Difference between revisions of "Bejaria racemosa"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
Flowers are white with a pink tinge with black, sticky dehiscent fruit <ref name="IFAS"/> <ref name=FNPS>[[http://www.fnps.org/plants/plant/bejaria-racemosa Florida Native Plant Society]]Accessed December 2, 2015</ref>. It has been observed flowering and fruiting May through August (FSU Herbarium). | Flowers are white with a pink tinge with black, sticky dehiscent fruit <ref name="IFAS"/> <ref name=FNPS>[[http://www.fnps.org/plants/plant/bejaria-racemosa Florida Native Plant Society]]Accessed December 2, 2015</ref>. It has been observed flowering and fruiting May through August (FSU Herbarium). | ||
| − | ===Seed dispersal=== | + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> |
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
For some species native to fire-prone habitats, chemicals in smoke may induce germination, signaling the seed that the environmental conditions are favorable for germination and growth (Lindon and Menges 2008). In a study done by Lindon and Menges (2008), they found that smoke exposure under five minutes did not effect the germination rate, however there was no germination for seeds exposed to smoke for more than five minutes. | For some species native to fire-prone habitats, chemicals in smoke may induce germination, signaling the seed that the environmental conditions are favorable for germination and growth (Lindon and Menges 2008). In a study done by Lindon and Menges (2008), they found that smoke exposure under five minutes did not effect the germination rate, however there was no germination for seeds exposed to smoke for more than five minutes. | ||
| − | + | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | |
| − | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Bejaria racemosa'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Bejaria racemosa'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | ||
| Line 55: | Line 53: | ||
Vespidae: ''Euodynerus boscii boharti, Monobia quadridens, Parancistrocerus histrio, P. salcularis rufulus, Pseudodynerus quadrisectus, Stenodynerus fundatiformis, Zethus spinipes'' | Vespidae: ''Euodynerus boscii boharti, Monobia quadridens, Parancistrocerus histrio, P. salcularis rufulus, Pseudodynerus quadrisectus, Stenodynerus fundatiformis, Zethus spinipes'' | ||
| − | + | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | |
| − | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
| − | ===Diseases and parasites=== | + | <!--==Conservation and Management==--> |
| − | ==Conservation and Management== | + | <!--==Cultivation and restoration==--> |
| − | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Revision as of 18:37, 19 January 2016
| Bejaria racemosa | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Michelle Smith at Archbold Biological Station | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Bejaria |
| Species: | B. racemosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Bejaria racemosa Vent. | |
| |
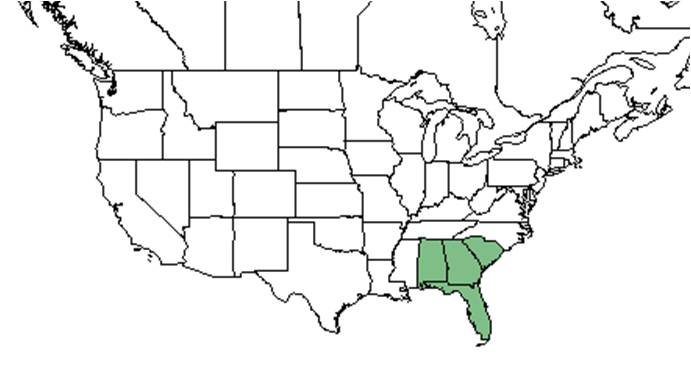
| Natural range of Bejaria racemosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: flyweed
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Befaria racemosa
Description
A description of Bejaria racemosa is provided in The Flora of North America.
