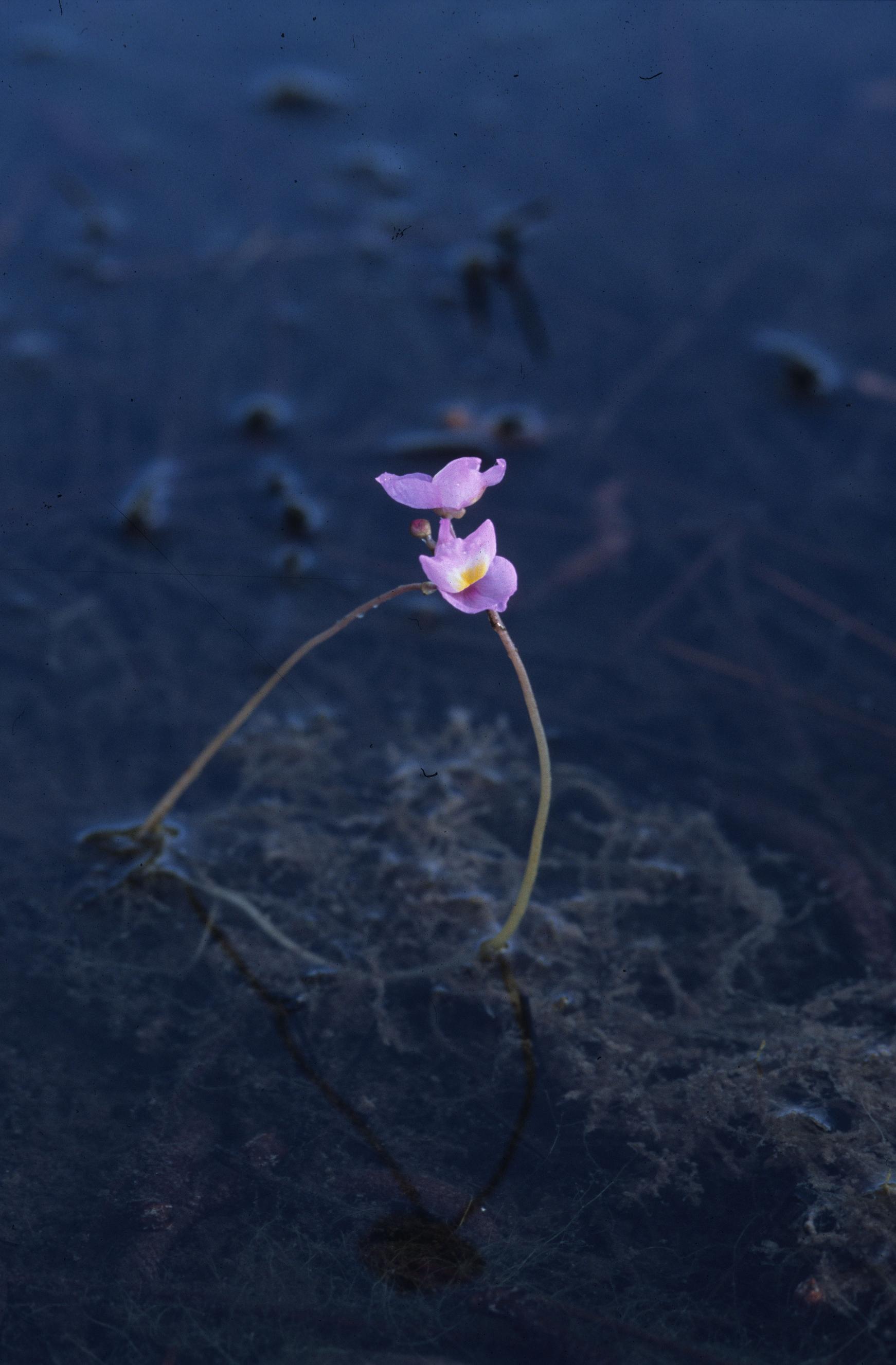
Utricularia purpurea
| Utricularia purpurea | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Lentibulariaceae |
| Genus: | Utricularia |
| Species: | U. purpurea |
| Binomial name | |
| Utricularia purpurea Walter | |
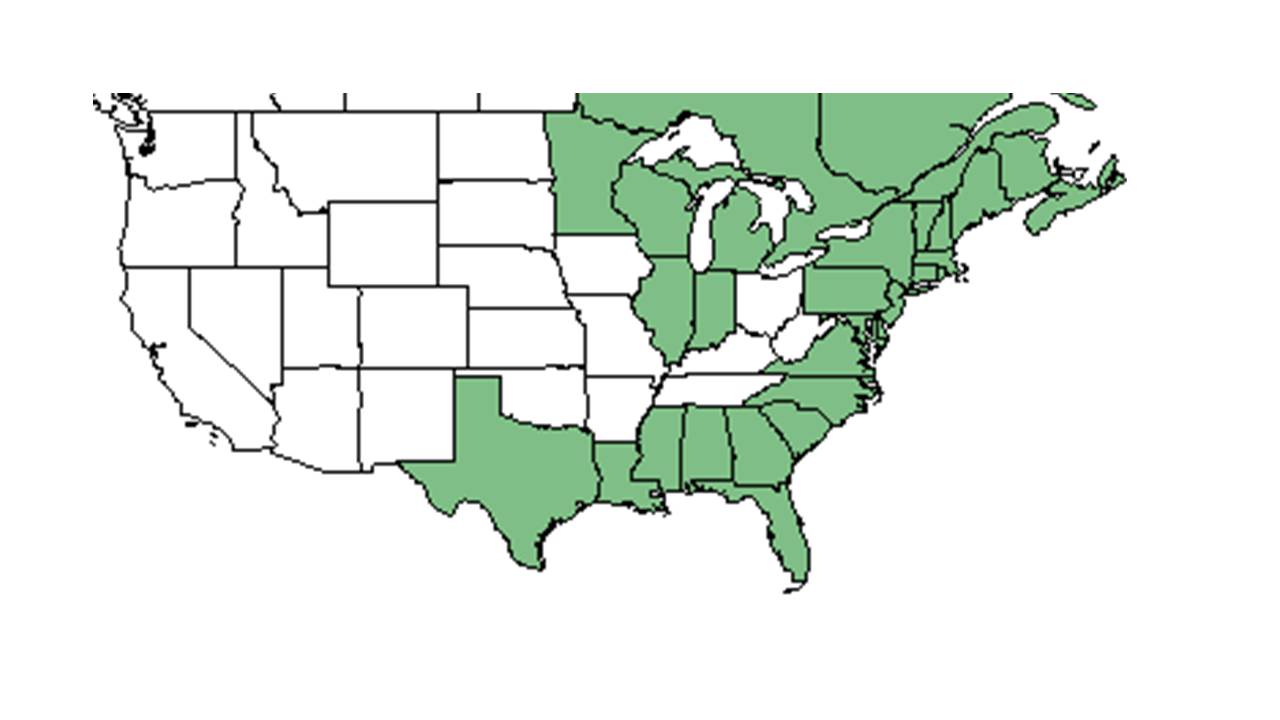
| |
| Natural range of Utricularia purpurea from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: eastern purple bladderwort
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
"Herbaceous aquatic or bog plants with bladders; stems submersed or subterranean, frequently capillary. Leaves alternate or whorled, rarely opposite, dissected or forked into filiform segments or linear when surficial. Scapes elongate, to 5 dm tall, 1-20 flowered; bract solitary at base of pedicel, bractlets paired with present, usually absent; pedicels 0.5-3 cm long. Calyx 2-lobed or lipped, upper lip entire or 2-lobed, lower lip usually 3-lobed, elevated inside as a palate and prolonged as a spur or sac. Capsules brown, globose; seeds usually numerous, brown or yellow." - Radford et al 1964
"Plant floating, branches whorled. Leaves whorled or opposite, segments frequently terminating in bladders. Scapes 5-9 cm tall, 1-3 flowered; bracts sessile, 1.5-3 mm long; pedicels spreading-ascending, 6-15 mm long. Calyx ca. 2.5 mm long, larger lobes ca. 2 mm long; corolla purple, 9-12 mm long, spur 3-5 mm long. Capsules 3-3.6 mm in diam.; seeds round, echinate or irregularly cristate, ca. 0.5 mm in diam." - Radford et al 1964
