Difference between revisions of "Phlox floridana"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''P. floridana'' has been documented to occur in a longleaf | + | ''P. floridana'' has been documented to occur on a sandy ridge in a longleaf pine/scrub-oak woodland; pine/hardwood habitat; open piney areas; sandy soil of open pine flatwoods; amongst grasses in a burned longleaf pinewoods; at the edge of pine-oak-hickory woods; semi-boggy slope of longleaf pine savanna and an annually burned savanna.It has been observed to grow on sandy roadsides, picnic areas, dry sand and gravel in an old field, cut and burned over pineflatwoods, and along a powerline corridor (FSU Herbarium). Soils observed include sand, dry sandy loam, drying loamy sand, and in shaded loose loamy sand (FSU Herbarium). |
Associated species include ''Pinus palustris, Tetragonotheca, Onosmodium, Pediomelum, Quercus laurifolia, Quercus margarettae, Quercus incana, Quercus laevis, Vaccinium arboreum, Vaccinium stamineum, Opuntia humifusa and Asclepias'' (FSU Herbarium). | Associated species include ''Pinus palustris, Tetragonotheca, Onosmodium, Pediomelum, Quercus laurifolia, Quercus margarettae, Quercus incana, Quercus laevis, Vaccinium arboreum, Vaccinium stamineum, Opuntia humifusa and Asclepias'' (FSU Herbarium). | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
Revision as of 09:12, 18 September 2015
| Phlox floridana | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Polemoniaceae |
| Genus: | Phlox |
| Species: | P. floridana |
| Binomial name | |
| Phlox floridana Benth. | |
| |
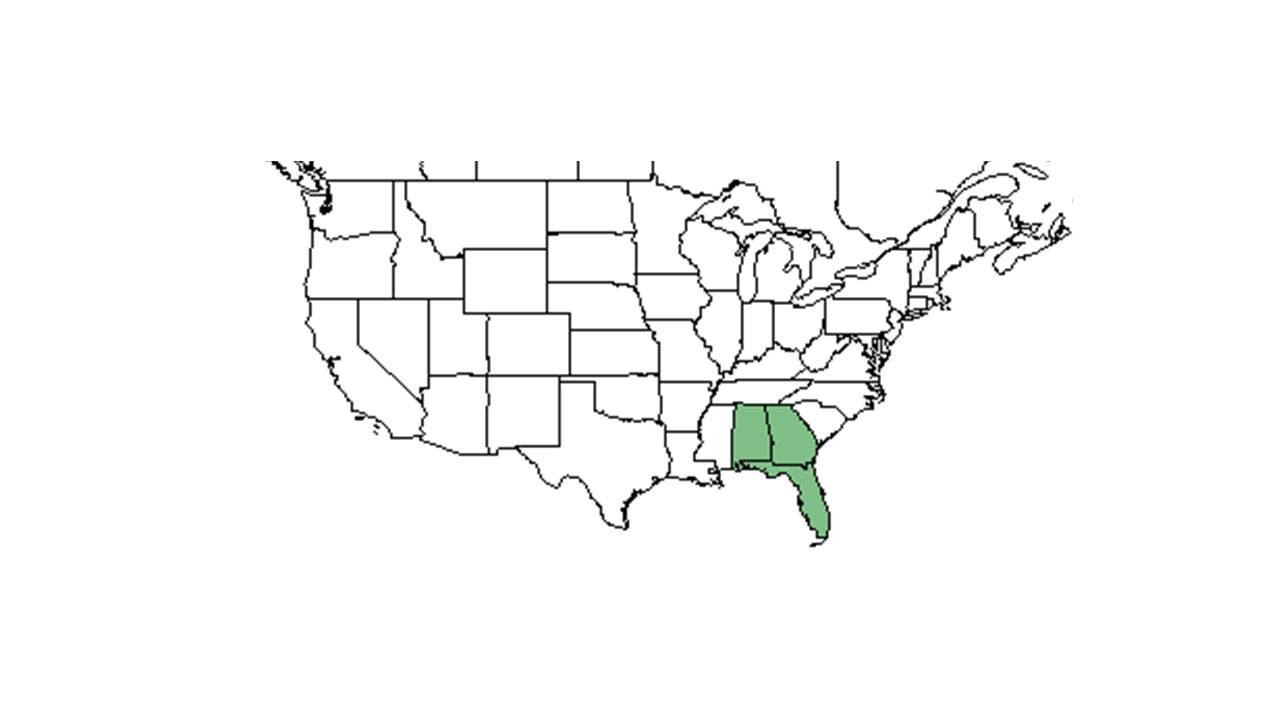
| Natural range of Phlox floridana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Common name: Florida phlox
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
P. floridana has been documented to occur on a sandy ridge in a longleaf pine/scrub-oak woodland; pine/hardwood habitat; open piney areas; sandy soil of open pine flatwoods; amongst grasses in a burned longleaf pinewoods; at the edge of pine-oak-hickory woods; semi-boggy slope of longleaf pine savanna and an annually burned savanna.It has been observed to grow on sandy roadsides, picnic areas, dry sand and gravel in an old field, cut and burned over pineflatwoods, and along a powerline corridor (FSU Herbarium). Soils observed include sand, dry sandy loam, drying loamy sand, and in shaded loose loamy sand (FSU Herbarium).
Associated species include Pinus palustris, Tetragonotheca, Onosmodium, Pediomelum, Quercus laurifolia, Quercus margarettae, Quercus incana, Quercus laevis, Vaccinium arboreum, Vaccinium stamineum, Opuntia humifusa and Asclepias (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It flowers within two months of burning in early summer (Robertson).
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Robertson, Kevin M. 2014. Personal observation.