Difference between revisions of "Quercus incana"
Laurenloria (talk | contribs) (→Seed dispersal) |
Laurenloria (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
''Quercus incana'' is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia.<ref name=ost>Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.</ref> | ''Quercus incana'' is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia.<ref name=ost>Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.</ref> | ||
| − | + | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | |
| + | It has been observed flowering in March and April.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 13 DEC 2016</ref> | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
This species disperses by gravity. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | This species disperses by gravity. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 13 December 2016
| Quercus incana | |
|---|---|
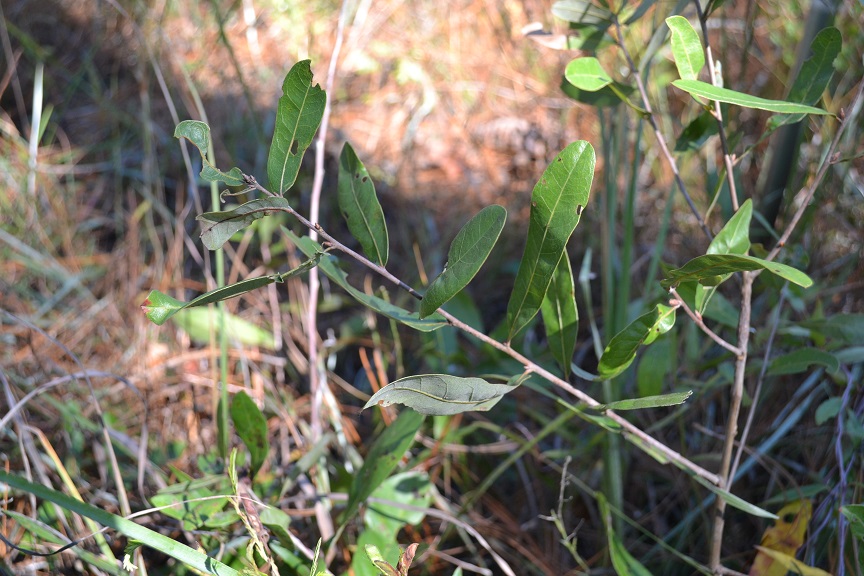

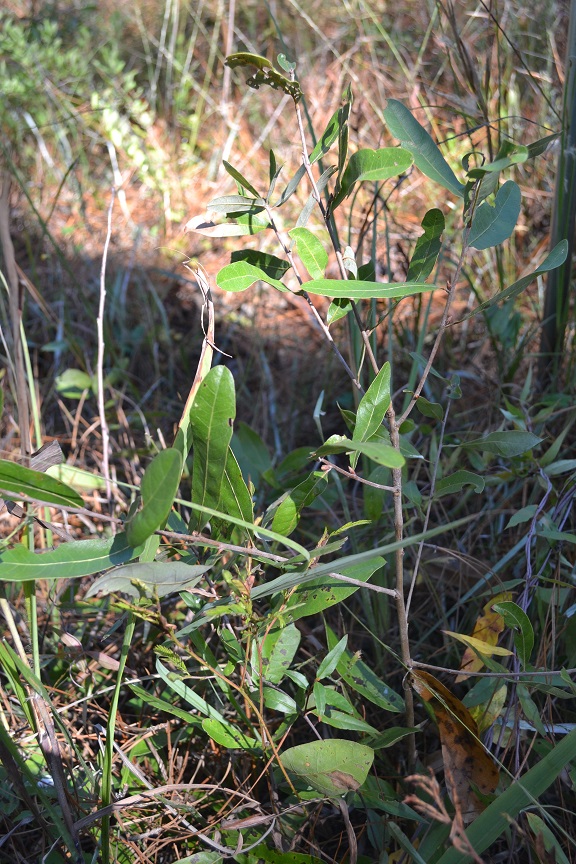
| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Tracheophyta- Vascular plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Fagaceae |
| Genus: | Quercus |
| Species: | Q. incana |
| Binomial name | |
| Quercus incana W. Bartram | |
| |
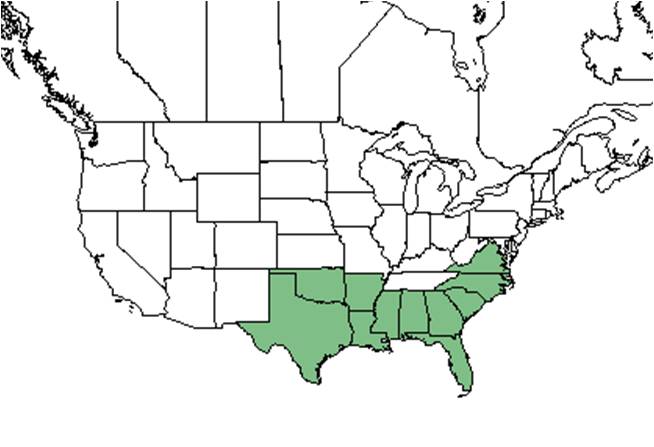
| Natural range of Quercus incana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Bluejack oak
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Quercus cinerea Michaux; Q. humilis Wlater
Description
A description of Quercus incana is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Quercus incana is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia.[1]
Phenology
It has been observed flowering in March and April.[2]
Seed dispersal
This species disperses by gravity. [3]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 13 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
