Difference between revisions of "Panicum capillare"
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
''P. capillare'' is considered weedy or invasive depending on the authority involved.<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ''P. capillare'' is considered weedy or invasive depending on the authority involved.<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Revision as of 13:47, 8 June 2021
Common Names: witchgrass[1], old-witch Grass[2]
| Panicum capillare | |
|---|---|
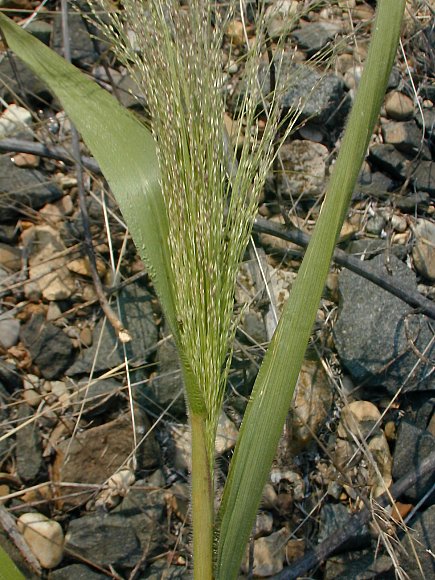

| |
| Photo by John Hilty hosted at IllinoisWildflowers.info | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Panicum |
| Species: | P. capillare |
| Binomial name | |
| Panicum capillare L. | |
| |
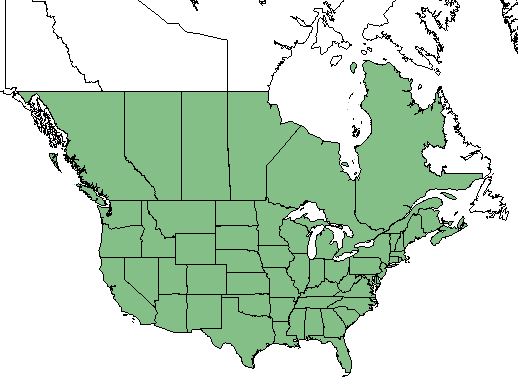
| Natural range of Panicum capillare from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: none.[3]
Varieties: none.[3]
Description
P. capillare is an annual graminoid of the Poaceae family that is native to North America.[1]
This plant is an annual that grows from a cluster of fibrous roots, without rhizomes or hard knotty crowns. The rachis, branches, and pedicels usually scabrous with barbs that are larger than .05 mm. The panicle is equal to or longer than a portion of culm below the panicle and basally included at maturity. Spikelets are 1.6-2.9 mm long, short- to long-acuminate, lanceolate, lance-ovoid, or lance-ellipsoid. The glume is 0.6-1.5 (-2) mm long; blades are more than 10 mm wide; sheaths are hispid to villous. The culm nodes usually pubescent to bearded, the internodes are hispid to glabrous, and the pulvini are pilose to villous, especially at lower primary branches.[3]
Distribution
P. capillare ranges east to central Canada, and south to Florida and Texas. It also grows in Bermuda.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
Considered a weed in cultivated soils, the common habitats for P. capillare include open sandy pr stony soils, fields, roadsides, and waste places.[4]
Specimens have been collected from habitats that include loamy limestone sands, old pocket gopher holes, in nursery beds, and other disturbed places.[5]
Phenology
P. capillare flowers from August through November.[3]
Seed dispersal
Seed dispersal commonly occurs between September and December.[6]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
P. capillare is considered weedy or invasive depending on the authority involved.[1]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Davis, J., J. Eric, et al. (2002). "Vascular flora of Piedmont Prairies: Evidence from several prairie remnants." Castanea 67(1): 1-12.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, William Platt, D.E. Boufford, E.W. WOod) States and counties: Florida (Jackson, Gadsden) Utah (Cache) Georgia (Thomas) Massachusetts (Middlesex)
- ↑ West, G. C. (1967). "Nutrition of tree sparrows during winter in central Illinois." Ecology 48(1): 58-67.