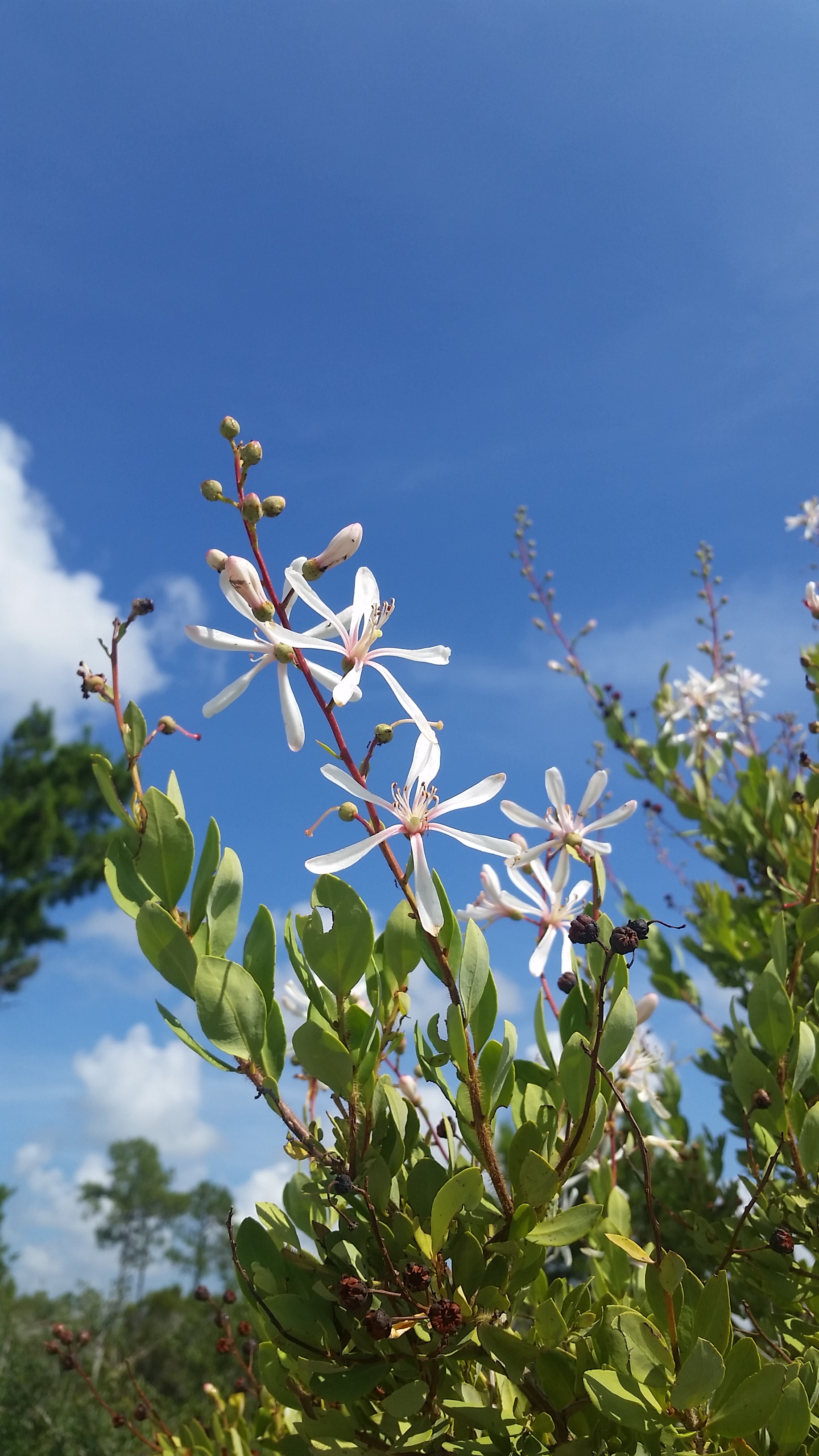
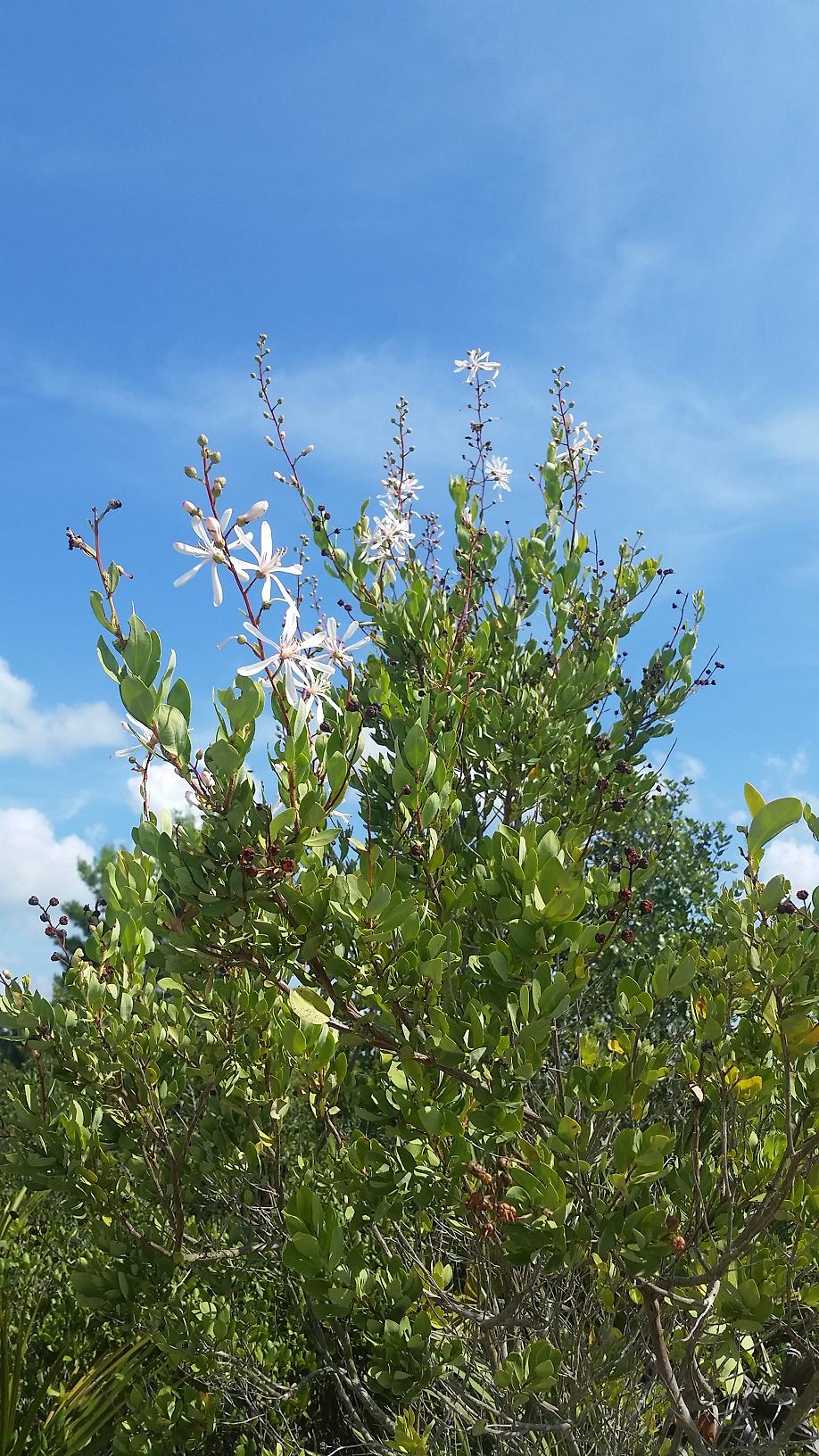
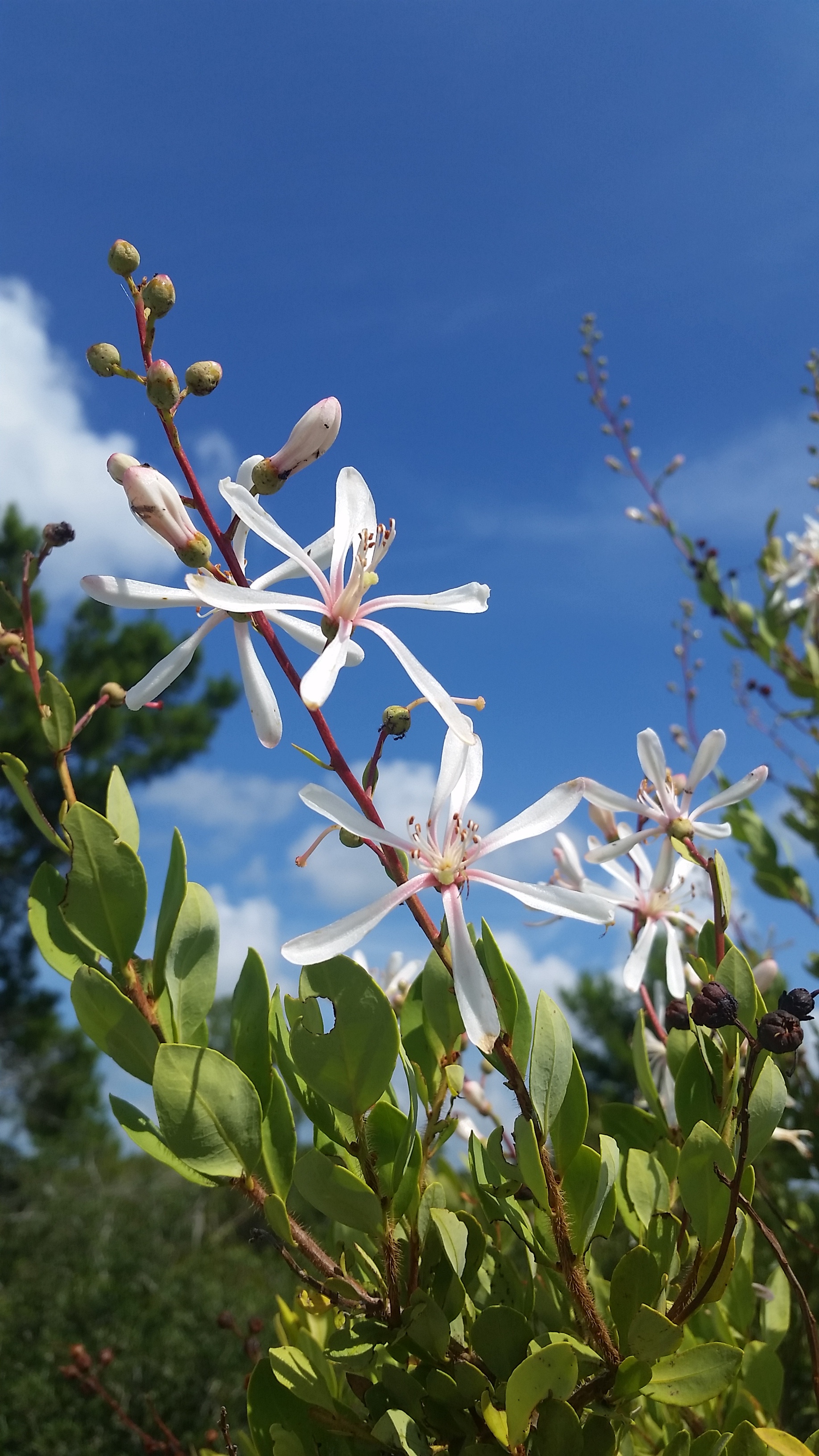
B. racemosa is a long live perennial shrub with leaves that are alternate, entire and coriaceous. The leaves and stems are covered with rough, firm, and stiff hairs [1]. It grows around 2 to 5 feet high and has large white flowers tinged pink. A viscid sticky substance that entraps insects is secreted on the stem below the flower (Webster 1893).
Species in the genus Bejaria have separate petals, radial symmetry, open rotate flowers, superior ovaries, and septicidal capsules; classifying them as the most primitive genus in Ericaceae (Kron 1997)
Distribution
It is a native to southeast Georgia and throughout Florida, except in the western panhandle and the keys [2].
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, B. racemosa has been found in pine flatwoods, scrub barrens, and sand pine scrubs (FSU Herbarium). It is drought tolerant and is found on well drained sandy soils in full sun to light shade [3]. Associated species include Callicarpa americana, Ceratiola ericoides, Rhus copallinum, slash pine, wax myrtle, and saw palmetto [2].
