Difference between revisions of "Warea carteri"
(→Photo Gallery) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| name = Warea carteri | | name = Warea carteri | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image = Ware_cart.jpg |
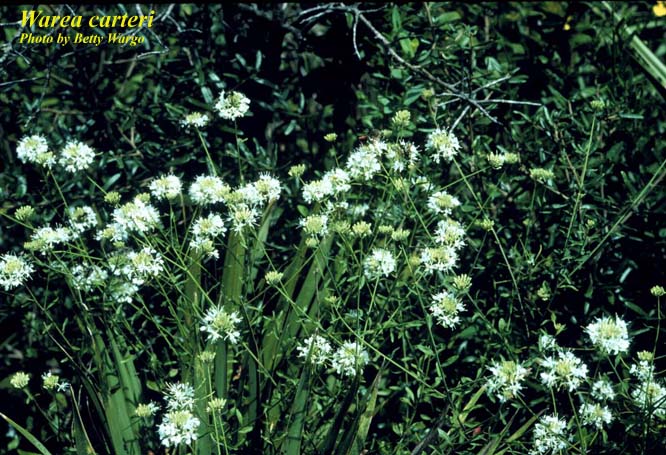
| − | | image_caption = | + | | image_caption = Photo by Betty Wargo, [http://www.florida.plantatlas.usf.edu/Default.aspx Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants] |
| regnum = Plantae | | regnum = Plantae | ||
| divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | | divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common | + | Common names: Carter's pineland-cress, Carter's mustard, Carter's warea |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | ''Warea carteri'' is most similar to ''Warea cuneifolia''. It differs by having a stronger pubescence of its petal claws and always having a white corolla. And it is geographically distinct from ''Warea cuneifolia''.<ref name="natureserve"> [[http://explorer.natureserve.org/servlet/NatureServe?searchName=Warea+carteri]] Nature Serve. Accessed: March 22, 2016.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | The only known populations are in the scrub habitats of the Lake Wales Ridge in Lake, Polk, and Highlands County, Florida.<ref name="SMS"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''W. carteri'' occurs in sand scrub, Quercus laevis | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''W. carteri'' occurs in sand scrub, Quercus laevis- ''Serenoa repens'' communities.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: W.P. Adams, Walter M. Buswell. States and Counties: Florida: Dade, Highlands. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> This species is endemic to south and central Florida and is found in sandhill, scrubby flatwoods, inland and coastal scrub habitats.<ref name="FNAI2000"> [[http://www.fnai.org/FieldGuide/pdf/Warea_carteri.pdf]] FNAI 2000. Accessed: March 22, 2016.</ref> The only known populations are in the scrub habitats of the Lake Wales Ridge in Lake, Polk, and Highlands County, Florida. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service considers ''W. carteri'' to be extirpated in Brevard and Miami-Dave County, Florida. Is commonly found in or near yellow sands. It is also seen in human disturbed areas such as ditches and roadsides.<ref name="SMS"> [[http://www.sms.si.edu/irlspec/Warea_carteri.htm]] Smithsonian Marine Station at Fort Pierce. Accessed: March 22, 2016.</ref> The soil ''Warea'' is found in is nutrient poor, moderately to extremely well drained upland oils.<ref name=”Weekley2007”> Weekley, Carl W., Eric S. Menges, and Pedro F. Quintana-Ascencio (2007). “Seedling emergence and survival of Warea carteri (Brassicaceae), an endangered annual herb of the Florida Scrub”. Canada Journal of Botany. Vol 85: 621-628</ref> This ''Warea'' species tends to grow in full sunlight or light shade areas. |
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''Pinus clausa, P. palustris, P. elliottii, Quercus laevis, Q. incana, Q geminate, Q. myrtifolia, Q. chapmanii, Carya floridana, Bumelia tenax, Asimina ob ovata, Chionanthus, Lyonia ferruginea, Ilex ambigua,'' and ''Serenoa repens''.<ref name="Kral1983"/> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | Flowers and fruits in November | + | Flowers and fruits in November.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> ''Warea carteri'' seems to be inconspicuous when not in flower.<ref name="SMS"/> Interesting phenology on Archbold’s website on ''Warea carteri'' states that “seedlings often remain as rosettes throughout the dry fall-spring season. Seedling mortality is generally highest late in the dry season (Apr-May). Plants that survive the spring drought typically bolt, often doubling in height from month to month. However, there appears to be considerable temporal and spatial variation in growth rates, perhaps having to do with differences in annual rainfall or in microhabitat. For example, seedlings recruiting in shadier microsites seem to elongate sooner than those in sunnier microsites”.<ref name=”ABSwarea”> [[http://www.archbold-station.org/html/research/plant/warcarsppacc.html]] Archbold Biological Station Warea carteri. Accessed: March 22, 2016.</ref> |
| + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
