Difference between revisions of "Pinus palustris"
(→Distribution) |
(→Ecology) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| − | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | + | ===Habitat=== |
| + | Habitat falls largely within the southeastern Atlantic coastal plain and Gulf coastal plain. They require warm, wet, and temperate climates that have a steady reliable annual precipitation of 43-69 inches. It is common in sandy, well-drained soils close to sea level. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
| + | <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
| − | + | ===Seed bank and germination=== | |
| + | Germination needs mineral soil and 1-2 weeks after dispersal. Most germination occurs during the fall and spring. Only after the first two years of development, seedlings will begin to develop stems and growth in height begins to occur rapidly. During the first two years, the root system is developing, preparing for a rapid growth to extreme heights. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | + | ===Use by animals=== | |
| + | Birds and small mammals eat the large seeds, ants will eat the seeds that are germinating, and razorback hogs eat the roots of the seedlings.<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The tree provides habitats for bobwhite quail, white tailed deer, wild turkey, and fox squirrel. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Red-cockaded woodpecker will use the old growth stands for nesting. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 14:52, 24 May 2018
| Pinus palustris | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Pinaceae |
| Genus: | Pinus |
| Species: | P. palustris |
| Binomial name | |
| Pinus palustris Mill. | |
| |
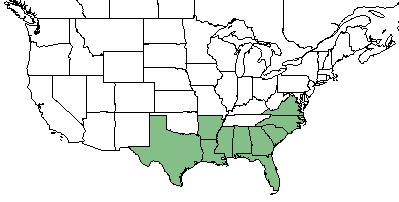
| Natural range of Pinus palustris from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: P. australis (Michaux)
Variety: none
Description
Pinus palustris is a perennial tree of the Pinaceae family that is native to North America. [1]
Distribution
P. palustris is found throughout the southeastern United States; specifically in Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Arkansas, and Texas. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
Habitat falls largely within the southeastern Atlantic coastal plain and Gulf coastal plain. They require warm, wet, and temperate climates that have a steady reliable annual precipitation of 43-69 inches. It is common in sandy, well-drained soils close to sea level. [1]
Seed bank and germination
Germination needs mineral soil and 1-2 weeks after dispersal. Most germination occurs during the fall and spring. Only after the first two years of development, seedlings will begin to develop stems and growth in height begins to occur rapidly. During the first two years, the root system is developing, preparing for a rapid growth to extreme heights. [1]
Use by animals
Birds and small mammals eat the large seeds, ants will eat the seeds that are germinating, and razorback hogs eat the roots of the seedlings.[1]
The tree provides habitats for bobwhite quail, white tailed deer, wild turkey, and fox squirrel. [1]
Red-cockaded woodpecker will use the old growth stands for nesting. [1]