Difference between revisions of "Pluchea odorata"
(→Ecology) |
(→Taxonomic notes) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
Common name: sweetscent, marsh fleabane | Common name: sweetscent, marsh fleabane | ||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: ''Pluchea odorata'' var. ''odorata''; ''P. odorata'' (Linnaeus) Cassini var. ''succulenta'' (Fernald) Cronquist; ''P. purpurascens'' (Swartz) A.P. de Candolle var. ''purpurascens''; ''P. purpurascens'' (Swartz) A.P. de Candolle var. ''succulenta'' Fernald; ''P. purpurascens'' (Swartz) A.P. de Candolle | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
Revision as of 14:59, 31 March 2016
| Pluchea odorata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Pluchea |
| Species: | P. odorata |
| Binomial name | |
| Pluchea odorata (L.) Cass. | |
| |
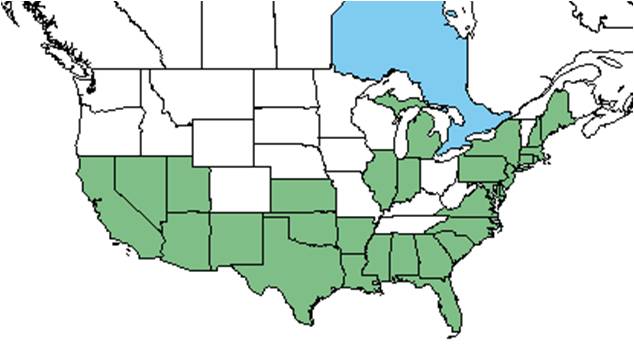
| Natural range of Pluchea odorata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: sweetscent, marsh fleabane
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Pluchea odorata var. odorata; P. odorata (Linnaeus) Cassini var. succulenta (Fernald) Cronquist; P. purpurascens (Swartz) A.P. de Candolle var. purpurascens; P. purpurascens (Swartz) A.P. de Candolle var. succulenta Fernald; P. purpurascens (Swartz) A.P. de Candolle
Description
A description of Pluchea odorata is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
It is distributed from southern Maine south to Florida, west to Texas and beyond, it is a largely coastal species[1]. It is an exotic weed in Hawaii, and is considered to be a serious problem (Alyokhin et al. 2001).
Ecology
Habitat
Pluchea odorata can be found in salt marshes, mangrove swamps, river banks, cypress swamps, marl prairies, cabbage palmetto-water hickory hammocks, pine flatwoods, coastal hammocks, and hickory mounds. It has also been found in disturbed areas such as calcareous borrow pits, roadside depressions, clear-cut pine flatwoods and drainage canals. Soil types include loamy sand, loam, and alluvial soils. Associated species include Cyperus, Juncus, Fuirena, Rhynchospora, Penthorum sedoides, Pluchea foetida, Boehmeria, Saururus, Pilea, and Murdannia keisak (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It has been observed flowering April through December (FSU Herbarium). It exhibits crystallofolia, which is an unusual feathery or ribbon like ice formation that appears on a plant during frost events when water is emitted along the steam during freezing[2].
Seed dispersal
Seeds are dispersed by wind (Alyokhi et al. 2001).
Seed bank and germination
Seeds may require wet, bare soils to germinate[3].
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Pluchea odorata at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Mellisodes communis
Halictidae: Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum nymphalis
Megachilidae: Anthidium maculifrons, Coelioxys germana, C. sayi, Dianthidium floridiense
Sphecidae: Ammophila procera
Vespidae: Leptochilus republicanus, Zeta argellaceum
Conservation and Management
P. odorata is an exotic weed in Hawaii, and is considered to be a serious problem. In attempt to control it, the flowerhead fly Acinia picturata was introduced in 1959 from Mexico (Alyokhin et al. 2001). The larvae feed on the seedheads of P. odorata. They occur more frequently in the immature flowers or buds than the older mature seedheads (Stegmaier 1967).
Cultivation and restoration
In the Caribbean countries, the leaves are used to make a tea that stimulates perspiration and urination[4]. It is also used to treat inflammation disorders (Blaschke et al. 2015).
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Alyokhin, A. V., R. H. Messing, et al. (2001). "Utilization of the Exotic Weed Pluchea odorata (Asteraceae) and Related Plants by the Introduced Biological Control Agent Acinia picturata (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Hawaii." Biocontrol Science and Technology 11(6): 703-710.
Blaschke, M., R. McKinnon, et al. (2015). "A eudesmane-type sesquiterpene isolated from Pluchea odorata (L.) Cass. combats three hallmarks of cancer cells: Unrestricted proliferation, escape from apoptosis and early metastatic outgrowth in vitro." Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis 777: 79-90.
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, L. Baltzell, Jane Brockmann, D. Burch, N. Chevalier, William J. Clark, G. Crosby, Delzie Demaree, R.F. Doren, G. Fleming, P. Genelle, Robert K. Godfrey, Norlan C. Henderson, C. Jackson, R. Komarek, O. Lakela, Robert L. Lazor, Robert J. Lemaire, R. Kral, Sidney McDaniel, Richard S. Mitchell, John Morrill, Jackie Patman, R.A. Norris, James D. Ray, Grady W. Reinert, Danielle Sherdan, Cecil R. Slaughter, Sydney Thompson, D.B. Ward, S.S. Ward. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Brevard, Broward, Citrus, Clay, Collier, Dixie, Flagler, Franklin, Hillsborough, Indian River, Jackson, Jefferson, Lake, Lee, Leon, Levy, Manatee, Monroe, Marion, Okeechobee, Orange, Osceola, Palm Beach, Pasco, Putnam, St. Lucie, Taylor, Wakulla. Countries: Belize, Cayman Islands. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Stegmaier, C. E. (1967). "Pluchea odorata, a New Host Record for Acinia picturata (Diptera, Tephritidae)." The Florida Entomologist 50(1): 53-55.