Difference between revisions of "Gratiola brevifolia"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ==Description== <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | ''Gratiola brevifolia'' is a dioecious annual or perennial that grows as a forb/herb.<ref name="USDA"/> | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 19:34, 2 February 2018
| Gratiola brevifolia | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Scrophulariaceae |
| Genus: | Gratiola |
| Species: | G. brevifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Gratiola brevifolia Raf. | |
| |
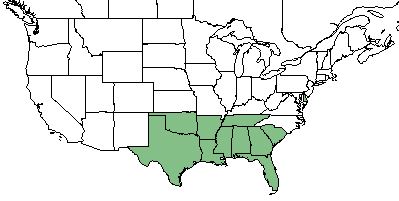
| Natural range of Gratiola brevifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name: sticky hedgehyssop[1]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Description
Gratiola brevifolia is a dioecious annual or perennial that grows as a forb/herb.[1]
Distribution
This species occurs from South Carolina, southward to central peninsular Florida, westward to eastern Texas, and inland to southeastern Oklahoma, central Arkansas, and Tennessee. It also is reported to occur disjunct in Delaware.[1][2] Throughout most of its range, it is considered rare or imperiled.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
G. brevifolia is found in sandy pinelands, oak barrens, sandy riverbanks,[2] floodplain forests, cypress swamps, and other wet places.[3] In the lower banks and bottoms of a ditched perennial stream, G. brevifolia consists of 1,500 individuals.[2]
Phenology
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 02 February 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Knapp WM, Estes D (2006) Gratiola brevifolia (Plantaginaceae) new to the flora of delaware, the delmarva peninsula, and the mid-Atlantic. SIDA 22(1):825-829.
- ↑ Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.