Difference between revisions of "Smilax rotundifolia"
(→Distribution) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| + | Leave and twigs of ''S. rotundifolia'' are known to have been consumed by the Florida marsh rabbit (''Sylvilagus palustris paludicola'').<ref name="Blair 1936">Blair WF (1936) The Florida marsh rabbit. Journal of Mammalogy 17(3):197-207. | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 16:23, 22 January 2018
| Smilax rotundifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Smilacaceae |
| Genus: | Smilax |
| Species: | S. rotundifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Smilax rotundifolia L. | |
| |
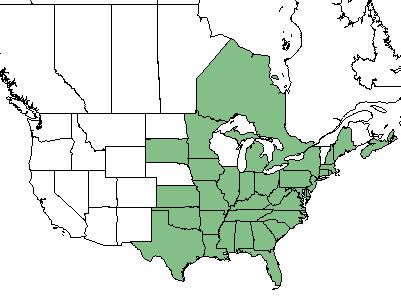
| Natural range of Smilax rotundifolia from USDA NRCS [1]. | |
Common Names: Common greenbriar; bullbriar; horsebriar[1]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Description
Distribution
The distribution of S. rotundifolia ranges from eastern Texas, westward to northern Florida, and northward into the provinces of Nova Scotia and Ontario Canada.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
S. rotundifolia is found in a variety of upland and wetland habitats.[1]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, S. rotundifolia flowers from April through May with fruiting occurring in September through November and persisting beyond.[1]
Use by animals
Leave and twigs of S. rotundifolia are known to have been consumed by the Florida marsh rabbit (Sylvilagus palustris paludicola).<ref name="Blair 1936">Blair WF (1936) The Florida marsh rabbit. Journal of Mammalogy 17(3):197-207.