Difference between revisions of "Stillingia sylvatica"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | It can be found in sandhill communities (Stamp and Lucas 1990). Included in study where the area was a mixed stand of slash and longleaf pine where soils are mainly sandy, siliceous, hypothermic ''Ultic haplaquod'' of the Pomona series (Moore et al 1982). | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
Revision as of 15:59, 17 June 2015
| Stillingia sylvatica | |
|---|---|

| |
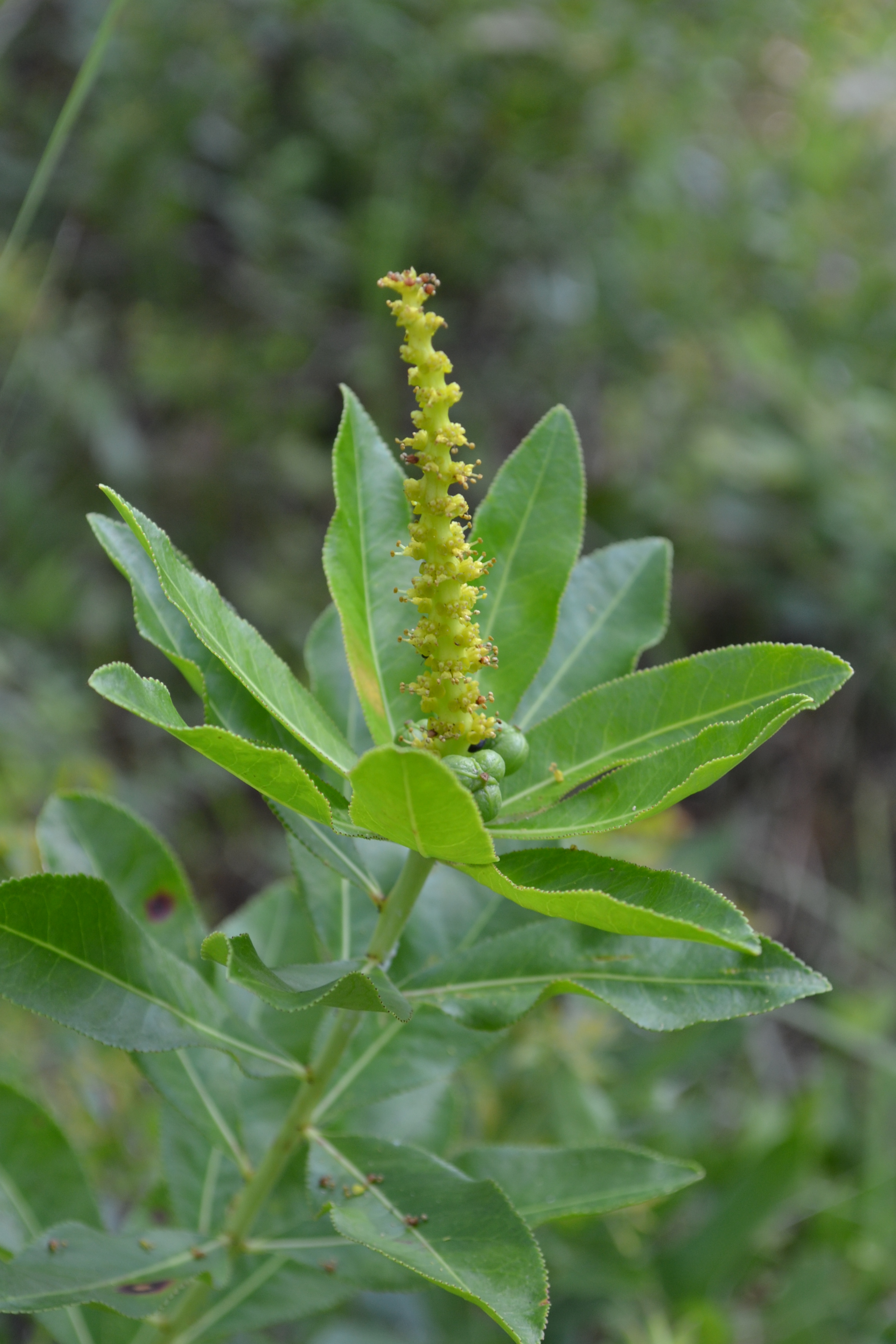
| Photo taken by Michelle M. Smith | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Stillingia |
| Species: | S. sylvatica |
| Binomial name | |
| Stillingia sylvatica L. | |
| |
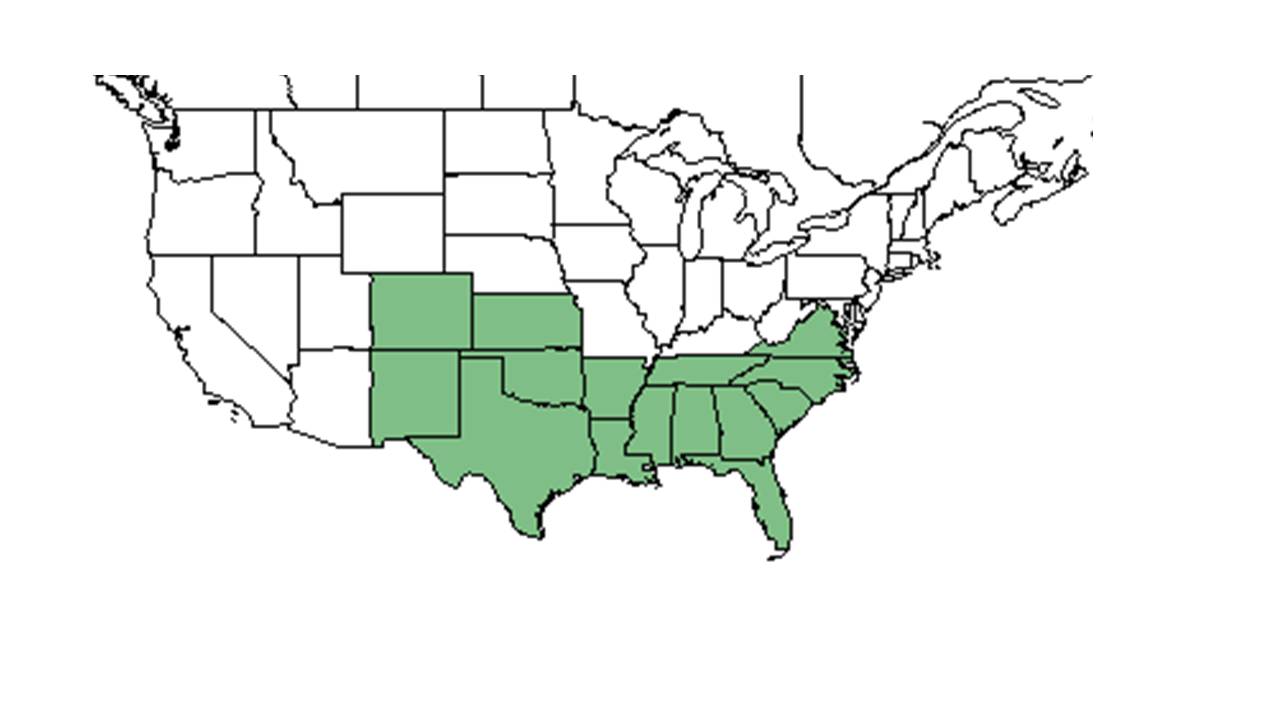
| Natural range of Stillingia sylvatica from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It can be found in sandhill communities (Stamp and Lucas 1990). Included in study where the area was a mixed stand of slash and longleaf pine where soils are mainly sandy, siliceous, hypothermic Ultic haplaquod of the Pomona series (Moore et al 1982).
Phenology
Seed dispersal
It is dispersed explosively (up to 3 meters); seeds are forcefully expelled after the fruit matures and dries. It can also be dispersed by ants (Stamp and Lucas 1990).
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It seems to respond positively to burning. In an experiment by Greenberg, he noted that the percent cover of S. sylvatica was highest 16 months after a May burn (2003).
Pollination
Use by animals
Because S. sylvatica seeds contain elaiosomes, they are collected by ants (Stamp and Lucas 1990). “Seeds were found in middens of harvester-ant nests of Pogonomyremex badius Latreille. In addition, seeds of all three plant species were observed being carried into the ant nests and then later deposited uneaten at the nest perimeter.” – Stamp and Lucas 1990.