Phenology
Flowers are white with a pink tinge with black, sticky dehiscent fruit [2] [4]. It has been observed flowering and fruiting May through August (FSU Herbarium).
Seed bank and germination
For some species native to fire-prone habitats, chemicals in smoke may induce germination, signaling the seed that the environmental conditions are favorable for germination and growth (Lindon and Menges 2008). In a study done by Lindon and Menges (2008), they found that smoke exposure under five minutes did not effect the germination rate, however there was no germination for seeds exposed to smoke for more than five minutes.
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Bejaria racemosa at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens, B. pennsylvanicus
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlorella aurata, A. gratiosa, Augochloropsis sumptuosa
Megachilidae: Anthidiellum perplexum, Anthidium maculifrons, Coelioxys sayi, Megachile brevis pseudobrevis, M. mendica, M. petulans
Vespidae: Euodynerus boscii boharti, Monobia quadridens, Parancistrocerus histrio, P. salcularis rufulus, Pseudodynerus quadrisectus, Stenodynerus fundatiformis, Zethus spinipes
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Michael B. Brooks, R.K. Godfrey, R. Kral, Sidney McDaniel, Jean W. Wooten. States and Counties: Florida: Dixie, Highlands, Palm Beach, St. Johns. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Kron, Kathleen A.. Phylogenetic Relationships of Rhododendroideae (Ericaceae). American Journal of Botany 84.7 (1997): 973–980.
Lindon, H. L. and E. Menges (2008). "Scientific note: effects of smoke on seed germination of twenty species of fire-prone habitats in Florida." Castanea 73: 106-110.
Webster, G. W.. Insectivorous Plants of South Florida. Science 22.546 (1893): 37–38.
- ↑ [IFAS Extension] Accessed: December 2, 2015
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 [IFAS Extension] Accessed: December 2, 2015
- ↑ [Natives for your neighborhood] Accessed: December 2, 2015.
- ↑ [Florida Native Plant Society]Accessed December 2, 2015

