Difference between revisions of "Diospyros virginiana"
(→Distribution) |
(→Ecology) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| − | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | + | ===Habitat=== |
| − | + | ''D. virginiana'' is easily adaptable to a variety of habitats. It is found in rocky hillsides, sandy woodlands, and even river bottoms. It prefers, terraces of streams and river bottoms that have clay in the soil. It prefers full sun but can tolerate shade. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | |
| + | <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | ===Phenology=== | ||
| + | ''D> virginiana'' commonly flowers in April and May. <ref name= "Pan Flora"> [http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Pan Flora]</ref> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| − | + | ===Fire ecology=== | |
| + | Prescribed burns can be used to control the species, but fire exclusion can decrease its likelihood of surviving. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | + | ===Use by animals=== | |
| + | Bess use the nectar from the flowers for honey. White-tailed deer eat the twigs and leaves. The fruit of the tree is eaten by squirrel, fox, skunk, deer, bear, coyote, racoon, opossum, quail, wild turkey, catbird, cedar waxwing and other various birds. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 19:20, 21 May 2018
| Diospyros virginiana | |
|---|---|
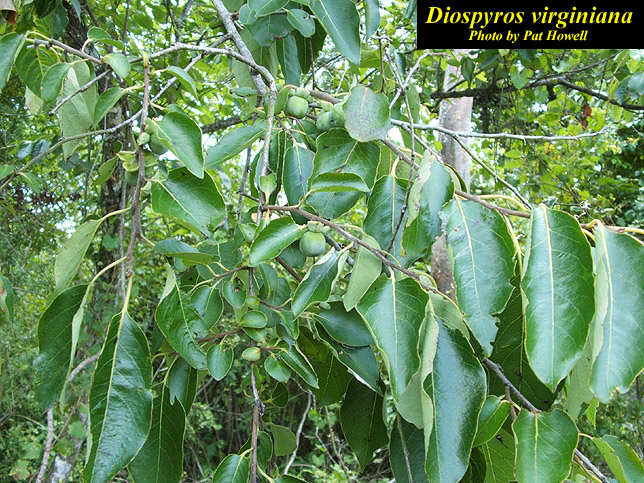

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Ebenales |
| Family: | Ebenaceae |
| Genus: | Diospyros |
| Species: | D. virginiana |
| Binomial name | |
| Diospyros virginiana L. | |
| |
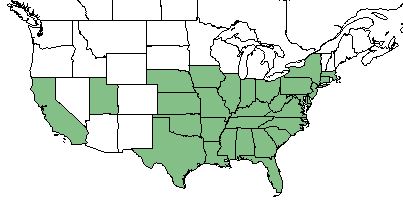
| Natural range of Diospyros virginiana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: D. virginiana var. pubescens (Pursh), D. virginiana var. platycarpa (Sargent), D. mosieri (Small)
Variety:none
Description
D. virginiana is a perennial tree of the Ebenaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
D. virginiana is found throughout the east coast and southeastern United States as well as California and Nevada. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
D. virginiana is easily adaptable to a variety of habitats. It is found in rocky hillsides, sandy woodlands, and even river bottoms. It prefers, terraces of streams and river bottoms that have clay in the soil. It prefers full sun but can tolerate shade. [1]
Phenology
D> virginiana commonly flowers in April and May. [2]
Fire ecology
Prescribed burns can be used to control the species, but fire exclusion can decrease its likelihood of surviving. [1]
Use by animals
Bess use the nectar from the flowers for honey. White-tailed deer eat the twigs and leaves. The fruit of the tree is eaten by squirrel, fox, skunk, deer, bear, coyote, racoon, opossum, quail, wild turkey, catbird, cedar waxwing and other various birds. [1]