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Utricularia purpurea can be found entirely under water and frequent with Utricularia foliosa and Nymphaea (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowering has been observed April through November and fruiting April through September (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
carnivorous plant – bladderwort (Hermann 1995).
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey, Richard S. Mitchell, Annette Mitchell, Robert Kral, Loran C. Anderson, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., W. P. Adams, Grady W. Reinert, John B. Nelson, Kathy Craddock Burks, Elmer C. Prichard, M. R. Vodicka, Ted Bradley, J Stevenson, R. M. Schuster, Harry E. Ahles, J. Haesloop, D. B. Ward, S. S. Ward, Jean W. Wooten, D E Harrison, F Henry, Joel A. Barnes, Wilson Baker, Ann Johnson, N. Hotchkiss, Cecil R Slaughter, Palmer Kinser, Joe Beck. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Collier, Franklin, Gulf, Hamilton, Highlands, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Orange, Osceola, Palm Beach, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla, Walton. Georgia: Grady, Thomas, Ware. Michigan: Schoolcraft. Mississippi: Jackson. New Hampshire: Grafton. North Carolina: Brunswick. South Carolina: Orangeburg. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Hermann, S. M. (1995). Status and management of Florida's carnivorous plant communities. Tallahassee, Florida Game and Fresh Water Fish Commission, Nongame Wildlife Program.