried Seed Banks and Canopy Coverage in a Kansas Tallgrass Prairie." The Southwestern Naturalists 33(1): 65-70. </ref> | ||
Revision as of 12:21, 8 June 2018
Common names: Big Bluestem; Turkeyfoot [1]
| Andropogon gerardii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Tracheobionta |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Andropogon |
| Species: | A. gerardii |
| Binomial name | |
| Andropogon gerardii Vitman | |
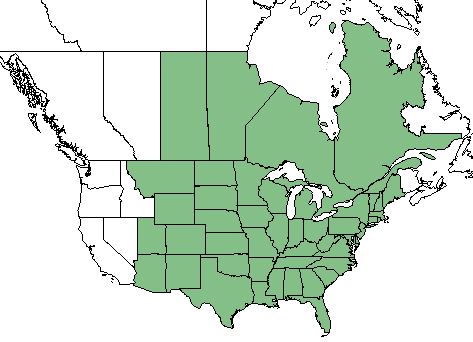
| |
| Natural range of Andropogon gerardii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Andropogon gerardi Vitman, Andropogon provincialis Lamark, and Andropogon furcatus Muhlenberd ex Willdenow
Varieties: none
Description
Also known as big bluestem or turkeyfoot, A. gerardii is a native perennial graminoid that is a member of the Poaceae family. It is tufted, and contains short, scaly rhizomes. It is known for being a tall graminoid, ranging from 6 to 8 feet tall, and is very leafy at the basal region with some leaves that are carried up on the stem. As well, big bluestem contains rhizomes that are usually 1 to 2 inches below the soil surface for clonal reproduction [1].
Distribution
A. gerardii is distributed across the United States and Canada, but not past New Mexico or Montana [1].
Ecology
Habitat
Big bluestem can be found in prairies, open woods, along riverbanks, meadows, and even roadsides. It is particularly abundant in lowland prairies and sandy areas [1]. It develops best in mesic communities. [2] It is usually the dominant species within the ground community. [3]
Associated species - Panicum virgatum, Schizachyrium scoparium, and Sorghastrum nutans [4]
Phenology
A. gerardii flowers from August until October [5].
Seed bank and germination
Seeds will usually germinate within 4 weeks when regularly irrigated [1].
Fire ecology
The rhizomes of A. gerardii are known to resprout after a fire disturbance, and regeneration following fires is much quicker in the springtime than the summertime since the rhizomes contain winter-stores with carbohydrates [1]. As well, flowering of A. gerardii has been seen to significantly increase in late-summer fires rather than early-spring fires. [2]
Use by animals
A. gerardii is utilized by birds and mammals for nesting and escape cover during the summer and winter, and contributes to the spring nesting habitats since it resists lodging under snow cover [1]. It is also one of the most important forage species for animals in the tallgrass prairie regions. [6]
Conservation and Management
For management, A. gerardii has a considerably weak seedling compared to its competition, so control of its competition is necessary, such as high mowing for weed control or even grazing of competing cool season grasses before the big bluestem is 1 inch tall in the spring [1].
Cultivation and restoration
There are several cultivars available of A. gerardii, including 'Bison' (ND), 'Bonilla' (SD), 'Champ' (NE, IA), 'Kaw' (KS), 'Earl' (TX), 'Niagara' (NY), 'Pawnee' (NE), and 'Rountree' (IA) [1].
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ANGE
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 Copeland, T. E., et al. (2002). "Fire season and dominance in an Illinois tallgrass prairie restoration." Restoration Ecology 10(2): 315-323.
- Jump up ↑ Howe, H. F. (1995). "Succession and Fire Season In Experimental Prairie Plantings." Ecology 76(6): 1917-1925.
- Jump up ↑ Abrams, M. (1988). "Effects of Burning Regime on Buried Seed Banks and Canopy Coverage in a Kansas Tallgrass Prairie." The Southwestern Naturalists 33(1): 65-70.
- Jump up ↑ Panflora URL: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/
- Jump up ↑ Gould, F. W. (1967). "The Grass Genus Andropogon in the United States." Brittonia 19(1): 70-76.