Difference between revisions of "Hypoxis juncea"
(Created page with "{{italic title}} <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> {{taxobox | name = Hypoxis juncea | image = Insert.jpg | image_caption = | regnum = Plant...") |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | It is a dry flatwoods/ sandhill species.<ref name="Glitzenstein et al 2003">Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, et al. (2003). "Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (Pinus palustris, P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA." Natural Areas Journal 23: 22-37.</ref> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | H. juncea appeared to have benefited from high fire frequencies in a study in 2003.<ref name="Glitzenstein et al 2003"/> Observed H. juncea respouting at least 10 days after a fire that occurred in June of 1993.<ref>Pavon, M. L. (1995). Diversity and response of ground cover arthropod communities to different seasonal burns in longleaf pine forests. Tallahassee, Florida A&M University.</ref> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| + | Deyrup observed this bee, Dialictus nymnphalis, on H. juncea.<ref>Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).</ref> “…Hypoxis is one of the most important plants for quail, which occurred (resprouted) in the ranking only the first 1 or 2 months after fire.<ref>Hughes, R. H. (1975). The native vegetation in south Florida related to month of burning. Asheville, NC, USDA Forest Service.</ref> | ||
===Diseases and parasites=== | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
| + | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 17:07, 11 June 2015
| Hypoxis juncea | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Liliaceae |
| Genus: | Hypoxis |
| Species: | H. juncea |
| Binomial name | |
| Hypoxis juncea Sm. | |
| |
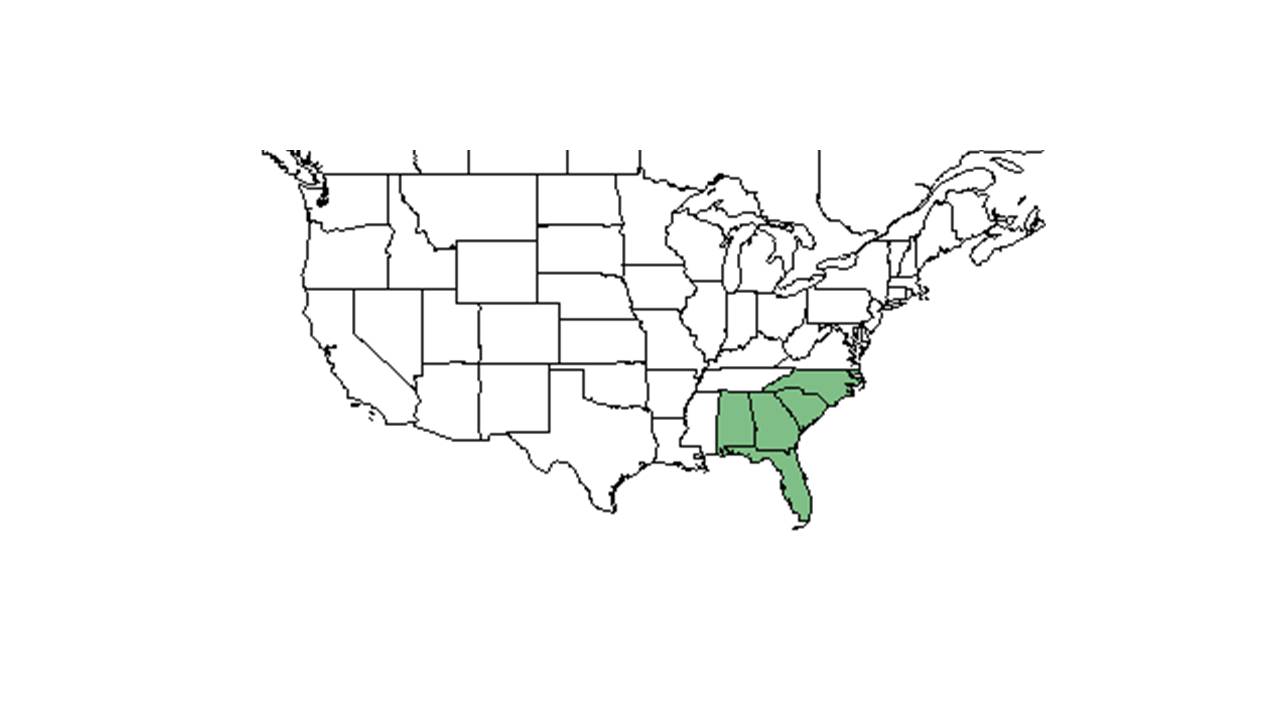
| Natural range of Hypoxis juncea from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It is a dry flatwoods/ sandhill species.[1]
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
H. juncea appeared to have benefited from high fire frequencies in a study in 2003.[1] Observed H. juncea respouting at least 10 days after a fire that occurred in June of 1993.[2]
Pollination
Use by animals
Deyrup observed this bee, Dialictus nymnphalis, on H. juncea.[3] “…Hypoxis is one of the most important plants for quail, which occurred (resprouted) in the ranking only the first 1 or 2 months after fire.[4]
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, et al. (2003). "Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (Pinus palustris, P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA." Natural Areas Journal 23: 22-37.
- ↑ Pavon, M. L. (1995). Diversity and response of ground cover arthropod communities to different seasonal burns in longleaf pine forests. Tallahassee, Florida A&M University.
- ↑ Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).
- ↑ Hughes, R. H. (1975). The native vegetation in south Florida related to month of burning. Asheville, NC, USDA Forest Service.