| − | |||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| + | Historically, there were over 200 known patches of ''Warea carteri'' on the Lake Wales Ridge but most of the area has been destroyed and converted into citrus groves and residential areas. ''W. carteri'' has large population fluctuations associated with fire, such as the population increases a year after a fire and then population decreases the following year. The character of these population fluctuations suggest that seed banks are present. The fruit and seed structures do not have any special characteristics to aid in dispersal. This species can reproduce via selfing (autogamy) which allows contributions to the seed bank after a fire occurs.<ref name=" | ||
| + | Evans2000"> Evans, Margaret E. Rebecca W. Dolan, Eric S. Menges, and Doria R. Gordon (2000). “Genetic diversity and reproductive biology in Warea carteri (Brassicaceae), a narrowly endemic Florida scrub annual”. American Journal of Botany, Vol. 87, No. 3: 372-381.</ref> Seed germination requires moisture and light, flowering is observed from September to October, fruiting is observed from October through November, and seed dispersal occurs in December.<ref name="Kral1983"> Kral, Robert (1983). “A Report on some rare, threatened, or endangered forest-related vascular plants of the south. Volume 1 Isoetaceae through Eurphorbiaceae. Pages 537-538.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | This species only appears after fire.<ref name="FNAI2000"/> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | + | Sweat bees such as ''Augochlorella aurata'' and ''Lasioglossum placidensis'' (family Halictidae), thread-waisted wasps such as ''Ectemnius rufipes ais'' and ''Isodontia exornata'' (family Sphecidae) and wasps such as ''Zethus slossonae'' (family Vespidae) were observed visiting flowers of ''Warea carteri'' at the Archbold Biological Station:<ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | |
| − | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology=== <!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc.--> | |
| − | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | |
| + | It has been listed federally as an endangered since January 21, 1987 due to habitat loss and fire suppression.<ref name="SMS"/> This species is endangered in Florida. To protect this species, land needs to be purchased or a conservation easement needs to be acquired for privately owned sandhill or scrub habitat. Manage these sites with prescribed fires and prevent trampling of habitat. Also eradicate invasive species in the area.<ref name="FNAI2000"/> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
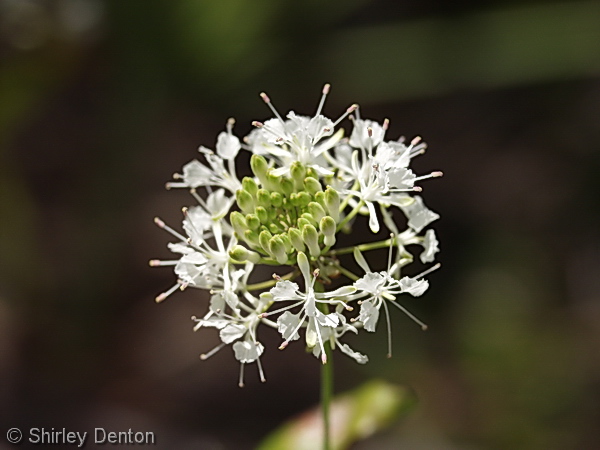
| + | File: Ware_carti_SDenton_NatPhotoflower3.jpg | <center> Flowers of ''Warea'' ''carteri'' <p> Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), [http://www.shirleydenton.com/welcome Nature Photography by Shirley Denton] </p> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 13:29, 18 July 2022
| Warea carteri | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Betty Wargo, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Capparales |
| Family: | Brassicaceae ⁄ Cruciferae |
| Genus: | Warea |
| Species: | W. carteri |
| Binomial name | |
| Warea carteri Small | |
| |
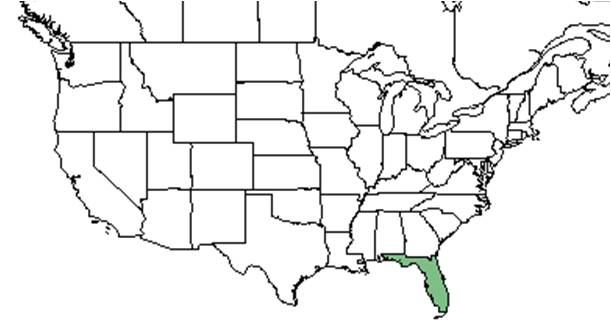
| Natural range of Warea carteri from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Carter's pineland-cress, Carter's mustard, Carter's warea
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Warea carteri is most similar to Warea cuneifolia. It differs by having a stronger pubescence of its petal claws and always having a white corolla. And it is geographically distinct from Warea cuneifolia.[1]
Description
A description of Warea carteri is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
The only known populations are in the scrub habitats of the Lake Wales Ridge in Lake, Polk, and Highlands County, Florida.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, W. carteri occurs in sand scrub, Quercus laevis- Serenoa repens communities.[3] This species is endemic to south and central Florida and is found in sandhill, scrubby flatwoods, inland and coastal scrub habitats.[4] The only known populations are in the scrub habitats of the Lake Wales Ridge in Lake, Polk, and Highlands County, Florida. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service considers W. carteri to be extirpated in Brevard and Miami-Dave County, Florida. Is commonly found in or near yellow sands. It is also seen in human disturbed areas such as ditches and roadsides.[2] The soil Warea is found in is nutrient poor, moderately to extremely well drained upland oils.[5] This Warea species tends to grow in full sunlight or light shade areas.
