Difference between revisions of "Sida cordifolia"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→Description) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''S. cordifolia'' is a shrub that grows up to 1.5 meters tall. Leaves are heart shaped, serrate and truncate. Flowers are small, yellow or white, solitary and axillaries. Seeds are grayish black and smooth<ref name="japsonline">[[http://japsonline.com/admin/php/uploads/16_pdf.pdf]]Accessed: March 15, 2016</ref> | + | ''S. cordifolia'' is a shrub that grows up to 1.5 meters tall. Leaves are heart shaped, serrate and truncate. Flowers are small, yellow or white, solitary and axillaries. Seeds are grayish black and smooth.<ref name="japsonline">[[http://japsonline.com/admin/php/uploads/16_pdf.pdf]]Accessed: March 15, 2016</ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 17:36, 18 August 2016
| Sida cordifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
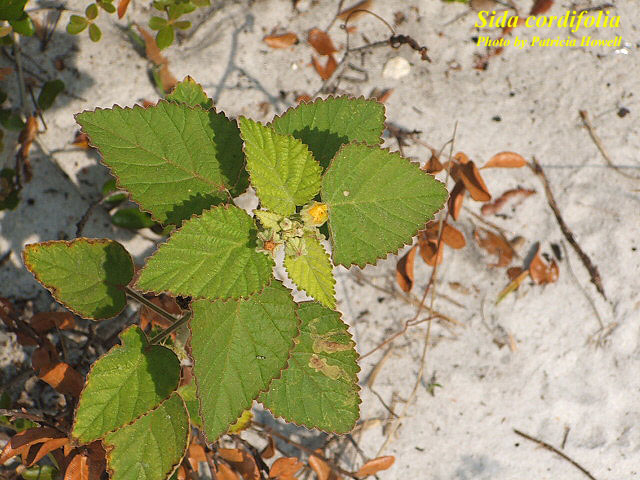
| Photo by Patricia Howell, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Malvales |
| Family: | Malvaceae |
| Genus: | Sida |
| Species: | S. cordifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Sida cordifolia L. | |
| |
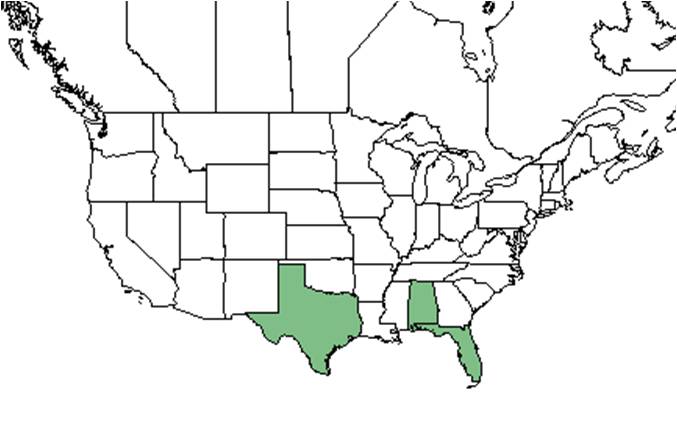
| Natural range of Sida cordifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: ‘ilima
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
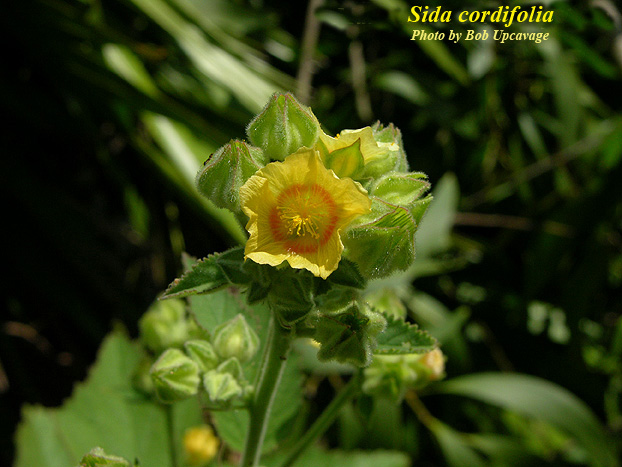
S. cordifolia is a shrub that grows up to 1.5 meters tall. Leaves are heart shaped, serrate and truncate. Flowers are small, yellow or white, solitary and axillaries. Seeds are grayish black and smooth.[1]
Distribution
It is a Native of India, however, it is also found in Florida, Alabama, and Texas[1].
Ecology
Habitat
Grows in damp climates and in waste areas[1].
Phenology
Flowers from August to December, fruits October to January[1].
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Sida cordifolia at Archbold Biological Station: [2]
Apidae: Apis mellifera
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochloropsis metallica, Lasioglossum pectoralis, L. placidensis, L. tamiamensis
Megachilidae: Anthidiellum notatum rufomaculatum, Anthidium maculifrons, Coelioxys mexicana, Megachile albitarsis, M. texana
Pompilidae: Ageniella faceta ventralis
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
S. cordifolia is highly recognized for its medicinal properties: it contains ephedrine, vasicinol, vasicinone, and N-methyl tryptophan. Traditional medicine has used it to treat chronic dysentery, and asthma[3].
Photo Gallery
Flowers of Sida cordifolia Photo by Bob Upcavage, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 [[1]]Accessed: March 15, 2016
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Sivanesan, I. and B. R. Jeong (2007). "Direct Shoot Regeneration from Nodal Explants of Sida Cordifolia Linn." In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology. Plant 43(5): 436-441.
