Difference between revisions of "Sorghastrum secundum"
(→Seed bank and germination) |
(→Ecology) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
This species is found on sandhills.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> | This species is found on sandhills.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | Flowering occurs in September and October<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> and germination seems to peak in January and February.<ref name="Coffey & Kirkman 2006"/> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
Revision as of 16:11, 16 January 2018
| Sorghastrum secundum | |
|---|---|
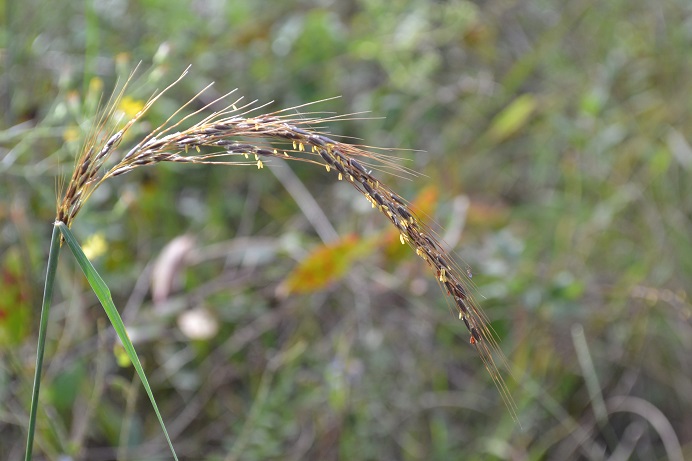

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Sorghastrum |
| Species: | S. secundum |
| Binomial name | |
| Sorghastrum secundum (Elliott) Nash | |
| |
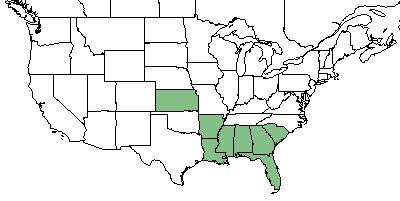
| Natural range of Sorghastrum secundum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): lopsided indiangrass[1][2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym(s): Andropogon secundus[2]
Description
Sorghastrum secundum is a monoecious perennial graminoid[2] that grows to 3-6 feet (0.91-1.83 m).[3]
Distribution
S. secundum occurs from southern South Carolina, south to southern Florida, and westward to southern Alabama.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found on sandhills.[1]
Phenology
Flowering occurs in September and October[1] and germination seems to peak in January and February.[4]
Seed bank and germination
In south Georgia, S. secundum buried in seed bags had a 26% germination rate after one year, 34% after two, and 9% after four.[4]
Use by animals
S. secundum consists of 2-5% of the diet for terrestrial birds.[5]
Diseases and parasites
Its seeds are more prone to mold destroying it prior to germination compared to other seeds.[4]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 16 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Plant database: Sorghastrum secundum. (16 January 2018) Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=SOSE5
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Coffey KL, Kirkman LK (2006) Seed germination strategies of species with restoration potential in a fire maintained pine savanna. Natural Areas Journal 26(3):289-299.
- ↑ Miller JH, Miller KV (1999) Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.