Associated species include Pinus clausa, P. palustris, P. elliottii, Quercus laevis, Q. incana, Q geminate, Q. myrtifolia, Q. chapmanii, Carya floridana, Bumelia tenax, Asimina ob ovata, Chionanthus, Lyonia ferruginea, Ilex ambigua, and Serenoa repens.[6]
Phenology
Flowers and fruits in November.[3][7] Warea carteri seems to be inconspicuous when not in flower.[2] Interesting phenology on Archbold’s website on Warea carteri states that “seedlings often remain as rosettes throughout the dry fall-spring season. Seedling mortality is generally highest late in the dry season (Apr-May). Plants that survive the spring drought typically bolt, often doubling in height from month to month. However, there appears to be considerable temporal and spatial variation in growth rates, perhaps having to do with differences in annual rainfall or in microhabitat. For example, seedlings recruiting in shadier microsites seem to elongate sooner than those in sunnier microsites”.[8]
Seed bank and germination
Historically, there were over 200 known patches of Warea carteri on the Lake Wales Ridge but most of the area has been destroyed and converted into citrus groves and residential areas. W. carteri has large population fluctuations associated with fire, such as the population increases a year after a fire and then population decreases the following year. The character of these population fluctuations suggest that seed banks are present. The fruit and seed structures do not have any special characteristics to aid in dispersal. This species can reproduce via selfing (autogamy) which allows contributions to the seed bank after a fire occurs.[9] Seed germination requires moisture and light, flowering is observed from September to October, fruiting is observed from October through November, and seed dispersal occurs in December.[6]
Fire ecology
This species only appears after fire.[4]
Pollination
Sweat bees such as Augochlorella aurata and Lasioglossum placidensis (family Halictidae), thread-waisted wasps such as Ectemnius rufipes ais and Isodontia exornata (family Sphecidae) and wasps such as Zethus slossonae (family Vespidae) were observed visiting flowers of Warea carteri at the Archbold Biological Station:[10]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
It has been listed federally as an endangered since January 21, 1987 due to habitat loss and fire suppression.[2] This species is endangered in Florida. To protect this species, land needs to be purchased or a conservation easement needs to be acquired for privately owned sandhill or scrub habitat. Manage these sites with prescribed fires and prevent trampling of habitat. Also eradicate invasive species in the area.[4]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
Flowers of Warea carteri Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), Nature Photography by Shirley Denton
References and notes
- ↑ [[1]] Nature Serve. Accessed: March 22, 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 [[2]] Smithsonian Marine Station at Fort Pierce. Accessed: March 22, 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: W.P. Adams, Walter M. Buswell. States and Counties: Florida: Dade, Highlands. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 [[3]] FNAI 2000. Accessed: March 22, 2016.
- ↑ Weekley, Carl W., Eric S. Menges, and Pedro F. Quintana-Ascencio (2007). “Seedling emergence and survival of Warea carteri (Brassicaceae), an endangered annual herb of the Florida Scrub”. Canada Journal of Botany. Vol 85: 621-628
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Kral, Robert (1983). “A Report on some rare, threatened, or endangered forest-related vascular plants of the south. Volume 1 Isoetaceae through Eurphorbiaceae. Pages 537-538.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021
- ↑ [[4]] Archbold Biological Station Warea carteri. Accessed: March 22, 2016.
- ↑ Evans, Margaret E. Rebecca W. Dolan, Eric S. Menges, and Doria R. Gordon (2000). “Genetic diversity and reproductive biology in Warea carteri (Brassicaceae), a narrowly endemic Florida scrub annual”. American Journal of Botany, Vol. 87, No. 3: 372-381.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
