Difference between revisions of "Rhododendron minus"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common | + | Common names: Piedmont rhododendron, Gorge rhododendron |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: none | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: ''Rh. minus var. minus'' | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 31: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''R. minus'' occurs in sandhill and pine flatwoods communities, as well as the edges of titi bogs. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Gary Schultz, Loran C. Anderson, Angus Gholson, Rick Holden, Robert K. Godfrey, Ann M. Redmond, Mark A Garland, J. O. Boynton, H. R. Totten, Addie Totten, Steve Leonard, and W. D. Reese. States and Counties: Florida: Clay, Gadsden, Gulf, Leon, and Liberty.</ref> However, it can also be found in disturbed areas, including titi swamps in heavily logged pinewoods and slash pine plantations. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> Associated species include ''Serenoa repens, Ilex glabra, Lyonia ferrugunea, Ilex coriacea, Lyonia lucida, Cyrilla, Quercus nigra, Cliftonia, Rhododendron canescens, Vaccimum arobreum, Hamamelis virginica, Pinus elliottii, Illicium floridanum, Quercus pumila,Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Quercus chapmanii, Quercus geminata,'' and ''Magnolia grandiflora.'' <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | ''R. minus'' occurs in sandhill and pine flatwoods communities, as well as the edges of titi bogs.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Gary Schultz, Loran C. Anderson, Angus Gholson, Rick Holden, Robert K. Godfrey, Ann M. Redmond, Mark A Garland, J. O. Boynton, H. R. Totten, Addie Totten, Steve Leonard, and W. D. Reese. States and Counties: Florida: Clay, Gadsden, Gulf, Leon, and Liberty.</ref> However, it can also be found in disturbed areas, including titi swamps in heavily logged pinewoods and slash pine plantations.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''Serenoa repens, Ilex glabra, Lyonia ferrugunea, Ilex coriacea, Lyonia lucida, Cyrilla, Quercus nigra, Cliftonia, Rhododendron canescens, Vaccimum arobreum, Hamamelis virginica, Pinus elliottii, Illicium floridanum, Quercus pumila,Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Quercus chapmanii, Quercus geminata,'' and ''Magnolia grandiflora.''<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
| − | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: | + | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: ''R. minus'' has been observed flowering in March and April, and fruiting in March, April, and July.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 13 DEC 2016</ref> |
| − | |||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> |
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:06, 15 July 2022
| Rhododendron minus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Rhododendron |
| Species: | R. minus |
| Binomial name | |
| Rhododendron minus Michx. | |
| |
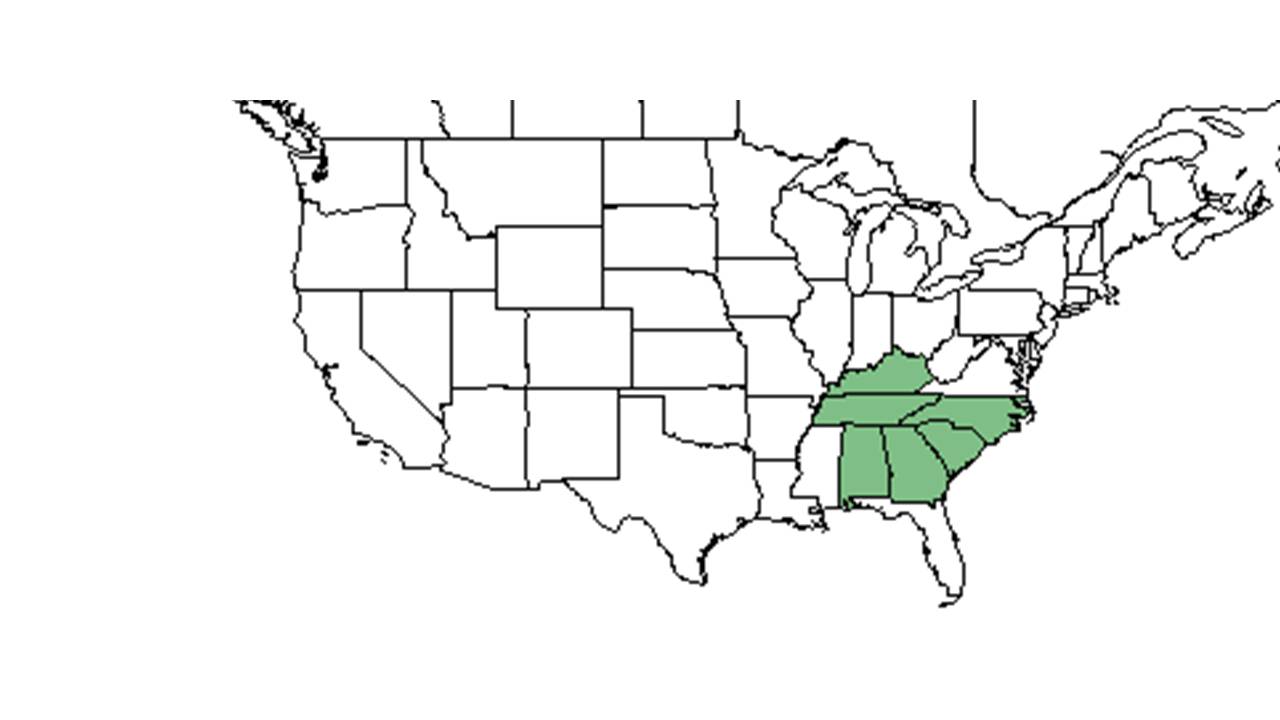
| Natural range of Rhododendron minus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Piedmont rhododendron, Gorge rhododendron
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none
Varieties: Rh. minus var. minus
Description
A description of Rhododendron minus is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
R. minus occurs in sandhill and pine flatwoods communities, as well as the edges of titi bogs.[1] However, it can also be found in disturbed areas, including titi swamps in heavily logged pinewoods and slash pine plantations.[1]
Associated species include Serenoa repens, Ilex glabra, Lyonia ferrugunea, Ilex coriacea, Lyonia lucida, Cyrilla, Quercus nigra, Cliftonia, Rhododendron canescens, Vaccimum arobreum, Hamamelis virginica, Pinus elliottii, Illicium floridanum, Quercus pumila,Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Quercus chapmanii, Quercus geminata, and Magnolia grandiflora.[1]
Phenology
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Gary Schultz, Loran C. Anderson, Angus Gholson, Rick Holden, Robert K. Godfrey, Ann M. Redmond, Mark A Garland, J. O. Boynton, H. R. Totten, Addie Totten, Steve Leonard, and W. D. Reese. States and Counties: Florida: Clay, Gadsden, Gulf, Leon, and Liberty.