Difference between revisions of "Scoparia dulcis"
(→Seed bank and germination) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
Found in seed banks of rosemary scrubs, pastures, and degraded scrub sites but not in above ground vegetation in south central Florida.<ref>Navarra, J. J. and P. F. Quintana-Ascencio 2012. Spatial pattern and composition of the Florida scrub seed bank and vegetation along an anthropegenic disturbance gradient. Applied Vegetation Science 15:349-358. </ref> | Found in seed banks of rosemary scrubs, pastures, and degraded scrub sites but not in above ground vegetation in south central Florida.<ref>Navarra, J. J. and P. F. Quintana-Ascencio 2012. Spatial pattern and composition of the Florida scrub seed bank and vegetation along an anthropegenic disturbance gradient. Applied Vegetation Science 15:349-358. </ref> | ||
| − | |||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| + | ===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> | ||
| + | ''Scoparia dulcis'' was observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host leafcutting bees such as ''Megachile albitarsis'' (family Megachilidae).<ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | ||
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Cultural use== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:04, 15 July 2022
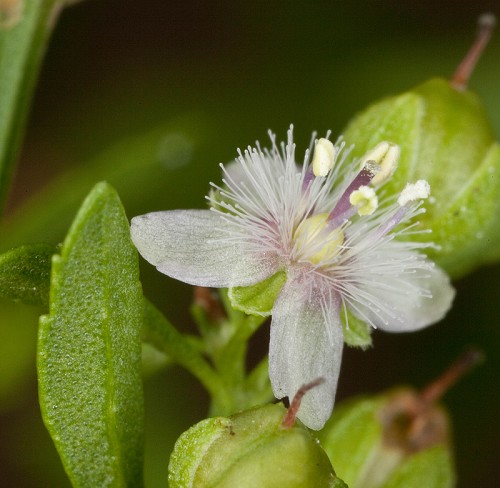
| Scoparia dulcis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Scrophulariaceae |
| Genus: | Scoparia |
| Species: | S. dulcis |
| Binomial name | |
| Scoparia dulcis L. | |
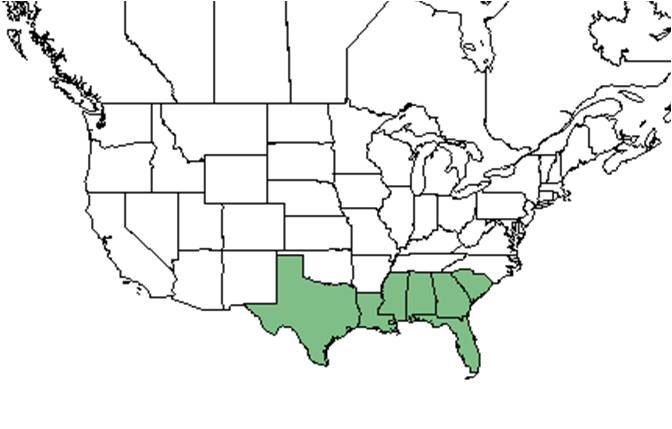
| |
| Natural range of Scoparia dulcis from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Licorice weed, Sweet-broom, Goat weed
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
It is a ruderal species.[1]
"Erect, profusely branched perennial, 3-8 dm tall, the stems pubescent. Especially about the nodes. Leaves glandular-punctate, opposite, ovate-lanceolate to rhombic-ovate, 1-3 cm long, 6-16 mm wide, the distal ½-2/3 serrate. Flowers axillary, usually solitary, pedicel shorter than the petiole of the subtending leaf; calyx 4-parted, 1.5-2 mm long, the lobes widely ovate to elliptic, equaling or much exceeding the tube; corolla 4-parted, white, rotate, regular, the throat lanose, lobes ca. 1 mm long; stamens 4. Capsule subglobose to widely ellipsoid, ca. 2 mm long or broad."[2]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, S. dulcis can occur in moist loam around ponds and bordering adjacent woodlands. It has been observed in disturbed sites such as waste areas, powerlines corridors, fallow fields, and the upper edge of a restored marshy area.[1]
Phenology
Seed bank and germination
Found in seed banks of rosemary scrubs, pastures, and degraded scrub sites but not in above ground vegetation in south central Florida.[3]
Herbivory and toxicology
Scoparia dulcis was observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host leafcutting bees such as Megachile albitarsis (family Megachilidae).[4]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
Flower of Scoparia dulcis Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Lisa Keppner, R. Komarek, Annie Schmidt, Cecil R. Slaughter. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty, Jefferson, St. Johns, Taylor, Washington. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 937. Print.
- ↑ Navarra, J. J. and P. F. Quintana-Ascencio 2012. Spatial pattern and composition of the Florida scrub seed bank and vegetation along an anthropegenic disturbance gradient. Applied Vegetation Science 15:349-358.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
