Difference between revisions of "Solidago altissima"
(→Seed dispersal) |
m (→Seed dispersal) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
Initial colonization occurs from seeds producing genets. Once established, increases within the population should occur via the production of ramets (clonal growth) according to a model.<ref name="Eriksson 1993">Eriksson O (1993) Dynamics of genets in clonal plants. Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 8(9):313-316.</ref> | Initial colonization occurs from seeds producing genets. Once established, increases within the population should occur via the production of ramets (clonal growth) according to a model.<ref name="Eriksson 1993">Eriksson O (1993) Dynamics of genets in clonal plants. Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 8(9):313-316.</ref> | ||
| − | ===Seed bank and germination=== | + | ===Seed bank and germination=== |
Seed set of ''S. altissima'' was 22-25.2% in a study by the University of Kentucky. | Seed set of ''S. altissima'' was 22-25.2% in a study by the University of Kentucky. | ||
Revision as of 12:18, 19 January 2018
| Solidago altissima | |
|---|---|
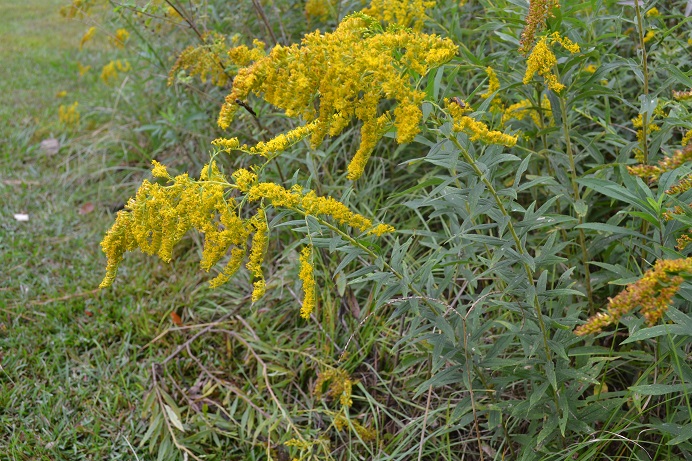

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Solidago |
| Species: | S. altissima |
| Binomial name | |
| Solidago altissima L. | |
| |
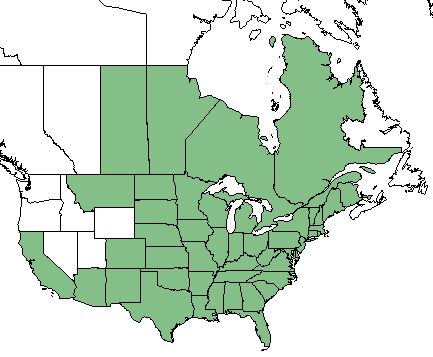
| Natural range of Solidago altissima from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): tall goldenrod; Great Plains tall goldenrod; southern tall goldenrod;[1] Canada goldenrod;[2] Canadian goldenrod; late goldenrod[3]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Varieties: S. altissima var. altissima; S. altissima var. pluricephala;[1][2] S. altissima var. gilvocanescens;[1] S. altissima var. procera[2]
Synonym(s): S. canadensis var. scabra; S. hirsutissima;[1][2] S. pruinosa; S. canadensis var. gilvocanescens;[1] S. lunellii[2]
Description
Solidago altissima is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.[2] This plant is rough, erect, and produces small yellow flowers that are arranged along upper side of branches, producing a plume. It reaches heights of 3-6 ft (0.91-1.83 m)[3] and forms large compact below-ground rhizome systems.[4]
Distribution
This species is found in all of the lower 48 United States, excluding Washington, Oregon, Nevada, Utah, Idaho, and Wyoming. It also occurs in the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan, Manitoba, Ontario, Quebec, and New Brunswick.[2] S. altissima is also an exotic invasive in Europe (as cited in [4]).
Ecology
Habitat
S. altissima is found in roadsides,[1][3] fields, disturbed areas,[1] thickets, prairies, open woods,[3] stream banks, and marshes.[5] It prefers moist to dry soils composed of clay, clay loam, medium loam, sandy loam, sandy and caliche.[3] In a Wisconsin Prairie, the frequency in 1951 was 32 and in 1961 was 48.[6] Also on Wisconsin prairies, aboveground biomass from 1987-1993 averaged 838.4 ± 92.8 g m-2 and mean percent cover ranging from 14.2-29.3% depending upon the fire regime.[7]
Phenology
Flowering occurs from August through November.[1][8]
Seed dispersal
Initial colonization occurs from seeds producing genets. Once established, increases within the population should occur via the production of ramets (clonal growth) according to a model.[9]
Seed bank and germination
Seed set of S. altissima was 22-25.2% in a study by the University of Kentucky.
Fire ecology
On a Wisconsin tallgrass prairie, two burn cycles of a 3 year interval showed increases in cover during spring and summer burns. However, an increase in cover also occurred on unburned sites, suggesting the burn cycle did not negatively affect S. altissima cover but may not be responsible for the increase.[7]
Pollination
S. altissima attracts birds, butterflies, and a large number of native bees.[3]
Use by animals
S. altissima responds to insect herbivory by spending energy to maintain itself, rather than producing seeds.[10] There are at least 103 species of insect herbivores of S. altissima, 42 (from 17 families) are specialists on Solidagospp.[11]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 118 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Plant database: Solidago altissima. (18 January 2018) Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=SOAL6
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Meyer AH, Schmid B (1999) Experimental demography of rhizome populations of establishing clones of Solidago altissima. Journal of Ecology 87(1):42-54. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Meyer & Schmid 1999" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Bostick PE (1971) Vascular plants of Panola Mountain, Georgia. Castanea 36(3):194-209.
- ↑ Anderson RC (1973) The use of fire as a management tool on the Curtis Prairie. Proceedings Annual [12th] Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: a quest for ecological understanding. Lubbock, TX pg 23-35.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Howe HF (1995) Succession and fire season in experimental prairie plantings. Ecology 76(6):1917-1925.
- ↑ Nelson G (18 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/
- ↑ Eriksson O (1993) Dynamics of genets in clonal plants. Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 8(9):313-316.
- ↑ Root RB (1996) Herbivore pressure on goldenrods (Solidago altissima): Its variation and cumulative effects. Ecology 77(4):1074-1087.
- ↑ Root RB & Cappuccino N (1992) Patterns in population change and the organization of the insect community associated with goldenrod. Ecological Monographs 62(3):393-420.