Paspalum praecox
| Paspalum praecox | |
|---|---|
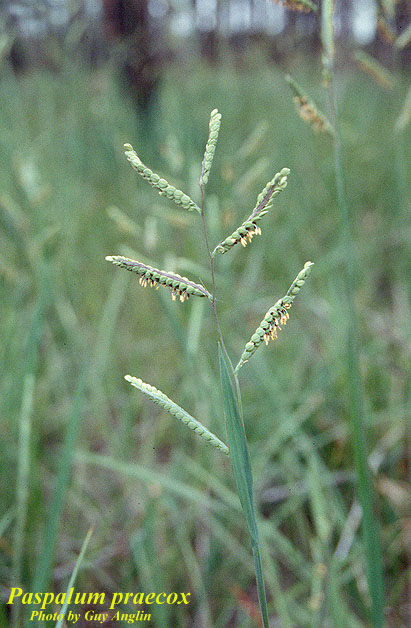

| |
| Photo by Guy Anglin, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Paspalum |
| Species: | P. praecox |
| Binomial name | |
| Paspalum praecox Walter | |
| |
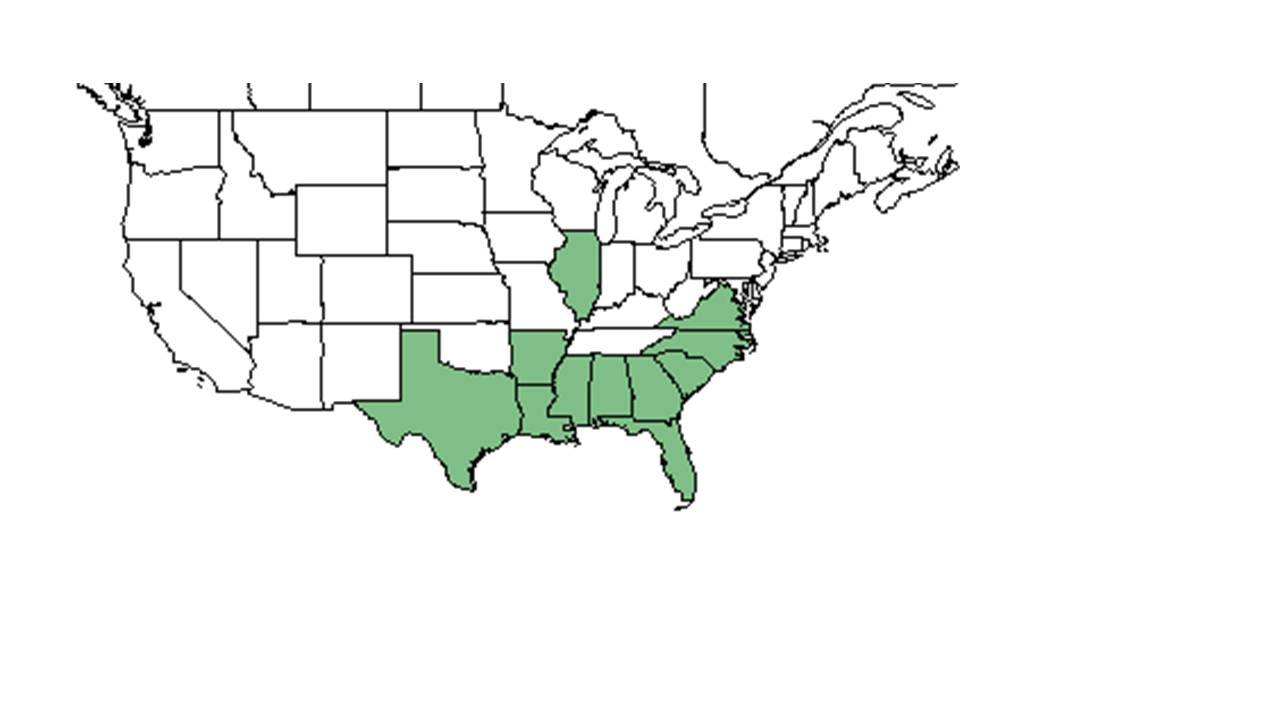
| Natural range of Paspalum praecox from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Early paspalum; Early crowngrass
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Paspalum lentiferum Lamarck
Varieties: P. praecox Walter var. curtisianum (Steudel) Vasey
Description
"Annuals or perennials. Leaves primarily basal and low cauline; blade margins usually scaberulous; ligules membranous. Spikelets plano-convex, terminal floret fertile, basal floret sterile. Frist glume usually absent, sterile lemma resembles 2nd glume; fertile lemma and paleas indurate, lustrous, yellowish or brownish. These plants are all important forage grasses." [1]
"Erect perennial from short rhizomes; culms 6-9 dm tall, nodes and internodes glabrous. Blades to 20 cm long, 1.5-4 mm wide, glabrous or villous on both surfaces, occasionally pilose basally above; sheaths glabrous, villous or sparsely papillose above, margins smooth; ligules 2-2.5 mm long. Racemes 3-5, racemose, ascending, 2-6 cm long; rachis wing scaberulous, 1-1.2 mm wide. Spikelets broadly obovoid to suborbicular, flattish, 2.2-3.2 mm long, in 4 rows, 2 rows rudimentary; pedicels scaberulous angled, 0.1-1 mm long. Second glume and sterile lemmas 3-nerved, yellowish green , margins scarious, obtuse 2.2-3.2 mm long; fertile lemma and palea nerveless, papillose, obtuse, 2.2-3.2 mm long. Grain brownish, broadly ellipsoid, flat, 2 mm long." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
This species has been found growing in open areas of longleaf and slash pine in wet, sandy and peaty soils. [2] It has also been found in moist, loose, and loamy sands of ditches along trails within pine plantations. [2] Associated species include Andropogon, Sorghastrum, and Pinus palustris. [2]
Phenology
P. praecox has been observed flowering in April[3] and July and fruiting in October. [2]
Fire ecology
This species can be found in burned, open longleaf pine areas. [2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 136. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Ann F. Johnson, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Komarek, Travis MacClendon, and Karen MacClendon. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Dixie, Liberty, and Wakulla. Georgia: Thomas.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016