Difference between revisions of "Passiflora lutea"
(→Phenology) |
Lsandstrum (talk | contribs) (→Habitat) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
Common environments for ''P. lutea'' include woodlands, forests, thickets, and maritime forests. <ref name= "Weakley"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> | Common environments for ''P. lutea'' include woodlands, forests, thickets, and maritime forests. <ref name= "Weakley"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> | ||
| − | Specimens have been recovered from edges of maritime hammocks, disturbed roadsides near woodlands, on bases of slopes, and pine-oak woodlands. <ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Leon, Liberty)</ref> | + | Specimens have been recovered from edges of maritime hammocks, disturbed roadsides near woodlands, on bases of slopes, and pine-oak woodlands. <ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Leon, Liberty)</ref> ''P. lutea'' responds negatively to agricultural-based soil disturbance in South Carolina coastal plain communities. This marks it as an indicator species for remnant woodland.<ref>Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.</ref> |
| + | |||
===Phenology=== | ===Phenology=== | ||
''P lutea'' has been observed flowering in June and July. <ref name= "Pan Flora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 24 MAY 2018</ref> | ''P lutea'' has been observed flowering in June and July. <ref name= "Pan Flora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 24 MAY 2018</ref> | ||
Revision as of 14:03, 4 July 2019
Common names: Yellow passionflower [1]
| Passiflora lutea | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Violales |
| Family: | Passifloraceae |
| Genus: | Passiflora |
| Species: | P. lutea |
| Binomial name | |
| Passiflora lutea L. | |
| |
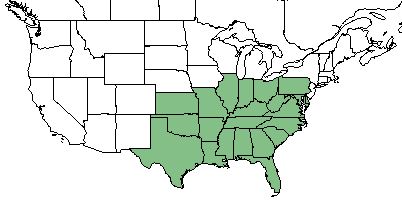
| Natural range of Passiflora lutea from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: none
Variety: glabriflora (Fernald)
Description
P. lutea is a perennial forb/herb/vine of the Passifloraceae family that is native to North America. [1]
Distribution
P. lutea is found throughout the southeastern United States; from Florida north to Pennsylvania, and west to Texas and Kansas. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
P. lutea has little tolerance for drought conditions and a low tolerance for fire. It is extremely tolerant of shade. [1]
Common environments for P. lutea include woodlands, forests, thickets, and maritime forests. [2]
Specimens have been recovered from edges of maritime hammocks, disturbed roadsides near woodlands, on bases of slopes, and pine-oak woodlands. [3] P. lutea responds negatively to agricultural-based soil disturbance in South Carolina coastal plain communities. This marks it as an indicator species for remnant woodland.[4]
Phenology
P lutea has been observed flowering in June and July. [5]
Use by animals
Birds will use the species for food. [1]
Conservation and Management
P. lutea is considered a weed in Illinois but is labeled as endangered in Pennsylvania. [1]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Leon, Liberty)
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 24 MAY 2018