Physalis heterophylla
| Physalis heterophylla | |
|---|---|
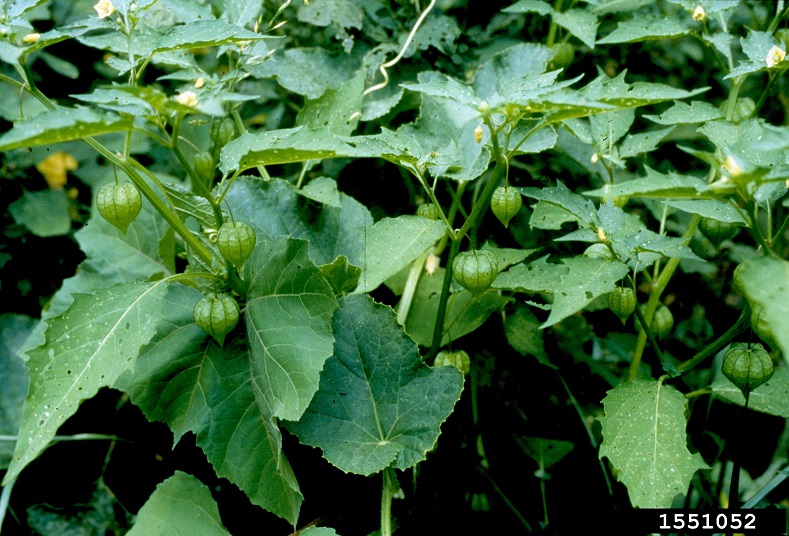

| |
| Photo by Ohio State Weed Lab, The Ohio State University, Bugwood.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Solanaceae |
| Genus: | Physalis |
| Species: | P. heterophylla |
| Binomial name | |
| Physalis heterophylla Nees | |
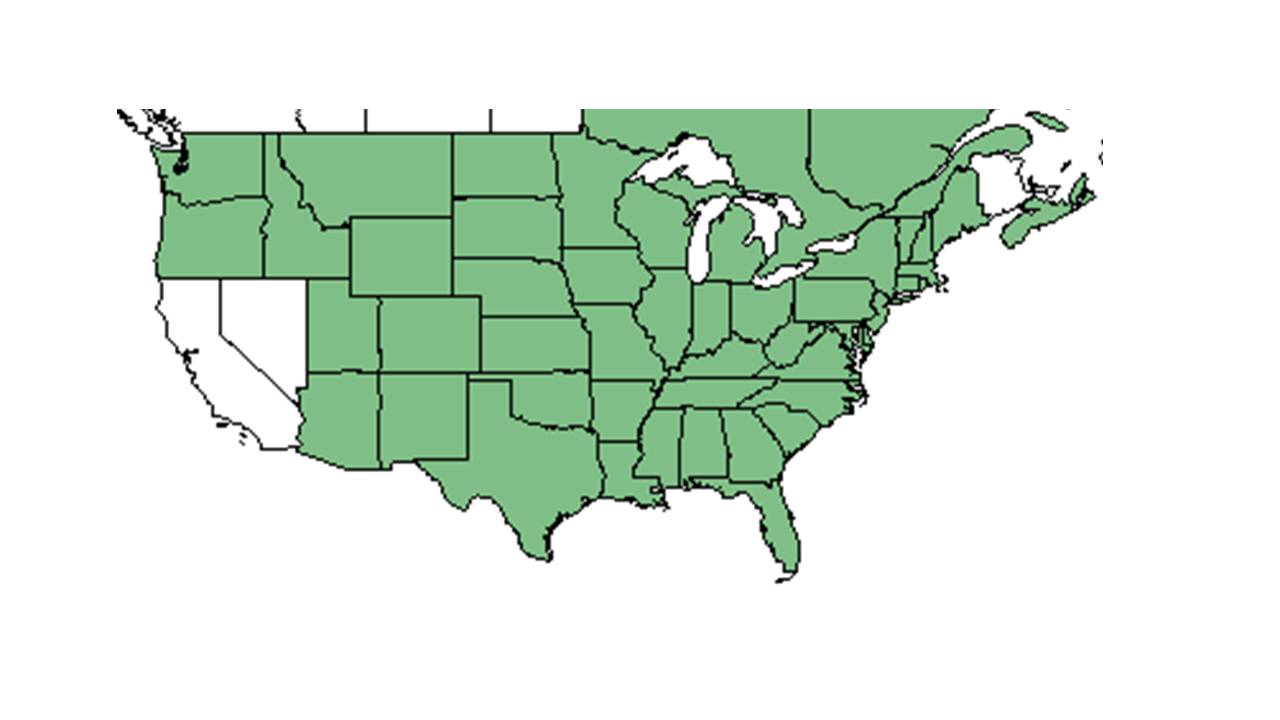
| |
| Natural range of Physalis heterophylla from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Clammy groundcherry
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: P. nyctaginea Dunal.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
"Annual or perennial, glabrous or pubescent herbs. Leaves petiolate, entire to coarsely dentate, the base tapered, subcordate or oblique. Flower axillary, solitary; the calyx tube expanding, papery and bluntly conical when mature, loosely enclosing the fruit. Corolla campanulate to subrotate, yellow, often with 5 dark spots in the base of the tube; stamens 5, erect, separate, anther yellow or blue, dehiscing by lateral slits berry somewhat mealy, 2-locular, globose."[2]
"Rhizomatous, often viscid perennial 2-9 dm tall. Stem pubescence of glandular trichomes mixed with both long and short nonglandular trichomes. Leaves widely ovate or oblanceolate to triangular or lanceolate, 3-11 cm long, 3-8 cm wide, sinuate-dentate or coarsely and irregularly dentate, rarely subentire, weakly cordate. Calyx 7-12 mm long, lobes triangular to lanceolate, shorter than the tube; corolla 10-18 mm long or broad, with 5 brownish basal spots; anthers yellow or rarely bluish, 3.5-4.5 mm long. Berry ca. 10 mm in diam., the fruiting calyx 2.5-3 cm long, about as broad."[2]
Distribution
P. heterophylla is widespread in the eastern and central United States, north to adjacent Canada, and south to northeastern and Panhandle Florida.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
P. heterophylla has been documented to grow in calcareous coastal hardwood hammocks, drying sand bordering woods, upland sandhills and annually burned longleaf pineland.[3] It has also been observed growing in old biocontrol plots and a fallow quail food patch. It has been documented in moist sandy loam and in the loam soils of the Red Hills Region.[3] Associated species include longleaf pine.[3] P. heterophylla responds positively to agricultural-based soil disturbance in South Carolina coastal plain communities. This marks it as an indicator species for post-agricultural woodland.[4]
Phenology
P. heterophylla flowers from May through September and fruits from July through September.[3][5]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by consumption by vertebrates.[6]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 927. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Andre F. Clewell, R. F. Doren, R. Komarek, J. M. Kane, Lisa Keppner. States and Counties:Florida: Calhoun, Leon, Nassau, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.